11 Chapter 11 – What are the biggest questions about the Universe?
OpenStax Astronomy Chapter 29: The Big Bang
What is the Fate of the Universe?
I.
A. Universe is , but expansion can
1. The of expansion determines the of the Universe
B. Rate of expansion and fate on (amount of ) in the universe
1. Because by bringing things together
2. Amount of gravity from both (both have mass)
3. The there is, the there is to the expansion
C. : gravity so rate of expansion (open universe)
D. Density: gravity so expansion and universe eventually (closed universe, Big Crunch)
E. Density: gravity expansion so keeps but expanding until
F. Best from predict universe will , maybe slowing, but
If the fate of the universe were determined ONLY by the density of matter, astronomers would predict that the universe will:
What is the Universe really made of?
II.
A. In the 1990s, discovered the , down as predicted
1. of expansion was actually in the
B. So, there must be a that to make it : called it
1. Gravity together, dark energy apart
2. We know it is as energy of , but don’t know what it is
III. The
A. Represents a for
-
-
- that and causes acceleration or the of space
-
B. Originally part of Einstein’s theory of (1915) because thought universe was or unchanging (didn’t know universe was expanding yet)
1. Put a in equations to keep the universe called the
C. After he saw and the Hubble-Lemaitre Law (about 10 years later), Einstein the cosmological constant of his equations
D. Now, scientists in to represent
When astronomers discovered that the universe was , some thought that Einstein’s cosmological constant would be useful to explain it.
A. Accelerating
B. Expanding
C. Contracting
D. Decelerating
How did the Universe get this way?
IV. the traditional
A. : The is too
1. Almost in directions
2. Means had to have been
3. But, (exchange energy) over the , takes to travel to make everything smooth
B. : CMB shows of universe is
1. Too to
2. Something must have it to be
V. Theory
A. Very at times (< 10-32 seconds)
1. exponentially and much than , but only very
B. Provides : and the early universe
1. initial will look when
2. Can to smaller (observable universe)
a. Should be , because was close to begin with
What solves the flatness and horizon problems of the Big Bang theory?
A. The universe used to be curved.
B. The universe will collapse.
C. The universe inflated quickly at early times.
D. The universe is accelerating.
VI. Universe if lasts forever (with Dark Energy)
A. Beginning: (< 10-30 second)
B. : plasma, only and subatomic until first atoms and first light at recombination (300,000 years)
C. Era (Era of stars): time, forming
D. Era: out, leaving brown dwarfs, (1014 years)
E. Era: all normal , leaving (1039 years)
F. Era: even black holes (10100 years), leaving only subatomic like cold photons, neutrinos, electrons, and positrons in universe
What do most astronomers today believe will be the final state of our universe?
A “Big Crunch” in which everything collapses back in on itself
B. An ever-expanding universe filled with only hydrogen and helium gas
C. A universe that stops expanding and is filled with nothing but white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes
D. An expanding universe filled with photons and elementary particles, but no matter or stars
Are there other Universes?
VII.
A. A almost identical to or very from ours
1. Many mathematical on how this might work, but most do have
B. universe could contain an number of observable universes
C. : This universe because this is the
1. Lots physical rates and values are to allow survival (CMB fluctuations, expansion, gravity, fusion, etc)
2. If there is more than one universe, this may be the just right for life
Do you think there is more than one universe?
Tutorial Activity – Dark Energy and Fate of the Universe
“Elementary Astronomy Worksheet Handout 24: Dark Matter, Dark Energy” (modified by Kaisa E. Young) by Catherine Whiting via OER Commons, licensed under CC BY 4.0, https://oercommons.org/courses/elementary-astronomy-worksheets
1. What is dark energy? In what sense is it “dark”?
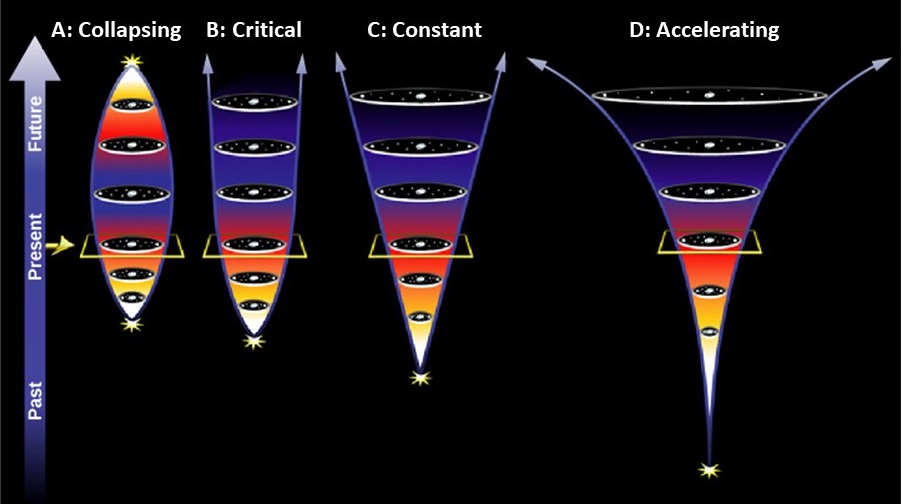
2. Consider the four types of universe in Figure 4 (A: Collapsing, B: Critical Density, C: Constant Expansion, D: Accelerating Expansion).
Figure 1: ”Four Possible Models of the Universe.” (Modified by Kaisa E. Young) by Andrew Fraknoi, David Morrison, and Sidney Wolf via OpenStax, licensed under CC BY 4.0
(a) Which model has the most amount of matter (normal and dark matter)? Why?
(b) Which model has dark energy included in the universe? Why?
(c) Which model best represents our universe based on current observations?
3. What do you think will ultimately happen to the universe? What will the universe be like in the far future?