18 3.7: Cross-Contamination vs Cross-Contact
3.7 CROSS-CONTAMINATION vs CROSS-CONTACT
In 2013, the FDA started distinguishing between the terms cross-contamination and cross-contact (Lupo, 2018). Cross-contamination, the more general of the two words, is the transfer of bacteria from foods, hands, utensils, or food preparation surfaces to food. Cross-contact is the unintentional incorporation of a food allergen into a food. The FDA guidelines for cutting boards state that one should be used for fresh produce and a separate one for raw meat, poultry, and seafood. While not mandatory, the food service industry develops color-coded cutting boards to help mitigate cross-contact:
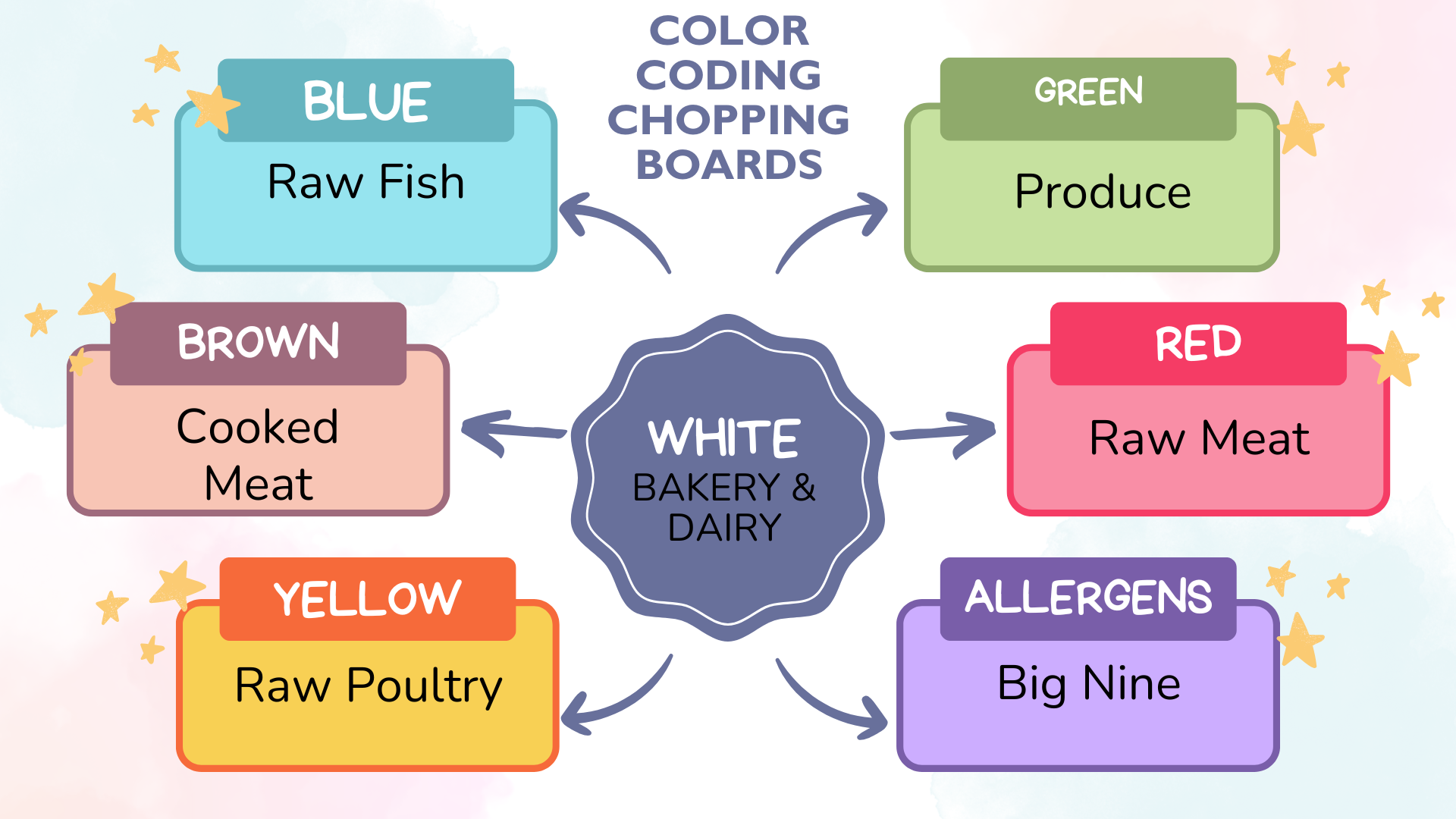
US cutting board color chart https://www.fooddocs.com/food-safety-templates/cutting-board-color-chart
Key Takeaways
To ensure food safety, understand that physical contamination involves foreign objects, chemical contamination involves harmful substances, and allergen contamination involves cross-contact with allergens, requiring strict separation and cleaning procedures.
