Water-Soluble Vitamins
water-soluble vitamins play a different kind of role in energy metabolism; they are required as functional parts of enzymes involved in energy release and storage. Vitamins and minerals that make up part of enzymes are referred to as coenzymes and cofactors, respectively. Coenzymes and cofactors are required by enzymes to catalyze a specific reaction. They assist in converting a substrate to an end-product. Coenzymes and cofactors are essential in catabolic pathways and play a role in many anabolic pathways too. In addition to being essential for metabolism, many vitamins and minerals are required for blood renewal and function. At insufficient levels in the diet these vitamins and minerals impair the health of blood and consequently the delivery of nutrients in and wastes out, amongst its many other functions. In this section we will focus on the vitamins that take part in metabolism and blood function and renewal.
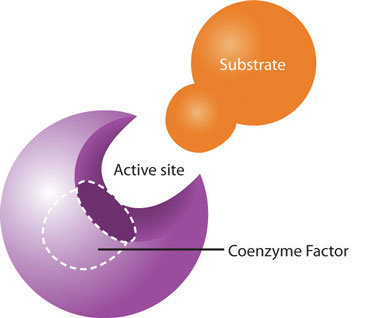
Coenzymes and cofactors are the particular vitamin or mineral required for enzymes to catalyze a specific reaction. (Source: University of Hawaii @ Manoa, CC-BY-NC-SA)
Vitamin C Functions and Health Benefits
Vitamin C, also commonly called ascorbic acid, is a water[-soluble micronutrient essential in the diet for humans, although most other mammals can readily synthesize it. Vitamin C’s ability to easily donate electrons makes it a highly effective antioxidant. It is effective in scavenging reactive oxygen species, reactive nitrogen species, and many other free radicals. It protects lipids both by disabling free radicals and by aiding in the regeneration of vitamin E.
In addition to its role as an antioxidant, vitamin C is a required part of several enzymes like signaling molecules in the brain, some hormones, and ]amino acids. Vitamin C is also essential for the synthesis and maintenance of collagen. Collagen is the most abundant protein in the body and used for different functions such as the structure for ligaments, tendons, and blood vessels and also scars that bind wounds together. Vitamin C acts as the glue that holds the collagen fibers together and without sufficient levels in the body, collagen strands are weak and abnormal. (Figure 9.8 “The Role of Vitamin C in Collagen Synthesis”)
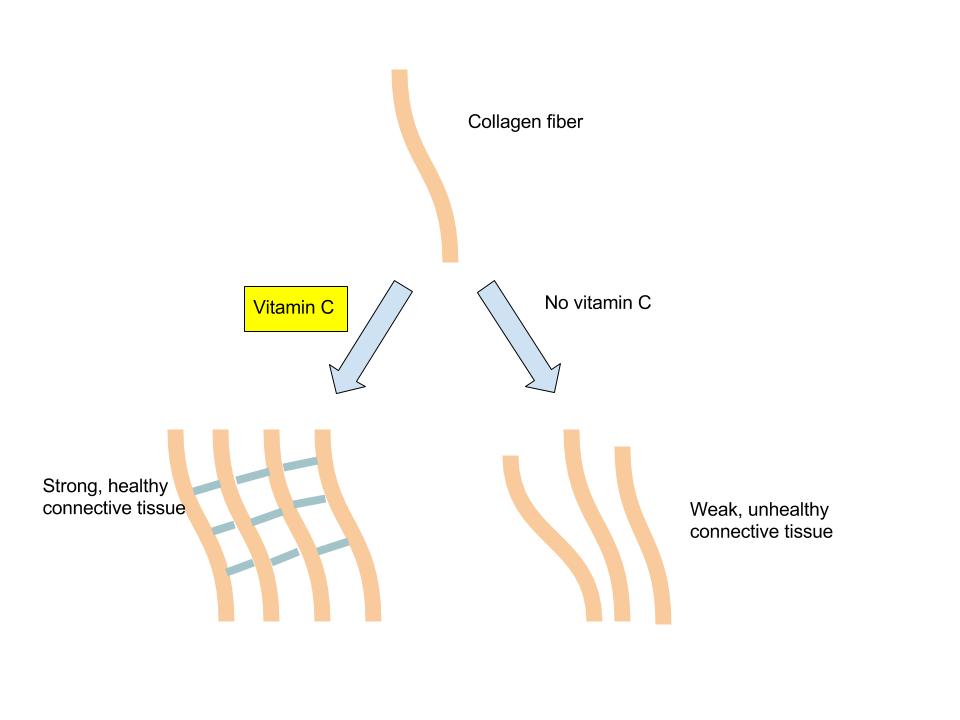
(Source: University of Hawaii @ Manoa, Allison Calabrese, CC-BY)
Vitamin C levels in the body are affected by the amount in the diet, which influences how much is absorbed and how much the kidney allows to be excreted, such that the higher the intake, the more vitamin C is excreted. Vitamin C is not stored in any significant amount in the body, but once it has reduced a free radical, it is very effectively regenerated and therefore it can exist in the body as a functioning antioxidant for many weeks.
The classic condition associated with vitamin C deficiency is scurvy. The signs and symptoms of scurvy include skin disorders, bleeding gums, painful joints, weakness, depression, and increased susceptibility to infections. Scurvy is prevented by having an adequate intake of fruits and vegetables rich in vitamin C.
