5.1 Confronting the National Debt: The Aftermath of the French and Indian War
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Discuss the status of Great Britain’s North American colonies in the years directly following the French and Indian War
- Describe the size and scope of the British debt at the end of the French and Indian War
- Explain how the British Parliament responded to the debt crisis
- Outline the purpose of the Proclamation Line, the Sugar Act, and the Currency Act
Great Britain had much to celebrate in 1763. The long and costly war with France had finally ended, and Great Britain had emerged victorious. British subjects on both sides of the Atlantic celebrated the strength of the British Empire. Colonial pride ran high; to live under the British Constitution and to have defeated the hated French Catholic menace brought great joy to British Protestants everywhere in the Empire. From Maine to Georgia, British colonists joyously celebrated the victory and sang the refrain of “Rule, Britannia! Britannia, rule the waves! Britons never, never, never shall be slaves!”
Despite the celebratory mood, the victory over France also produced major problems within the British Empire, problems that would have serious consequences for British colonists in the Americas. During the war, many Native American tribes had sided with the French, who supplied them with guns. After the 1763 Treaty of Paris that ended the French and Indian War (or the Seven Years’ War), British colonists had to defend the frontier, where French colonists and their tribal allies remained a powerful force. The most organized resistance, Pontiac’s Rebellion, highlighted tensions the settlers increasingly interpreted in racial terms.
The massive debt the war generated at home, however, proved to be the most serious issue facing Great Britain. The frontier had to be secure in order to prevent another costly war. Greater enforcement of imperial trade laws had to be put into place. Parliament had to find ways to raise revenue to pay off the crippling debt from the war. Everyone would have to contribute their expected share, including the British subjects across the Atlantic.
Problems on the American Frontier
With the end of the French and Indian War, Great Britain claimed a vast new expanse of territory, at least on paper. Under the terms of the Treaty of Paris, the French territory known as New France had ceased to exist. British territorial holdings now extended from Canada to Florida, and British military focus shifted to maintaining peace in the king’s newly enlarged lands. However, much of the land in the American British Empire remained under the control of powerful native confederacies, which made any claims of British mastery beyond the Atlantic coastal settlements hollow. Great Britain maintained ten thousand troops in North America after the war ended in 1763 to defend the borders and repel any attack by their imperial rivals.
British colonists, eager for fresh land, poured over the Appalachian Mountains to stake claims. The western frontier had long been a “middle ground” where different imperial powers (British, French, Spanish) had interacted and compromised with native peoples. That era of accommodation in the “middle ground” came to an end after the French and Indian War. Virginians (including George Washington) and other land-hungry colonists had already raised tensions in the 1740s with their quest for land. Virginia landowners in particular eagerly looked to diversify their holdings beyond tobacco, which had stagnated in price and exhausted the fertility of the lands along the Chesapeake Bay. They invested heavily in the newly available land. This westward movement brought the settlers into conflict as never before with Native American tribes, such as the Shawnee, Seneca-Cayuga, Wyandot, and Delaware, who increasingly held their ground against any further intrusion by White settlers.
The treaty that ended the war between France and Great Britain proved to be a significant blow to native peoples, who had viewed the conflict as an opportunity to gain additional trade goods from both sides. With the French defeat, many Native Americans who had sided with France lost a valued trading partner as well as bargaining power over the British. Settlers’ encroachment on their land, as well as the increased British military presence, changed the situation on the frontier dramatically. After the war, British troops took over the former French forts but failed to court favor with the local tribes by distributing ample gifts, as the French had done. They also significantly reduced the amount of gunpowder and ammunition they sold to the Native Americans, worsening relationships further.
Native Americans’ resistance to colonists drew upon the teachings of Delaware (Lenni Lenape) prophet Neolin and the leadership of Ottawa war chief Pontiac. Neolin was a spiritual leader who preached a doctrine of shunning European culture and expelling Europeans from native lands. Neolin’s beliefs united Native Americans from many villages. In a broad-based alliance that came to be known as Pontiac’s Rebellion, Pontiac led a loose coalition of these native tribes against the colonists and the British army.
