46 8.3: Thawing Food Safely
8.3 Thawing Food Safely
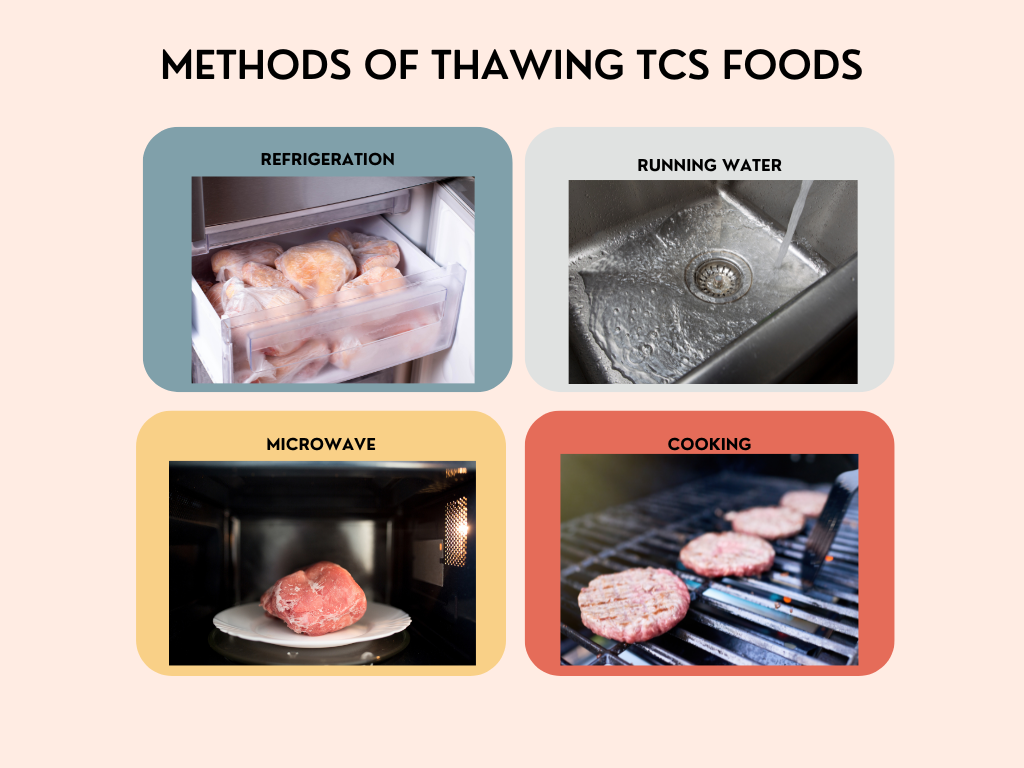
There are four approved methods of thawing TCS food properly. Frozen TCS food can be thawed:
In the refrigerator- With proper advanced planning,food can be thawed under refrigeration. Depending on the item, it can take several hours or days to thaw.
Under cold running water ≤ 70°F (21℃)- The food should be submerged and potable running water should run over the item until it is thawed. The sink used must also be cleaned and sanitized before thawing.
As part of the cooking process-Some frozen food can be thawed as it cooks. Since the item will pass through the temperature danger zone quickly, it can be cooked from the frozen state.
In the microwave- Thawing in the microwave is allowed if and only if the food is cooked immediately after thawing.
Special Preparation Considerations
Some TCS foods require extra care in their preparation to ensure safety. This is especially true for foods that will be served to highly-susceptible populations. These are some guidelines where extra attention should be in food preparation:
Reduced-oxygen packaging (ROP) fish- Frozen fish in reduced-oxygen packaging should remain frozen until being prepared for service and should be removed from packaging before thawing under refrigeration. If the fish is thawed under running water, it must be removed from its packaging immediately after thawing is complete.
Eggs- Eggs are sometimes cracked and put together in a common container. The term used to describe the combined eggs is pooled eggs. Pooled eggs must be stored at 41℉ (5℃) or cooked right away. Several foods are made by using eggs that are raw or undercooked. Hollandaise sauce, meringue, and traditional Caesar dressing are all made with eggs that require little to no cooking. To make menu items like this safer to eat, they should be prepared with eggs that have been pasteurized. Pasteurized eggs should be used in facilities that serve highly-susceptible populations as an added safety precaution.
Fresh Juice- Fresh fruit and vegetable juices are typically not cooked and therefore may contain harmful bacteria. Pasteurization reduces pathogens to a safe level. Any fresh juice that is not pasteurized should come with a consumer warning label and should not be served to highly susceptible populations.
Ice-Ice is actually considered to be a food. Therefore, it is susceptible to becoming contaminated like any other food. Ice can be used in helping keep food cold like on a salad bar. Ice is also used to cool down food and drinks. It is imperative that the water ice is made from is safe to drink. Additionally, ice that is used for keeping food cold should never be used as ice for consumption. Ice scoops should be stored outside of the machine in a covered receptacle and the food employee should only use the scoop to retrieve ice. Hands, cups, or glasses should never be used to retrieve ice.
Variance Procedures- Some operations process foods that require special permissions in the way those foods are prepared. A variance is a document issued by the regulatory authority that allows a standard compliance procedure be waived or changed for a specific food’s processing. Some examples of food requiring a variance would be live shellfish sold and prepared from a display tank, cured foods, sprouting seeds or beans, and foods that have additives to preserve them so they no longer need to be temperature controlled for safety.
The figure below shows the examples of these special preparation considerations.