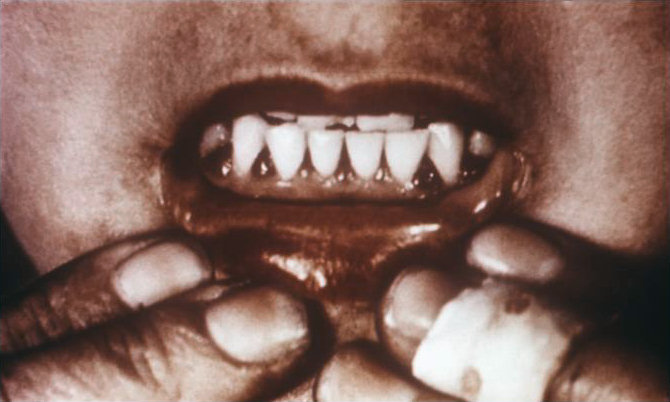
(Source: Wikimedia Commons, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Public Domain)
Cardiovascular Disease
Vitamin C’s ability to prevent disease has been debated for many years. Overall, higher dietary intakes of vitamin C (via food intake, not supplements), are linked to decreased disease risk. A review of multiple studies published in the April 2009 issue of the Archives of Internal Medicine concludes there is moderate scientific evidence supporting the idea that higher dietary vitamin C intakes are correlated with reduced cardiovascular disease risk, but there is insufficient evidence to conclude that taking vitamin C supplements influences cardiovascular disease risk.[1] Vitamin C levels in the body have been shown to correlate well with fruit and vegetable intake, and higher plasma vitamin C levels are linked to reduced risk of some chronic diseases. In a study involving over twenty thousand participants, people with the highest levels of circulating vitamin C had a 42 percent decreased risk for having a stroke.[2]
Cancer
There is some evidence that a higher vitamin C intake is linked to a reduced risk of cancers of the mouth, throat, esophagus, stomach, colon, and lung, but not all studies confirm this is true. As with the studies on cardiovascular disease, the reduced risk of cancer results from eating foods rich in vitamin C, such as fruits and vegetables, not from taking vitamin C supplements. In these studies, the specific protective effects of vitamin C cannot be separated from the many other beneficial chemicals in fruits and vegetables.
Immunity
Vitamin C does have several roles in the immune system, and many people increase vitamin C intake either from diet or supplements when they have a cold. Many others take vitamin C supplements routinely to prevent colds. Contrary to this popular practice, however, there is no good evidence that vitamin C prevents a cold. A review of more than fifty years of studies published in 2004 in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews concluded that taking vitamin C routinely does not prevent colds in most people, but it does slightly reduce cold severity and duration. Moreover, taking megadoses (up to 4 grams per day) at the onset of a cold provides no benefits.[3]
Gout is a disease caused by elevated circulating levels of uric acid and is characterized by recurrent attacks of tender, hot, and painful joints. There is some evidence that a higher intake of vitamin C reduces the risk of gout.
Vitamin C Toxicity
High doses of vitamin C have been reported to cause numerous problems, but the only consistently shown side effects are gastrointestinal upset and diarrhea. To prevent these discomforts the IOM has set a UL for adults at 2,000 milligrams per day (greater than twenty times the RDA).
At very high doses in combination with iron, vitamin C has sometimes been found to increase oxidative stress, reaffirming that getting your antioxidants from foods is better than getting them from supplements, as that helps regulate your intake levels. There is some evidence that taking vitamin C supplements at high doses increases the likelihood of developing kidney stones, however, this effect is most often observed in people that already have multiple risk factors for kidney stones.
Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C
The RDAs and ULs for different age groups for vitamin C are listed in Table 9.11, “Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin C”.[4] They are considered adequate to prevent scurvy. Vitamin C’s effectiveness as a free radical scavenger motivated the Institute of Medicine (IOM) to increase the RDA for smokers by 35 milligrams, as tobacco smoke is an environmental and behavioral contributor to free radicals in the body.
| Age Group | RDA Males and Females mg/day | UL |
|---|---|---|
| Infants (0–6 months) | 40* | – |
| Infants (7–12 months) | 50* | – |
| Children (1–3 years) | 15 | 400 |
| Children (4–8 years) | 25 | 650 |
| Children (9–13 years) | 45 | 1200 |
| Adolescents (14–18 years) | 75 (males), 65 (females) | 1800 |
| Adults (> 19 years) | 90 (males), 75 (females) | 2000 |
| *denotes Adequate Intake |
Dietary Sources of Vitamin C
Citrus fruits are great sources of vitamin C and so are many vegetables. In fact, British sailors in the past were often referred to as “limeys” as they carried sacks of limes onto ships to prevent scurvy. Vitamin C is not found in significant amounts in animal-based foods.
Because vitamin C is water-soluble, it leaches away from foods considerably during cooking, freezing, thawing, and canning. Up to 50 percent of vitamin C can be boiled away. Therefore, to maximize vitamin C intake from foods, you should eat fruits and vegetables raw or lightly steamed. For the vitamin C content of various foods, see Table 9.12 “Vitamin C Content of Various Foods”.[5]
| Food | Serving | Vitamin C (mg) | Percent Daily Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Orange juice | 6 oz. | 93 | 155 |
| Grapefruit juice | 6 oz. | 70 | 117 |
| Orange | 1 medium | 70 | 117 |
| Strawberries | 1 c. | 85 | 164 |
| Tomato | 1 medium | 17 | 28 |
| Sweet red pepper | ½ c. raw | 95 | 158 |
| Broccoli | ½ c. cooked | 51 | 65 |
| Romaine lettuce | 2 c. | 28 | 47 |
| Cauliflower | 1 c. boiled | 55 | 86 |
| Potato | 1 medium, baked | 17 | 28 |
Thiamin (B1 ) Functions and Health Benefits
Thiamin is especially important in glucose metabolism. It acts as a cofactor for enzymes that break down glucose for energy production (Figure 9.7 “Enzyme Active Site for Cofactors” ). Thiamin plays a key role in nerve cells as the glucose that is catabolized by thiamin is needed for an energy source. Additionally, thiamin plays a role in the synthesis of neurotransmitters and is therefore required for RNA, DNA, and ATP synthesis.
The brain and heart are most affected by a deficiency in thiamin. Thiamin deficiency, also known as beriberi, can cause symptoms of fatigue, confusion, movement impairment, pain in the lower extremities, swelling, and heart failure. It is prevalent in societies whose main dietary staple is white rice. During the processing of white rice, the bran is removed, along with what were called in the early nineteenth century, “accessory factors,” that are vital for metabolism. Dutch physician Dr. Christiaan Eijkman cured chickens of beriberi by feeding them unpolished rice bran in 1897. By 1912, Sir Frederick Gowland Hopkins determined from his experiments with animals that the “accessory factors,” eventually renamed vitamins, are needed in the diet to support growth, since animals fed a diet of pure carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and minerals failed to grow.[6]Eijkman and Hopkins were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology (or Medicine) in 1929 for their discoveries in the emerging science of nutrition.
