15 Chapter 15 – What’s the difference between asteroids and comets?
OpenStax Astronomy Chapter 13 (Comets & Asteroids) & Chapter 14 (Meteorites)
Asteroids
I.
A. Most in between
1. of asteroids, but
B. shaped planetesimals
1. of small rocks to a few across, are
2. Jupiter’s prevented them a planet
C. Most are made of
D. Possible for them to have small
Comets
II.
A. found in either:
1. : flat , just beyond , 30 – 1,000 AU
2. : beyond Kuiper Belt, of objects surrounding the Solar System, out to of AU
B. of the time, comets are just a with
1. : (water, methane, ammonia) and mix
2. Range of , up to several across
III. comets
A. (in Kuiper Belt or Oort Cloud), only comet
B. But, if orbit comes , comets become
C. Sun the nucleus and material is forming:
1. (head): spherical of gas and dust around
2. : (charged) makes a tail
3. : grains of fall away to make a tail
D. Comet tails always point from the Sun.
When a comet is in the Oort cloud, what would it look like?
Meteors & Meteorites
IV. Solar System
A. Debris :
1. disintegration, during active stage
2.
B. Usually the of
1. pieces from asteroids called
C. When debris in the called a
1. Also known as , but not a star
D. Earth through debris results in
1. of meteors from particular in sky – paths make look like radiating from point
2. Happen about a times a year, example:
V.
A. meteoroids that the atmosphere and fall to are called
1. debris almost always in atmosphere
2. If asteroid fragment is about as big as your , it can make it to the surface
B. Over 90% are , contain like Earth rocks so hard to identify
C. meteorites have lots of metal like iron and
D. meteorites are a and are more rare
Tutorial Activity – Small Bodies
“Elementary Astronomy Worksheet Handout 16: Small Solar System Bodies” (modified by Kaisa E. Young) by Catherine Whiting via OER Commons, licensed under CC BY 4.0, https://oercommons.org/courses/elementary-astronomy-worksheets
1. The terms asteroid, meteoroid, meteor, and meteorite often are used interchangeably, but they have different meanings in astronomy, even though they all refer to the same types of objects:
Asteroid = a large rocky object, typically found in the asteroid belt
Meteoroid = a small rocky object moving through space
Meteor = a meteoroid that enters Earth’s atmosphere creating a bright streak in the sky (also called a shooting star).
Meteorite = a leftover piece of a meteor that was big enough to make it through Earth’s atmosphere and hit the ground.
(a) If you find a rock on the ground that came from space, what would you call it?
(b) Last night I saw a bright in the sky when I was stargazing.
(c) A(n) is discovered to be on a collision course with Earth in 2030.
2. Why is there an asteroid belt?
3. (a) Do all comets have tails?
(b) What do comets look like most of the time?
4. The blue ellipse is an orbit of a comet around the Sun. The orange circle is approximately Earth’s orbit. Which of the locations will the comet have a tail? For each of those locations, sketch the direction of the tail.
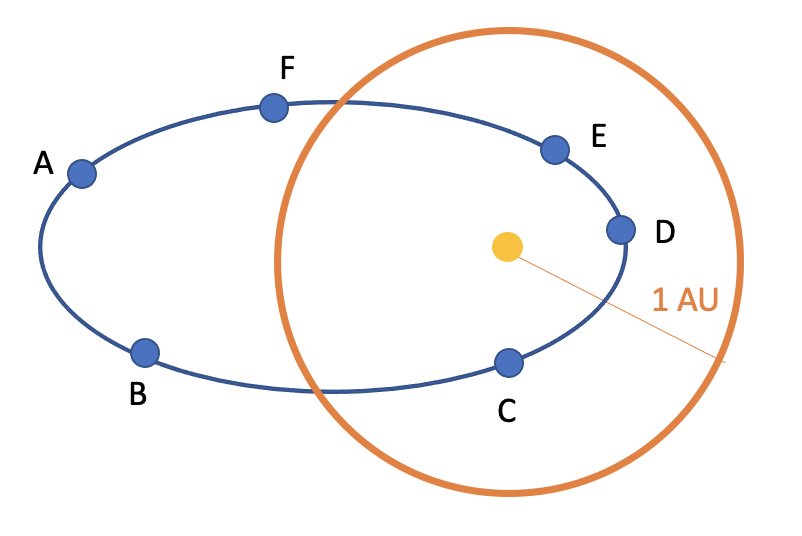
Figure 1: Comet Tail by Catherine Whiting, licensed under CC BY 4.0
5. (a) What is a meteor shower?
(b) Why is there a meteor shower every year at the same time in August called the Perseid shower?

