3 Chapter 3 – Why are there seasons?
OpenStax Astronomy Chapter 4 Section 2: The Seasons
Earth’s Tilt
I. are due to Earth’s tilt
A. reasons:
1. The is more when Earth is tilted the Sun (Summer), energy is more concentrated
2. The Sun is in the sky in the , more hours of daylight
B. in : direct sunlight, tilted away, Sun in sky time
C. of the Northern Hemisphere
1. When the Northern Hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun, the Southern is tilted away
D. This has to do with
1. Earth will be to the Sun in and farthest in July because orbit not quite circular
Solstices and Equinoxes
From a Northern Hemisphere viewpoint
II. :
A. Solstice
1. Sun most directly in direction of , farthest at sunrise/sunset
2. day – around 20 – 22 in Northern Hemisphere
3. Sun in sky it will ever get at noon
4. Hemisphere – solstice in , Sun moves toward South Pole
B. Solstice
1. Sun most directly of North Celestial Pole, farthest
2. day – around 21 – 22 (Northern Hemisphere)
3. Sun at noon
III. :
A. (fall) Equinox
1. Sun on the where it crosses the ecliptic
2. Sun moving farther , lower, in sky
3. of day and night – around 22 – 23 (Northern Hemisphere)
4. Hemisphere – autumnal equinox is in
B. (spring) Equinox
1. Sun again on the celestial equator, moving in sky
2. Equal hours of day and night – around 20 – 21 (Northern Hemisphere)
When would the sun be in the sky for the longest (most daylight hours)?
I. Northern Hemisphere in June
II. Southern Hemisphere in June
III. Northern Hemisphere in December
IV. Southern Hemisphere in December
If the ecliptic was at the celestial equator, what would happen to the seasons?
A. Nothing. They would be the same.
B. Each season would be longer.
C. Each season would be shorter.
D. We would not have seasons.
Resources
NAAP Seasons and Ecliptic simulation: https://astro.unl.edu/naap/motion1/animations/seasons_ecliptic.html
Tutorial Activity – Seasons
“Elementary Astronomy Worksheet Handout 3: Motions of Stars, Seasons” (modified by Kaisa E. Young) by Catherine Whiting via OER Commons, licensed under CC BY 4.0, https://oercommons.org/courses/elementary-astronomy-worksheets
1. What property of the Earth’s motion causes seasons? Explain the 2 reasons why that property causes seasons.
2. In Figure 1 below, label the positions of Earth when it is the Summer and Winter Solstices, and the Spring
(Vernal) and Fall (Autumnal) Equinoxes in the Northern Hemisphere. Also include the (approximate) dates when these occur.
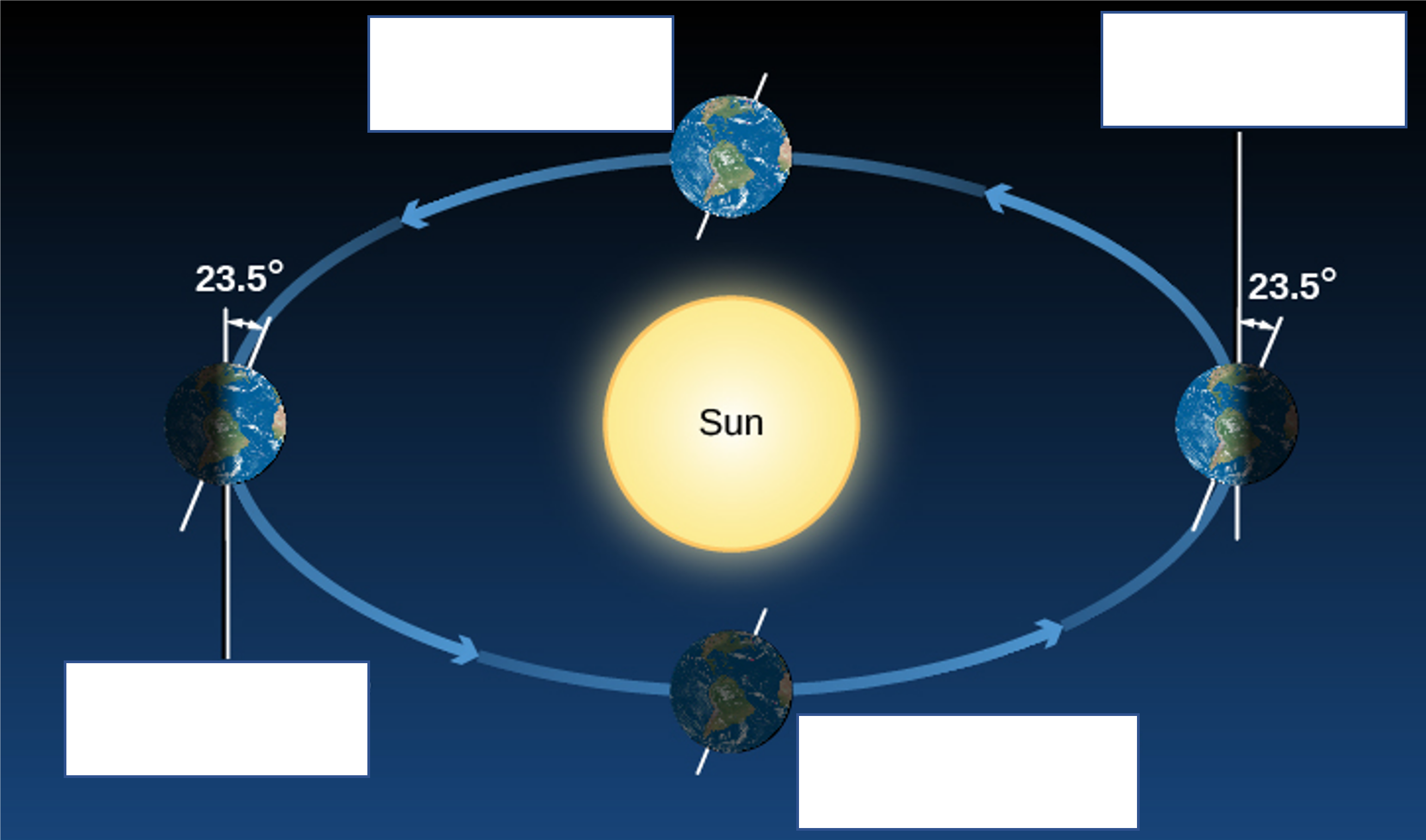
Figure 1: ”Seasons” (modified by Catherine Whiting) by Andrew Fraknoi, David Morrison, and Sidney
Wolff via OpenStax, licensed under CC BY 4.0
3. When is the ecliptic (Sun):
a) High in the sky?
b) Low in the sky?
c) When does the Sun cross the Celestial Equator?
4. What would change about the Earth if its axis were tilted by 45° instead of 23.5°?
5. What would change about the Earth if the ecliptic lined up with the celestial equator?

