The Role of Proteins in Foods: Cooking and Denaturation
In addition to having many vital functions within the body, proteins perform different roles in our foods by adding certain functional qualities. Protein provides food with structure and texture and enables water retention. For example, proteins foam when agitated. (Picture whisking egg whites to make angel food cake. The foam bubbles give the angel food cake its airy texture.) Yogurt is another good example of proteins providing texture. Milk proteins called caseins coagulate, increasing yogurt’s thickness. Cooked proteins add color and flavor to foods as the amino group binds with carbohydrates, producing a brown pigment and aroma. Eggs are between 10 and 15 percent protein by weight. Most cake recipes use eggs because the egg proteins help bind all the other ingredients into a uniform cake batter. The proteins aggregate into a network during mixing and baking, which gives the cake its structure.

Protein Denaturation: Unraveling the Fold
When a cake is baked, the proteins are denatured. Denaturation refers to the physical changes that take place in a protein exposed to abnormal conditions in the environment. Heat, acid, high salt concentrations, alcohol, and mechanical agitation can cause proteins to denature. When a protein denatures, its complicated folded structure unravels, and it becomes just a long strand of amino acids again. Weak chemical forces that hold tertiary and secondary protein structures together are broken when a protein is exposed to unnatural conditions. Because proteins’ function is dependent on their shape, denatured proteins are no longer functional.
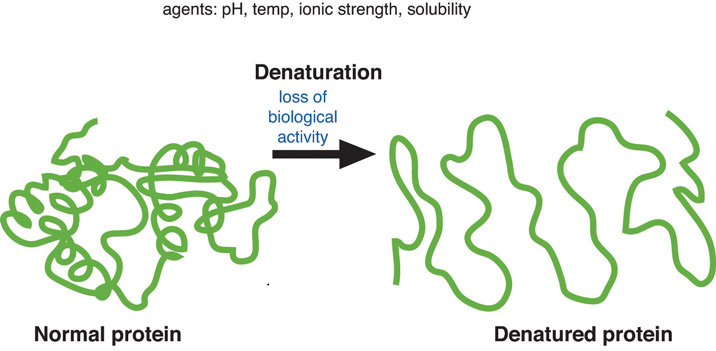
When a protein is exposed to a different environment, such as increased temperature, it unfolds into a single strand of amino acids. (Source: University of Hawaii @ Manoa, CC-BY-NC-SA)
Learning Activities
Technology Note: The second edition of the Human Nutrition Open Educational Resource (OER) textbook features interactive learning activities. These activities are available in the web-based textbook and are not in downloadable versions (EPUB, Digital PDF, Print_PDF, or Open Document).
Learning activities may be used across various mobile devices; however, for the best user experience, it is strongly recommended that users complete these activities using a desktop or laptop computer.
A class of compounds composed of linked amino acids. They contain carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and sometimes other atoms in specific configurations.
The loss of a protein’s functional three-dimensional structure due to environmental influences such as temperature or pH.
The molecules from which proteins are built, each protein being composed of a specific sequence of linked amino acids.