Another common thiamin deficiency known as Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome can cause similar symptoms as beriberi, such as confusion, loss of coordination, vision changes, hallucinations, and may progress to coma and death. This condition is specific to alcoholics as diets high in alcohol can cause thiamin deficiency. Other individuals at risk include individuals who also consume diets typically low in micronutrients such as those with eating disorders, elderly, and individuals who have gone through gastric bypass surgery.[7]
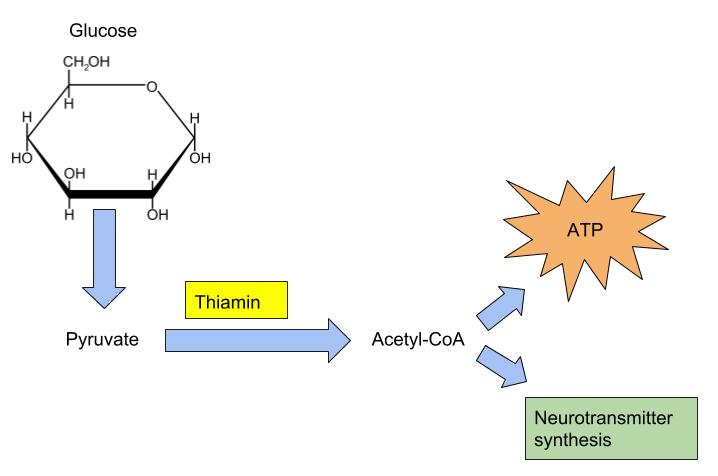
(Source: University of Hawaii @ Manoa, Allison Calabrese, CC-BY)
Dietary Reference Intakes
The RDAs and ULs for different age groups for thiamin are listed in Table 9.13 “Dietary Reference Intakes for Thiamin”.[8] There is no UL for thiamin because there have not been any reports on toxicity when excess amounts are consumed from food or supplements.
| Age Group | RDA Males and Females mg/day |
|---|---|
| Infants (0–6 months) | 0.2 * |
| Infants (7–12 months) | 0.3 |
| Children (1–3 years) | 0.5 |
| Children (4–8 years) | 0.6 |
| Children (9–13 years) | 0.9 |
| Adolescents (14–18 years) | 1.2 (males), 1.0 (females) |
| Adults (> 19 years) | 1.2 (males), 1.1 (females) |
| *denotes Adequate Intake |
Dietary Sources
Whole grains, meat and fish are great sources of thiamin. The United States as well as many other countries, fortify their refined breads and cereals. For the thiamin content of various foods, see Table 9.14 “Thiamin Content of Various Foods”.[9]
| Food | Serving | Thiamin (mg) | Percent Daily Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breakfast cereals, fortified | 1 serving | 1.5 | 100 |
| White rice, enriched | ½ c. | 1.4 | 73 |
| Pork chop, broiled | 3 oz. | 0.4 | 27 |
| Black beans, boiled | ½ c. | 0.4 | 27 |
| Tuna, cooked | 3 oz. | 0.2 | 13 |
| Brown rice, cooked, not enriched | ½ c. | 0.1 | 7 |
| Whole wheat bread | 1 slice | 0.1 | 7 |
| 2% Milk | 8 oz. | 0.1 | 7 |
| Cheddar cheese | 1 ½ oz | 0 | 0 |
| Apple, sliced | 1 c. | 0 | 0 |
Riboflavin (B2) Functions and Health Benefits
Riboflavin is an essential component of flavoproteins, which are coenzymes involved in many metabolic pathways of carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism. Flavoproteins aid in the transfer of electrons in the electron transport chain. Furthermore, the functions of other B-vitamin coenzymes, such as vitamin B6 and folate, are dependent on the actions of flavoproteins. The “flavin” portion of riboflavin gives a bright yellow color to riboflavin, an attribute that helped lead to its discovery as a vitamin. When riboflavin is taken in excess amounts (supplement form) the excess will be excreted through your kidneys and show up in your urine. Although the color may alarm you, it is harmless. There are no adverse effects of high doses of riboflavin from foods or supplements that have been reported.
Riboflavin deficiency, sometimes referred to as ariboflavinosis, is often accompanied by other dietary deficiencies (most notably protein) and can be common in people that suffer from alcoholism. This deficiency will usually also occur in conjunction with deficiencies of other B vitamins because the majority of B vitamins have similar food sources. Its signs and symptoms include dry, scaly skin, cracking of the lips and at the corners of the mouth, sore throat, itchy eyes, and light sensitivity.
Dietary Reference Intakes
The RDAs for different age groups for riboflavin are listed in Table 9.15 “Dietary Reference Intakes for Riboflavin”.[10] There is no UL for riboflavin because no toxicity has been reported when an excess amount has been consumed through foods or supplements.
