8 Chapter 8 – What’s our Milky Way galaxy like?
OpenStax Astronomy Chapter 25 – The Milky Way Galaxy
Shape of the Milky Way
I.
A. The Milky Way has a substantial and a modest at the center
B. major and several other arms in the
1. spiral: SBbc galaxy, brightness of bulge and tightness of arms
2. The is about between the and the in the Orion Spur (between arms)
C. Disk is about light years and about light years
D. of and surrounds the disk
E. at the center, in Sagittarius
F. extends beyond globular cluster halo
1. Has a rotation curve
Imagine that you could travel at the speed of light. Starting from Earth, about how long would it take you to travel to the center of the Milky Way Galaxy?
A. 2 years
B. 20 years
C. 250 years
D. 2,500 years
E. 25,000 years
Globular Clusters
II. in the Halo
A. group of gravitationally
1. at the but depending on
2. About stars in a cluster, and about clusters in the Milky Way
B. parts of galaxy ( billion years old), formed
1. Know age because stars and stars have all (plot on HR diagram)
C. Very so can be seen from
D. Use to find and map the
1. Contain : stars with used to find distance
E. Globular clusters around the of the Milky Way in spherical halo
1. Used to find center of Milky Way: lightyears from the
Formation of the Galaxy
III. (Milky Way and others)
A. Initially with
B. (globular clusters) likely before gas was concentrated into the disk
C. Then collected in and formed
D. probably formed by the of many
E. , keep in the
In the disk of the Milky Way, stars are in the halo.
A. younger than
B. older than
C. the same age as
F. Several orbit the today
1. Examples: Sagittarius Dwarf, Large and Small
2. About total
G. Milky Way is
1. Protogalaxies continue with Milky Way
2. Eventually Milky Way will merge with
The Milky Way galaxy
A. Has been exactly the same since it first formed
B. Has only changed in number of stars since it first formed
C. Is still evolving, consuming nearby galaxies
D. Is finished evolving, and will not change any more
Tutorial Activity – The Milky Way
“Elementary Astronomy Worksheet Handout 21: Milky Way Galaxy, Galaxies” (modified by Kaisa E. Young) by Catherine Whiting via OER Commons, licensed under CC BY 4.0, https://oercommons.org/courses/elementary-astronomy-worksheets
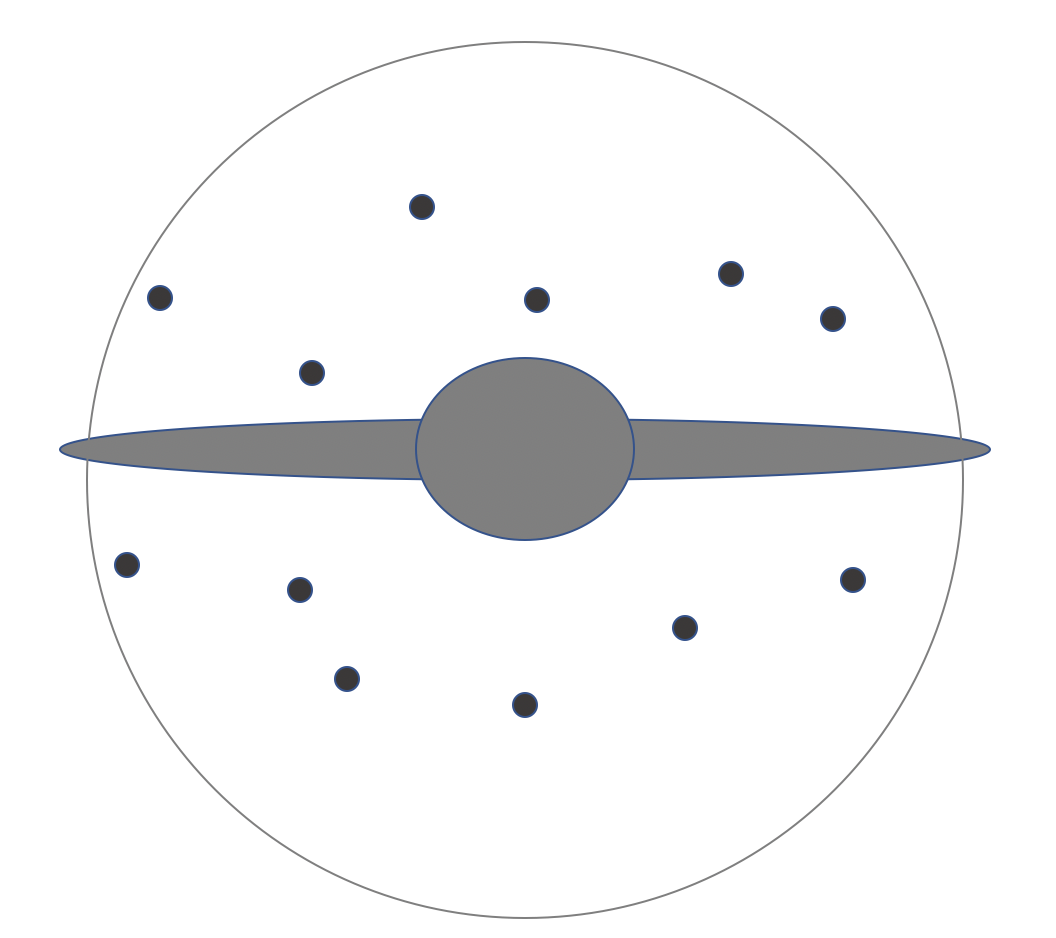
Figure 1: Schematic of Milky Way Galaxy by Catherine Whiting, licensed under CC BY 4.0
1. On Figure 1 of the schematic diagram of the Milky Way, seen edge on, label the following: Disk, Bulge, Halo, Globular Clusters, Sun’s approximate location.
2. What is the halo of a galaxy?
3. (a) What are globular clusters?
(b) What do globular clusters orbit around?
4. (a) About how big (how far across) is the disk of the Milky Way?
(b) About how far is the Sun from the center of the Milky Way?
5. On Figure 1 above, add a dot at approximately the correct distance and label the following stars:
(a) Star A is 500 light years from the Sun.
(b) Star B is 10,000 light years from the Sun.
(c) Star C is 50,000 light years from the Sun.