Pontiac started bringing his coalition together as early as 1761, urging Native Americans to “drive [the Europeans] out and make war upon them.” The conflict began in earnest in 1763, when Pontiac and several hundred Ojibwas, Potawatomis, and Hurons laid siege to Fort Detroit. At the same time, Senecas, Shawnees, and Delawares laid siege to Fort Pitt. Over the next year, the war spread along the backcountry from Virginia to Pennsylvania. Pontiac’s Rebellion (also known as Pontiac’s War) triggered horrific violence on both sides. Firsthand reports of Native American attacks tell of murder, scalping, dismemberment, and burning at the stake. These stories incited a deep racial hatred among colonists against all Native Americans.
The actions of a group of Scots-Irish settlers from Paxton (or Paxtang), Pennsylvania, in December 1763 illustrate the deadly situation on the frontier. Forming a mob known as the Paxton Boys, these frontiersmen attacked a nearby group of Conestoga of the Susquehannock tribe. The Conestoga had lived peacefully with local settlers, but the Paxton Boys viewed all Native Americans as savages, and they brutally murdered the six Conestoga they found at home and burned their houses. When Governor John Penn put the remaining fourteen Conestoga in protective custody in Lancaster, Pennsylvania, the Paxton Boys broke into the building and killed and scalped the Conestoga they found there (Figure 5.3). Although Governor Penn offered a reward for the capture of any Paxton Boys involved in the murders, no one ever identified the attackers. Some colonists reacted to the incident with outrage. Benjamin Franklin described the Paxton Boys as “the barbarous Men who committed the atrocious act, in Defiance of Government, of all Laws human and divine, and to the eternal Disgrace of their Country and Colour,” stating that “the Wickedness cannot be covered, the Guilt will lie on the whole Land, till Justice is done on the Murderers. The blood of the innocent will cry to heaven for vengeance.” Yet, as the inability to bring the perpetrators to justice clearly indicates, the Paxton Boys had many more supporters than critics.

Click and Explore
Read the full text of Benjamin Franklin’s “Benjamin Franklin, An Account of the Paxton Boys’ Murder of the Conestoga Indians, 1764.”
Pontiac’s Rebellion and the Paxton Boys’ actions were examples of early American race wars, in which both sides saw themselves as inherently different from the other and believed the other needed to be eradicated. The prophet Neolin’s message, which he said he received in a vision from the Master of Life, was “Wherefore do you suffer the whites to dwell upon your lands? Drive them away; wage war against them.” Pontiac echoed this idea in a meeting, exhorting tribes to join together against the British: “It is important for us, my brothers, that we exterminate from our lands this nation which seeks only to destroy us.” In his letter suggesting “gifts” to the natives of smallpox-infected blankets, Field Marshal Jeffrey Amherst said, “You will do well to inoculate the Indians by means of blankets, as well as every other method that can serve to extirpate this execrable race.” Pontiac’s Rebellion came to an end in 1766, when it became clear that the French, whom Pontiac had hoped would side with his forces, would not be returning. The repercussions, however, would last much longer. Race relations between Native Americans and White people remained poisoned on the frontier.
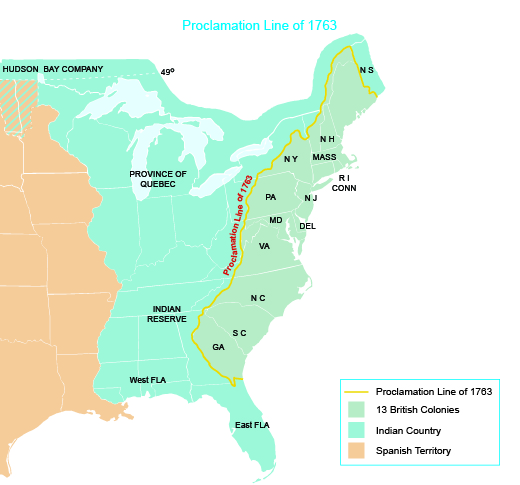
Well aware of the problems on the frontier, the British government took steps to try to prevent bloodshed and another costly war. At the beginning of Pontiac’s uprising, the British issued the Proclamation of 1763, which forbade White settlement west of the Proclamation Line, a borderline running along the spine of the Appalachian Mountains (Figure 5.4). The Proclamation Line aimed to forestall further conflict on the frontier, the clear flashpoint of tension in British North America. British colonists who had hoped to move west after the war chafed at this restriction, believing the war had been fought and won to ensure the right to settle west. The Proclamation Line therefore came as a setback to their vision of westward expansion.