| Age Group | RDA Males and Females mg/day |
|---|---|
| Infants (0–6 months) | 0.3 * |
| Infants (7–12 months) | 0.4* |
| Children (1–3 years) | 0.5 |
| Children (4–8 years) | 0.6 |
| Children (9–13 years) | 0.9 |
| Adolescents (14–18 years) | 1.3 (males), 1.0 (females) |
| Adults (> 19 years) | 1.3 (males), 1.1 (females) |
| *denotes Adequate Intake |
Dietary Sources
Riboflavin can be found in a variety of different foods but it is important to remember that it can be destroyed by sunlight. Milk is one of the best sources of riboflavin in the diet and was once delivered and packaged in glass bottles. This packaging has changed to cloudy plastic containers or cardboard to help block the light from destroying the riboflavin in milk. For the riboflavin content of various foods, see Table 9.16 Riboflavin Content of Various Foods”.[11]
| Food | Serving | Riboflavin (mg) | Percent Daily Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beef liver | 3 oz. | 2.9 | 171 |
| Breakfast cereals, fortified | 1 serving | 1.7 | 100 |
| Instant oats, fortified | 1 c. | 1.1 | 65 |
| Plain yogurt, fat free | 1 c. | 0.6 | 35 |
| 2% milk | 8 oz. | 0.5 | 29 |
| Beef, tenderloin steak | 3 oz. | 0.4 | 24 |
| Portabella mushrooms, sliced | ½ c. | 0.3 | 18 |
| Almonds, dry roasted | 1 oz. | 0.3 | 18 |
| Egg, scrambled | 1 large | 0.2 | 12 |
| Quinoa | 1 c. | 0.2 | 12 |
| Salmon, canned | 3 oz. | 0.2 | 12 |
| Spinach, raw | 1 c. | 0.1 | 6 |
| Brown rice | ½ c. | 0 | 0 |
Niacin (B3) Functions and Health Benefits
Niacin is a component of the coenzymes NADH and NADPH, which are involved in the catabolism and/or anabolism of carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. NADH is the predominant electron carrier and transfers electrons to the electron-transport chain to make ATP. NADPH is also required for the anabolic pathways of fatty-acid and cholesterol synthesis. In contrast to other vitamins, niacin can be synthesized by humans from the amino acid tryptophan in an anabolic process requiring enzymes dependent on riboflavin, vitamin B6, and iron. Niacin is made from tryptophan only after tryptophan has met all of its other needs in the body. The contribution of tryptophan-derived niacin to niacin needs in the body varies widely and a few scientific studies have demonstrated that diets high in tryptophan have very little effect on niacin deficiency. Niacin deficiency is commonly known as pellagra and the symptoms include fatigue, decreased appetite, and indigestion. These symptoms are then commonly followed by the four D’s: diarrhea, dermatitis, dementia, and sometimes death.
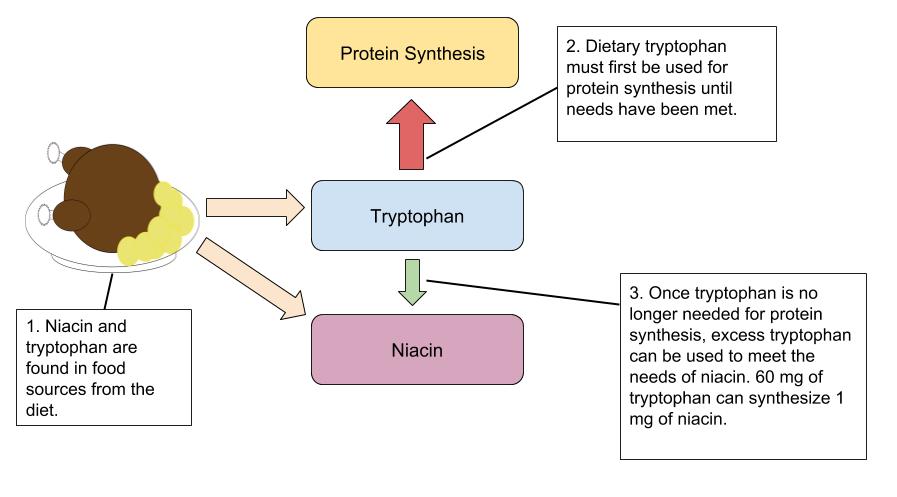
(Source: University of Hawaii @ Manoa, Allison Calabrese, CC-BY)
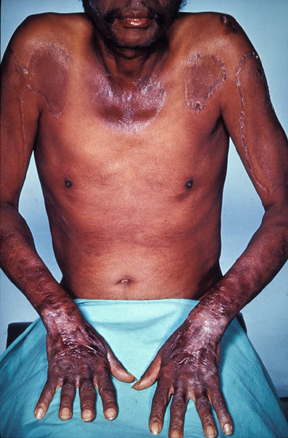
(Source: Wikimedia Commons, Fred L. Herbert, MD & Hendrik A. van Dijk, CC-BY-SA)
Dietary Reference Intakes
The RDAs and ULs for different age groups for Niacin are listed in Table 9.17 “Dietary Reference Intakes for Niacin “.[12] Because Niacin needs can be met from tryptophan, The RDA is expressed in niacin equivalents (NEs). The conversions of NE, Niacin, and tryptophan are: 1 mg NE= 60 mg tryptophan= 1 mg niacin
| Age Group | RDA Males and Females mg NE/day) | UL |
|---|---|---|
| Infants (0–6 months) | 2 * | Not possible to establish |
| Infants (7–12 months) | 4* | Not possible to establish |
| Children (1–3 years) | 6 | 10 |
| Children (4–8 years) | 8 | 15 |
| Children (9–13 years) | 12 | 20 |
| Adolescents (14–18 years) | 16 (males), 14 (females) | 30 |
| Adults (> 19 years) | 16 (males), 14 (females) | 35 |
| *denotes Adequate Intake |
Dietary Sources
Niacin can be found in a variety of different foods such as yeast, meat, poultry, red fish, and cereal. In plants, especially mature grains, niacin can be bound to sugar molecules which can significantly decrease the niacin bioavailability. For the niacin content of various foods, see Table 9.18 “Niacin Content of Various Foods”.[13]
