10 Chapter 10 – Does the Universe have a beginning?
OpenStax Astronomy Chapter 26: Galaxies
OpenStax Astronomy Chapter 29: The Big Bang
Expansion of the Universe
I. The is
A. We know from :
1. Galaxies are from us
2. Galaxies are moving away than nearby ones
II. galaxies due to
A. (color) of in a spectrum on of object
B. (except nearby) have a
1. wavelength is than
C. absorption lines means movement
1. Movement results in a
D. We can measure and of galaxies with the
1. redshift means galaxy is moving and is away
A bright star is moving away from Earth. Which of the choices best completes the following statement describing the spectrum of this star?
A(n) spectrum that is relative to an unmoving star.
A. absorption, blueshifted
B. emission, redshifted
C. continuous, blueshifted
D. absorption, redshifted
E. continuous, redshifted
III. Know move from
A. observed galaxy (1914)
B. suggested the is (1927)
C. observed variable (standard candles) in other to find
1. Found and of galaxies are (1929)
D. : The of a galaxy with
1. A galaxy from us is moving away , redshift
E. Conclusion:
1. you are in the universe, you see other galaxies moving away and their speed increases with distance
If our universe is expanding and all galaxies have a redshift, where is the center of the Universe?
A. Earth is at the center
B. The Sun is at the center
C. The Milky Way Galaxy is at the center
D. There is no center of the Universe
The Big Bang
IV.
A. Hubble-Lemaitre’s law says the universe is , so:
1. Galaxies will be in the
2. Galaxies were together in the
3. was once
B. : time when between was
1. Gives of of the universe: years old
C. The Hubble Time is also called
1. ! Matter is away from some point
2. itself is or expanding (Everywhere Stretch)
V.
A. The has
B. The Big Bang
C. The does affect
1. Atoms and objects bound together by nuclear
D. in the was once in a
E. was created from after Big Bang:
Imagine watching the history of the Universe in reverse. As we get closer to the beginning, what is true?
A. Objects get farther apart
B. The universe becoming denser
C. The temperature of the universe drops
D. Regions of space become smaller
E. More than one of the above are true.
Which of the following best describes the Big Bang?
A. An explosion of matter and energy at the beginning of the universe that threw matter into empty space
B. An explosion of matter and energy at the beginning of the universe that threw matter into regions of space where other matter already existed
C. The expansion and cooling of the universe from an originally hot and dense state
D. More than one of the above
VI. How the Universe
A. We see as they were because they have a large
1. Look-back time: Time takes to from a distant object, because speed of light is
2. Allows us to about the by most
B. The universe is than what
1. : what we because light has had enough to reach us
2. the size of the observable universe, but can’t see beyond the because universe is still expanding
C. of galaxies are to normal shifts
1. Galaxies really , but space
2. : light is with space as it through the universe
If the universe is expanding, what is actually causing galaxies to have redshifts?
A. Galaxies are moving quickly through space.
B. Light from the galaxies is moving faster now than in the past.
C. There are more red stars in far away galaxies.
D. Light from the galaxies is being stretched as it travels through space.
Evidence for the Big Bang Theory
VII. for the Big Bang Theory: (CMB)
A. If (energy) was in a , it was (plasma)
1. Would have been to , bounce around like inside a star
B. at a time called
1. When free and become the first around years after the Big Bang
2. The of the universe was several degrees
C. Due to , first away from visible light, and temperatures
D. : from universe now in
1. in 1948 by Alpher, Bethe, & Gamow: CMB should at a of about Kelvin
E. in 1965 by with a telescope at a temperature of about
1. Modern of Big Bang Theory very well
Tutorial Activity – Expansion
“Elementary Astronomy Worksheet Handout 22: Distance Ladder, Hubble’s Law” (modified by Kaisa E. Young) by Catherine Whiting via OER Commons, licensed under CC BY 4.0, https://oercommons.org/courses/elementary-astronomy-worksheets
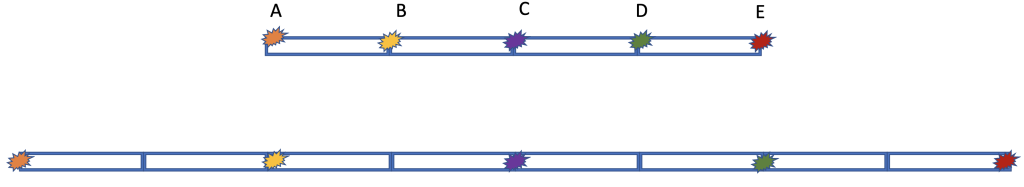
Figure 1: Expansion of the Universe by Catherine Whiting, licensed under CC BY 4.0
1. Suppose the universe is 1D, but expanding as shown in Figure 1. Imagine 5 galaxies, A – E, equally spaced by 1 Mpc (megaparsec), indicated by the length of a blue box. The universe expands to double its initial size after 1 year.