The British National Debt
Great Britain’s newly enlarged empire meant a greater financial burden, and the mushrooming debt from the war was a major cause of concern. The war nearly doubled the British national debt, from £75 million in 1756 to £133 million in 1763. Interest payments alone consumed over half the national budget, and the continuing military presence in North America was a constant drain. The Empire needed more revenue to replenish its dwindling coffers. Those in Great Britain believed that British subjects in North America, as the major beneficiaries of Great Britain’s war for global supremacy, should certainly shoulder their share of the financial burden.
The British government began increasing revenues by raising taxes at home, even as various interest groups lobbied to keep their taxes low. Powerful members of the aristocracy, well represented in Parliament, successfully convinced Prime Minister John Stuart, third earl of Bute, to refrain from raising taxes on land. The greater tax burden, therefore, fell on the lower classes in the form of increased import duties, which raised the prices of imported goods such as sugar and tobacco. George Grenville succeeded Bute as prime minister in 1763. Grenville determined to curtail government spending and make sure that, as subjects of the British Empire, the American colonists did their part to pay down the massive debt.
Imperial Reforms
The new era of greater British interest in the American colonies through imperial reforms picked up pace in the mid-1760s. In 1764, Prime Minister Grenville introduced the Currency Act of 1764, prohibiting the colonies from printing additional paper money and requiring colonists to pay British merchants in gold and silver instead of the colonial paper money already in circulation. The Currency Act aimed to standardize the currency used in Atlantic trade, a logical reform designed to help stabilize the Empire’s economy. This rule brought American economic activity under greater British control. Colonists relied on their own paper currency to conduct trade and, with gold and silver in short supply, they found their finances tight. Not surprisingly, they grumbled about the new imperial currency regulations.
Grenville also pushed Parliament to pass the Sugar Act of 1764, which actually lowered duties on British molasses by half, from six pence per gallon to three. Grenville designed this measure to address the problem of rampant colonial smuggling with the French sugar islands in the West Indies. The act attempted to make it easier for colonial traders, especially New England mariners who routinely engaged in illegal trade, to comply with the imperial law.
To give teeth to the 1764 Sugar Act, the law intensified enforcement provisions. Prior to the 1764 act, colonial violations of the Navigation Acts had been tried in local courts, where sympathetic colonial juries refused to convict merchants on trial. However, the Sugar Act required violators to be tried in vice-admiralty courts. These crown-sanctioned tribunals, which settled disputes that occurred at sea, operated without juries. Some colonists saw this feature of the 1764 act as dangerous. They argued that trial by jury had long been honored as a basic right of Englishmen under the British Constitution. To deprive defendants of a jury, they contended, meant reducing liberty-loving British subjects to political slavery. In the British Atlantic world, some colonists perceived this loss of liberty as parallel to the enslavement of Africans.
As loyal British subjects, colonists in America cherished their Constitution, an unwritten system of government that they celebrated as the best political system in the world. The British Constitution prescribed the roles of the King, the House of Lords, and the House of Commons. Each entity provided a check and balance against the worst tendencies of the others. If the King had too much power, the result would be tyranny. If the Lords had too much power, the result would be oligarchy. If the Commons had the balance of power, democracy or mob rule would prevail. The British Constitution promised representation of the will of British subjects, and without such representation, even the indirect tax of the Sugar Act was considered a threat to the settlers’ rights as British subjects. Furthermore, some American colonists felt the colonies were on equal political footing with Great Britain. The Sugar Act meant they were secondary, mere adjuncts to the Empire. All subjects of the British crown knew they had liberties under the constitution. The Sugar Act suggested that some in Parliament labored to deprive them of what made them uniquely British.