| Food | Serving | Niacin (mg) | Percent Daily Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chicken | 3 oz. | 7.3 | 36.5 |
| Tuna | 3 oz. | 8.6 | 43 |
| Turkey | 3 oz. | 10.0 | 50 |
| Salmon | 3 oz. | 8.5 | 42.5 |
| Beef (90% lean) | 3 oz. | 4.4 | 22 |
| Cereal (unfortified) | 1 c. | 5 | 25 |
| Cereal (fortified) | 1 c. | 20 | 100 |
| Peanuts | 1 oz. | 3.8 | 19 |
| Whole wheat bread | 1 slice | 1.3 | 6.5 |
| Coffee | 8 oz. | 0.5 | 2.5 |
Pantothenic Acid (B5) Functions and Health Benefits
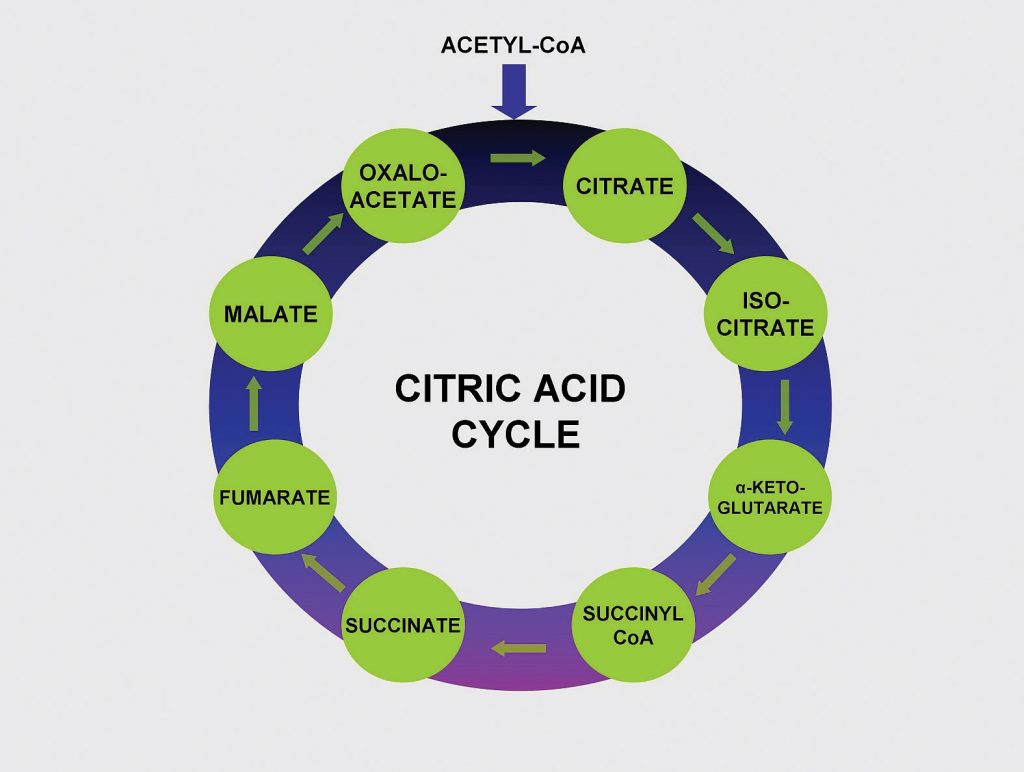
Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5) makes up coenzyme A, which carries the carbons of glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids into the citric acid cycle as Acetyl-CoA. (Source: University of Hawaii @ Manoa, CC-BY-NC-SA)
Pantothenic acid forms coenzyme A, which is the main carrier of carbon molecules in a cell. Acetyl-CoA is the carbon carrier of glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids into the citric acid cycle (Figure 9.14 “Pantothenic Acid’s Role in the Citric Acid Cycle”). Coenzyme A is also involved in the synthesis of lipids, cholesterol, and acetylcholine (a neurotransmitter). A pantothenic acid deficiency is exceptionally rare. Signs and symptoms include fatigue, irritability, numbness, muscle pain, and cramps. You may have seen pantothenic acid on many ingredients lists for skin and hair care products; however there is no good scientific evidence that pantothenic acid improves human skin or hair.
Dietary Reference Intakes
Because there is little information on the requirements for pantothenic acids, the Food and Nutrition Board (FNB) has developed Adequate Intakes (AI) based on the observed dietary intakes in healthy population groups. The AI for different age groups for pantothenic acid are listed in Table 9.19 “Dietary Reference Intakes for Pantothenic Acid “.[14]
| Age Group | AI Males and Females mg/day) |
|---|---|
| Infants (0–6 months) | 1.7 |
| Infants (7–12 months) | 1.8 |
| Children (1–3 years) | 2 |
| Children (4–8 years) | 3 |
| Children (9–13 years) | 4 |
| Adolescents (14–18 years) | 5 |
| Adults (> 19 years) | 5 |
Dietary Sources
Pantothenic Acid is widely distributed in all types of food, so a deficiency in this nutrient is rare. Pantothenic Acid comes from the Greek word “pantothen,” which means “from everywhere.” For the pantothenic acid content of various foods, see Table 9.20 Pantothenic Acid Content of Various Foods”.[15]
| Food | Serving | Pantothenic Acid (mg) | Percent Daily Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sunflower seeds | 1 oz. | 2 | 20 |
| Fish, trout | 3 oz. | 1.9 | 19 |
| Yogurt, plain nonfat | 8 oz. | 1.6 | 16 |
| Lobster | 3 oz. | 1.4 | 14 |
| Avocado | ½ fruit | 1 | 10 |
| Sweet potato | 1 medium | 1 | 10 |
| Milk | 8 fl oz. | 0.87 | 8.7 |
| Egg | 1 large | 0.7 | 7 |
| Orange | 1 whole | 0.3 | 3 |
| Whole wheat bread | 1 slice | 0. 21 | 2.1 |
Biotin (B7) Functions and Health Benefits
Biotin, also known as vitamin B7, is required as a coenzyme in the citric acid cycle and in lipid metabolism. It is also required as an enzyme in the synthesis of glucose and some nonessential amino acids. A specific enzyme, biotinidase, is required to release biotin from protein to be absorbed in the gut. Some bacterial synthesis of biotin occurs in the colon; however, this is not a significant source of biotin. Biotin deficiency is rare, but it can be caused by eating large amounts of egg whites over an extended time. This is because a protein in egg whites tightly binds to biotin, making it unavailable for absorption. A rare genetic disease-causing malfunction of the biotinidase enzyme also results in biotin deficiency. Symptoms of biotin deficiency are similar to those of other B vitamins, but may also include hair loss when severe.
