7 Chapter 7 – What is light?
OpenStax Astronomy Chapter 5: Radiation and Spectra
Light as a Wave
I. Light = , Light =
A. Can tell us about:
B. Use to collect light of all
1. Light is just what our eyes can see
II. Light as a
A. Light is a wave – up and down, ripples in a pond
B. Sound is a wave – Requires a to travel through, like air
1. No sound in , because no medium
III. Properties of Waves
A. (λ): length between peaks of wave
B. (ν): number of waves that pass by each second
C. Wavelength and frequency are related to the (c)
1. c = (wavelength times frequency)
2. c is a speed, c = 186,000 miles/s or 670,000,000 mph
a. Light takes to travel across space
D. Light with a wavelength has frequency, because the speed of light is always the
E. Light with a short has a high (fast)
Light as a Particle
IV. Light as a
A. Light behaves like a wave and a particle (wave-particle duality)
B. : particle or packet of light
C. Photons carry specific amounts of
D. photons = light with frequency and wavelength
1. Examples:
E. photons = light with frequency and wavelength
1. Examples:
F. Application: Two laser beams with the same energy (intensity) but different will emit different in one second
1. low energy photons needed to create amount of energy, same level of intensity
2. Blue laser: energy, emits photons (quarters)
3. Red laser: energy, emits photons (pennies)
Car radios usually have 2 different frequency ranges: FM and AM.
- FM: 88 to 107 MHz (million cycles per second)
- AM: 570 to 1600 kHz (thousand cycles per second)
Which statement(s) are true?
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
V. Electromagnetic (EM)
A. Light is an wave – caused by electric and magnetic fields
B. EM Spectrum: light (meaning all types of energy waves) sorted by
C. From to wavelength (high to low frequency):
Which of the following has the shortest wavelength?
A. A photon of ultraviolet light
B. Blue electromagnetic radiation
C. An X-ray
D. A radio wave
E. Infrared radiation
D. light is only a part of EM Spectrum
E. order (ROYGBIV) is wavelength
1. Red is the wavelength: 700 nanometers
2. (astronomers often just say “blue”) is the shortest: 350 nm
Which of the following is true?
A. Infrared light has lower energy and travels slower than X-rays.
B. Infrared light has lower energy, but travels at the same speed as X-rays.
C. Infrared light has higher energy and travels faster than X-rays.
Tutorial Activity – Light
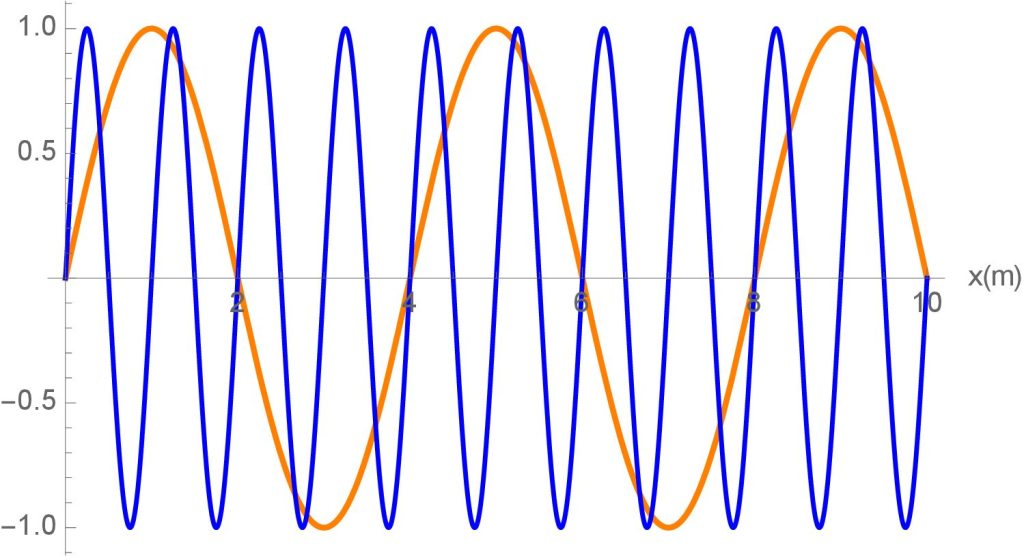
(b) What is the wavelength of the blue wave?
(c) If both of these waves represent visible light, is one traveling at a faster speed than the other?
(e) Which one has the largest/highest energy?
(a) List the types of electromagnetic waves in order of smallest wavelength to largest, including visible (red and blue) light.
(b) What type has the highest frequency?
(c) What type has the smallest/lowest energy?
3. Why is it dangerous to be exposed to X-rays but not as dangerous to be exposed to radio waves?