(a) Consider being in galaxy A:
i. How far has galaxy B moved in one year?
ii. How fast has galaxy B moved away in one year? (speed = how much distance in how much time)
iii. How far has galaxy D moved in one year?
iv. How fast has galaxy D moved away?
(b) Now consider being in galaxy C:
i. How fast has galaxy A moved away in one year?
ii. How fast has galaxy B moved away?
(c) Now consider being in galaxy E:
i. Rank the speeds of the other galaxies from slowest to fastest.
2. Is what you found consistent with the Hubble-Lemaitre Law? Why or why not?
3. Are galaxies A and E at the edge of the universe? Is galaxy C at the center?
Tutorial Activity – Big Bang Video Response
Video Response Writing: Think about what you learned in the video, write at least 5 sentences about your thoughts. Full credit is based on the length and content of your responses. Responses should be relevant and thoughtful.
To get you started, here are some prompts. You may want to start with one of the following (but don’t have to):
When the narrator said , I thought….
I was confused when he said , because….
The video made me wonder about ….
I have a hard time believing , because ….
I was surprised when he said , because …
Tutorial Activity – Big Bang
“Elementary Astronomy Worksheet Handout 23: Big Bang” (modified by Kaisa E. Young) by Catherine Whiting via OER Commons, licensed under CC BY 4.0, https://oercommons.org/courses/elementary-astronomy-worksheets
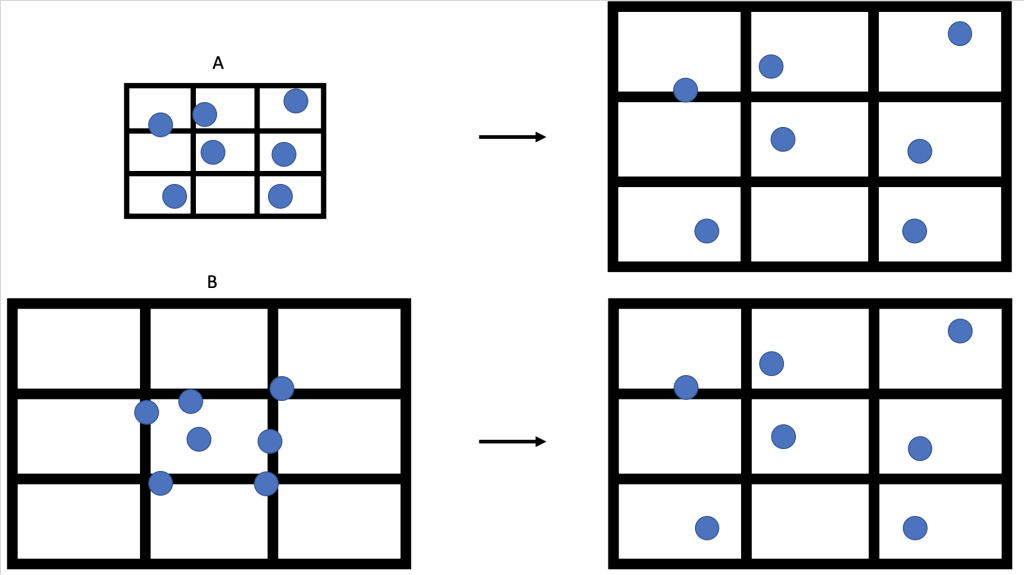
Figure 2: Expansion vs. Explosion of the Universe by Catherine Whiting, licensed under CC BY 4.0
1. According to the Big Bang Theory, which of the two possible universes in Figure 2 (A or B) best represents our universe? Explain why.
2. How did the density, pressure and temperature of the early universe compare to today?
3. (a) What is the Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation?
(b) Why do observations of the CMB support the Big Bang Theory?