Dietary Reference Intakes
Because there is little information on the requirements for biotin, the FNB has developed Adequate Intakes (AI) based on the observed dietary intakes in healthy population groups. The AI for different age groups for biotin are listed in Table 9.21 “Dietary Reference Intakes for Biotin”.[16]
| Age Group | AI Males and Females mcg/day) |
|---|---|
| Infants (0–6 months) | 5 |
| Infants (7–12 months) | 6 |
| Children (1–3 years) | 8 |
| Children (4–8 years) | 12 |
| Children (9–13 years) | 20 |
| Adolescents (14–18 years) | 25 |
| Adults (> 19 years) | 30 |
Dietary Sources
Biotin can be found in foods such as eggs, fish, meat, seeds, nuts and certain vegetables. For the pantothenic acid content of various foods, see Table 9.22 Biotin Content of Various Foods”.[17]
| Food | Serving | Biotin (mcg) | Percent Daily Value* |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eggs | 1 large | 10 | 33.3 |
| Salmon, canned | 3 oz. | 5 | 16.6 |
| Pork chop | 3 oz. | 3.8 | 12.6 |
| Sunflower seeds | ¼ c. | 2.6 | 8.6 |
| Sweet potato | ½ c. | 2.4 | 8 |
| Almonds | ¼ c. | 1.5 | 5 |
| Tuna, canned | 3 oz. | 0.6 | 2 |
| Broccoli | ½ c. | 0.4 | 1.3 |
| Banana | ½ c. | 0.2 | 0.6 |
| * Current AI used to determine the Percent Daily Value |
Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) Functions and Health Benefits
Vitamin B6 is the coenzyme involved in a wide variety of functions in the body. One primary function is the nitrogen transfer between amino acids, which plays a role in amino-acid synthesis and catabolism. Also, it functions to release glucose from glycogen in the catabolic pathway of glycogenolysis. It is required by enzymes for the synthesis of multiple neurotransmitters and hemoglobin (Figure 9.15 “The Function of Vitamin B6 in Amino Acid Metabolism”).
Vitamin B6 is also a required coenzyme for the synthesis of hemoglobin. A deficiency in vitamin B6 can cause anemia, but it is different from that caused by insufficient folate, cobalamin, or iron; although the symptoms are similar. The size of red blood cells is normal or somewhat smaller but the hemoglobin content is lower. This means each red blood cell has less capacity for carrying oxygen, resulting in muscle weakness, fatigue, and shortness of breath. Other deficiency symptoms of vitamin B6 can cause dermatitis, mouth sores, and confusion.
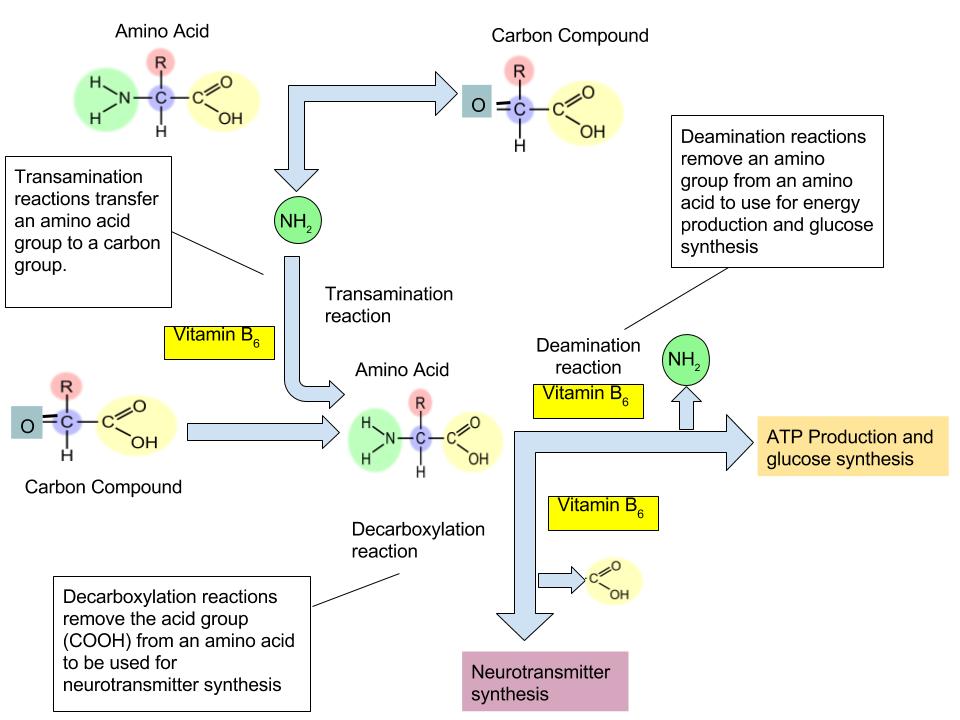
(Source: University of Hawaii @ Manoa, Allison Calabrese, CC-BY)
The vitamin B6 coenzyme is needed for a number of different reactions that are essential for amino acid synthesis, catabolism for energy, and the synthesis of glucose and neurotransmitters.
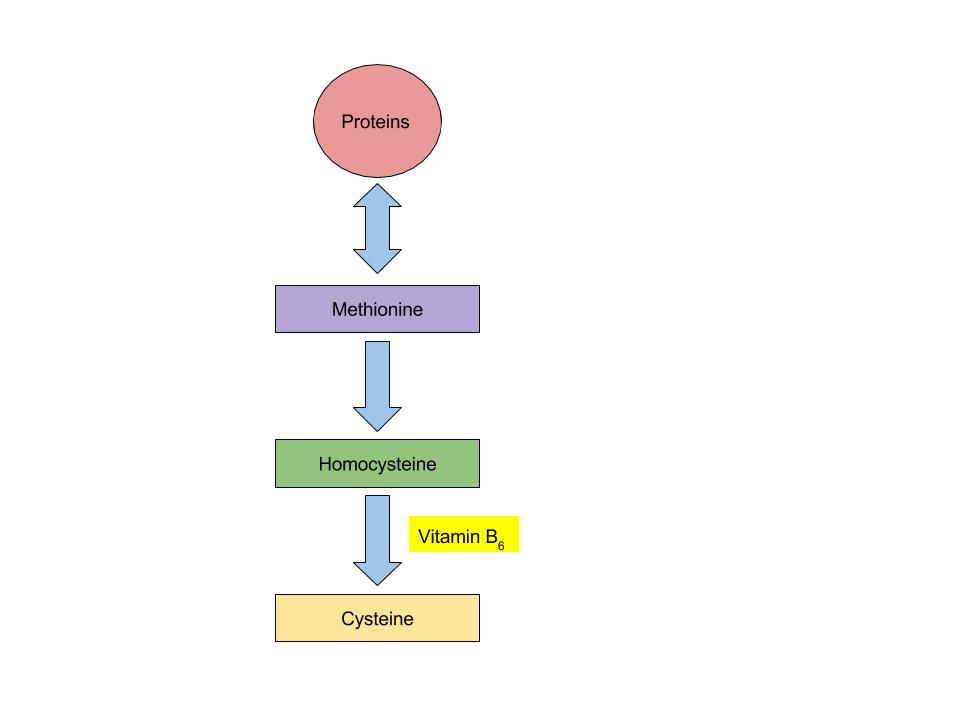
(Source: University of Hawaii @ Manoa, Allison Calabrese, CC-BY)
Vitamin B6 coenzyme is essential for the conversion of amino acid methionine into cysteine. With low levels of Vitamin B6, homocysteine will build up in the blood. High levels of homocysteine increases the risk for heart disease.
