14 3.3: Chemical Hazards
3.3 CHEMICAL HAZARDS
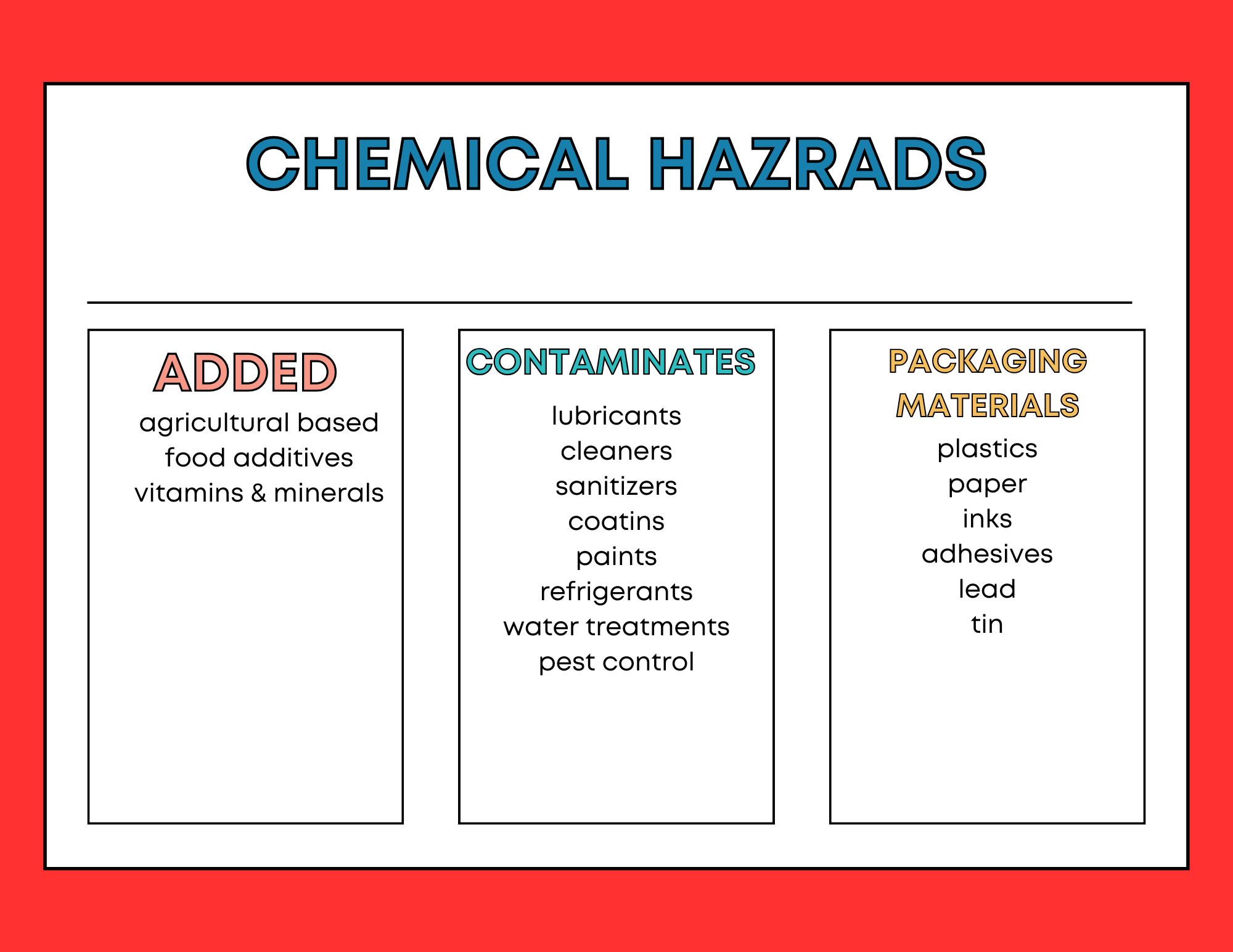
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is responsible for determining which substances can be safely added to food for human consumption. Food can be contaminated (made impure) by chemicals used in manufacturing, packaging, processing, handling, and agricultural production. Various chemicals are used throughout the food production process, from growing to packaging, to preserve quality, enhance nutritional value, extend shelf life, and protect against harmful microorganisms. Food can also become contaminated with harmful chemicals. These contaminants may include pesticides used to control pests in agricultural fields or kitchens, certain cleaning agents, and chemicals that leach from improper storage or cooking containers. For example, using galvanized containers to store food can be dangerous and should be avoided, as they can release toxic substances. https://ask.usda.gov/s/article/What-is-food-contamination
Environmental contaminants such as lead, arsenic, or mercury may also enter the food supply through soil, water, or air during the growing, raising, or processing stages. Additionally, certain unwanted chemicals may form during food processing methods like heating, drying, or fermenting.To manage and mitigate these risks, the FDA issues regulations, provides guidance, and conducts inspections to ensure food chemical safety. (https://www.fda.gov/food/food-ingredients-packaging/food-chemical-safety) In addition, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) plays a key role in regulating pesticide use and establishing safe residue limits on crops to protect consumers from pesticide exposure.
Chemical hazards can vary based on the aspect of production they are related to. Some potential chemical hazard contamination could happen prior to a processor receiving product, such as the improper use of pesticides or antimicrobial residues.
 Others could be chemicals used on processing equipment to lubricate such as oils or cleaners and sanitizers used on manufacturing equipment. Other potential chemical hazards may include substances that are deemed safe at certain lower levels but can cause illness or injury if consumed at too high of a level.
Others could be chemicals used on processing equipment to lubricate such as oils or cleaners and sanitizers used on manufacturing equipment. Other potential chemical hazards may include substances that are deemed safe at certain lower levels but can cause illness or injury if consumed at too high of a level.
The FDA helps safeguard the food supply through safety evaluations of chemicals as food ingredients and in substances that come into contact with food, such as through food packaging, storage, or other handling, to ensure they are safe for use. The FDA also ensures that the industry is preventing, when possible, and mitigating, when prevention is not possible, unsafe exposure to chemical contaminants that can enter the food supply through the growing and processing environment. The FDA assists the food industry through creation of regulations, guidance documents, and regulatory programs.