Vitamin B6 Toxicity
Currently, no adverse effects have been associated with a high dietary intake of vitamin B6, but large supplemental doses can cause severe nerve impairment. The UL for adults is set at 100 mg/day to prevent this from occurring.
Dietary Reference Intakes
The RDAs and ULs for different age groups for vitamin B6 are listed in Table 9.23 “Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin B6“.[18]
| Age Group | RDA Males and Females mg/day | UL |
|---|---|---|
| Infants (0–6 months) | 0.1* | Not possible to determine |
| Infants (7–12 months) | 0.3* | Not possible to determine |
| Children (1–3 years) | 0.5 | 30 |
| Children (4–8 years) | 0.6 | 40 |
| Children (9–13 years) | 1 | 60 |
| Adolescents (14–18 years) | 1.3 (males), 1.2 (females) | 80 |
| Adults (> 19 years) | 1.3 | 100 |
| *denotes Adequate Intake |
Dietary Sources
Vitamin B6 can be found in a variety of foods. The richest sources include fish, beef liver, and other organ meats, potatoes, and other starchy vegetables and fruits. For the Vitamin B6 content of various foods, see Table 9.24 “Vitamin B6 Content of Various Foods”.[19]
| Food | Serving | Vitamin B6 (mg) | Percent Daily Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chickpeas | 1 c. | 1.1 | 55 |
| Tuna, fresh | 3 oz. | 0.9 | 45 |
| Salmon | 3 oz. | 0.6 | 30 |
| Potatoes | 1 c. | 0.4 | 20 |
| Banana | 1 medium | 0.4 | 20 |
| Ground beef patty | 3 oz. | 0.3 | 10 |
| White rice, enriched | 1 c. | 0.1 | 5 |
| Spinach | ½ c | 0.1 | 5 |
Folate (B9) Functions and Health Benefits
Folate is a required coenzyme for the synthesis of the amino acid methionine, and for making RNA and DNA. Therefore, rapidly dividing cells are most affected by folate deficiency. Red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are continuously being synthesized in the bone marrow from dividing stem cells. When folate is deficient, cells cannot divide normally A consequence of folate deficiency is macrocytic or megaloblastic anemia. Macrocytic and megaloblastic mean “big cell,” and anemia refers to fewer red blood cells or red blood cells containing less hemoglobin. Macrocytic anemia is characterized by larger and fewer red blood cells. It is caused by red blood cells being unable to produce DNA and RNA fast enough—cells grow but do not divide, making them large in size.
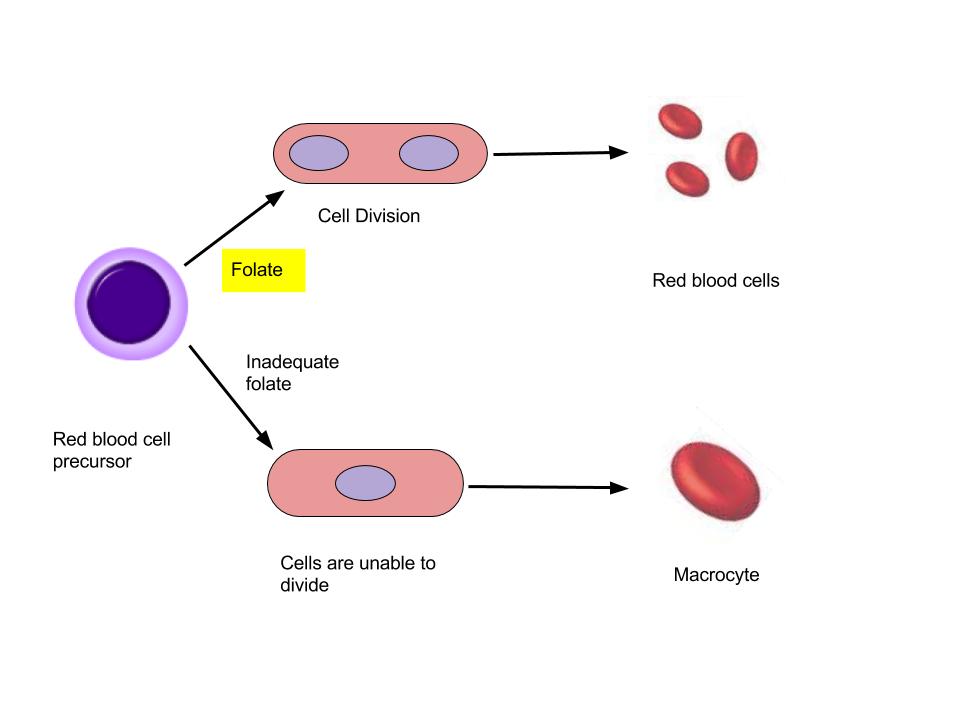
(Source: University of Hawaii @ Manoa, Allison Calabrese, CC-BY)
Folate is especially essential for the growth and specialization of cells of the central nervous system. Children whose mothers were folate-deficient during pregnancy have a higher risk of neural-tube birth defects. Folate deficiency is causally linked to the development of spina bifida, a neural-tube defect that occurs when the spine does not completely enclose the spinal cord. Spina bifida can lead to many physical and mental disabilities (Figure 9.18 “Spina Bifida in Infants” ). Observational studies show that the prevalence of neural-tube defects was decreased after the fortification of enriched cereal grain products with folate in 1996 in the United States (and 1998 in Canada) compared to before grain products were fortified with folate.
Additionally, results of clinical trials have demonstrated that neural-tube defects are significantly decreased in the offspring of mothers who began taking folate supplements one month before becoming pregnant and throughout the pregnancy. In response to the scientific evidence, the Food and Nutrition Board of the Institute of Medicine (IOM) raised the RDA for folate to 600 micrograms per day for pregnant women. Some were concerned that higher folate intakes may cause colon cancer, however scientific studies refute this hypothesis.
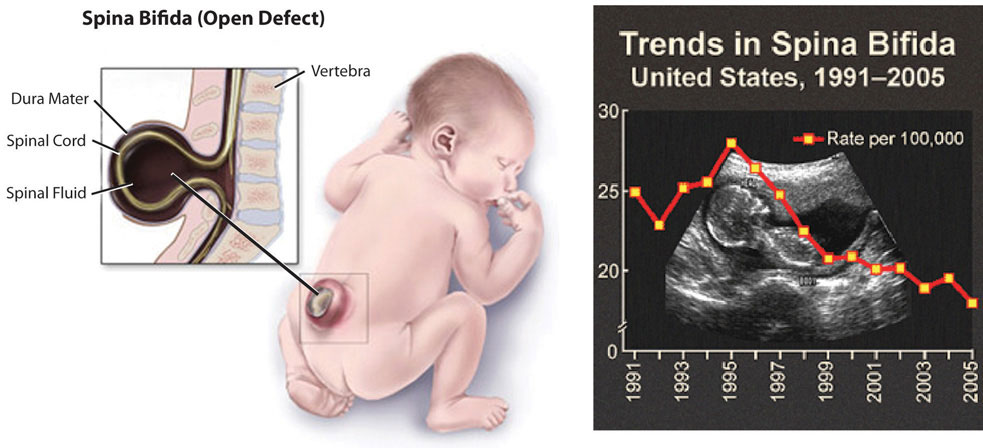
Spina bifida is a neural-tube defect that can have severe health consequences.
(Source: University of Hawaii @ Manoa, CC-BY-NC-SA)
Dietary Reference Intakes
The RDAs and ULs for different age groups for folate are listed in Table 9.25 “Dietary Reference Intakes for Folate”.[20] Folate is a compound that is found naturally in foods. Folic acid, however, is the chemical structure form that is used in dietary supplements as well as enriched foods such as grains. The FNB has developed dietary folate equivalents (DFE) to reflect the fact that folic acid is more bioavailable and easily absorbed than folate found in food. The conversions for the different forms are listed below.
1 mcg DFE = 1 mcg food folate
1mcg DFE = 0.6 mcg folic acid from fortified foods or dietary supplements consumed with foods
1 mcg DFE = 0.5 mcg folic acid from dietary supplements taken on an empty stomach
| Age Group | RDA Males and Females mcg DFE/day | UL |
|---|---|---|
| Infants (0–6 months) | 65* | Not possible to determine |
| Infants (7–12 months) | 80* | Not possible to determine |
| Children (1–3 years) | 150 | 300 |
| Children (4–8 years) | 200 | 400 |
| Children (9–13 years) | 300 | 600 |
| Adolescents (14–18 years) | 400 | 800 |
| Adults (> 19 years) | 400 | 1000 |
| *denotes Adequate Intake |
Dietary Sources
Folate is found naturally in a wide variety of foods, especially in dark leafy vegetables, fruits, and animal products. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) began requiring manufacturers to fortify enriched breads, cereals, flours, and cornmeal to increase folate consumption in the American diet. For the folate content of various foods, see Table 9.26 “Folate Content of Various Foods”.[21]
| Food | Serving | Folate (mcg DFE) | Percent Daily Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beef Liver | 3 oz. | 215 | 54 |
| Fortified breakfast cereals | ¾ c. | 400 | 100 |
| Spinach | ½ c. | 131 | 33 |
| White rice, enriched | ½ c. | 90 | 23 |
| Asparagus | 4 spears | 85 | 20 |
| White bread, enriched | 1 slice | 43 | 11 |
| Broccoli | 2 spears | 45 | 10 |
| Avocado | ½ c. | 59 | 15 |
| Orange juice | 6 oz. | 35 | 9 |
| Egg | 1 large | 22 | 6 |
Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) Functions and Health Benefits
Vitamin B12 contains cobalt, making it the only vitamin that contains a metal ion. Vitamin B12 is an essential part of coenzymes. It is necessary for fat and protein catabolism, for folate coenzyme function, and for hemoglobin synthesis. A folate-dependent enzyme, requiring vitamin B12, is needed to synthesize DNA. Thus, a deficiency in vitamin B12 has similar consequences to health as folate deficiency. In children and adults, vitamin B12 deficiency causes macrocytic anemia, and in babies born to cobalamin-deficient mothers, there is an increased risk for neural-tube defects. For the human body to absorb vitamin B12, the stomach, pancreas, and small intestine must function correctly. Cells in the stomach secrete a protein called intrinsic factor that is necessary for vitamin B12 absorption, which occurs in the small intestine. Impairment of secretion of this protein either caused by an autoimmune disease or by chronic inflammation of the stomach (such as that occurring in some people with H.pylori infection), can lead to the disease pernicious anemia, a type of macrocytic anemia. Vitamin B12 malabsorption is most common in the elderly, who may have impaired functioning of digestive organs, a normal consequence of aging. Pernicious anemia is treated by large oral doses of vitamin B12 or by putting the vitamin under the tongue, where it is absorbed into the bloodstream without passing through the intestine. In patients that do not respond to oral or sublingual treatment vitamin B12 is given by injection.
Vitamin B12 Relationship with Folate and Vitamin B6
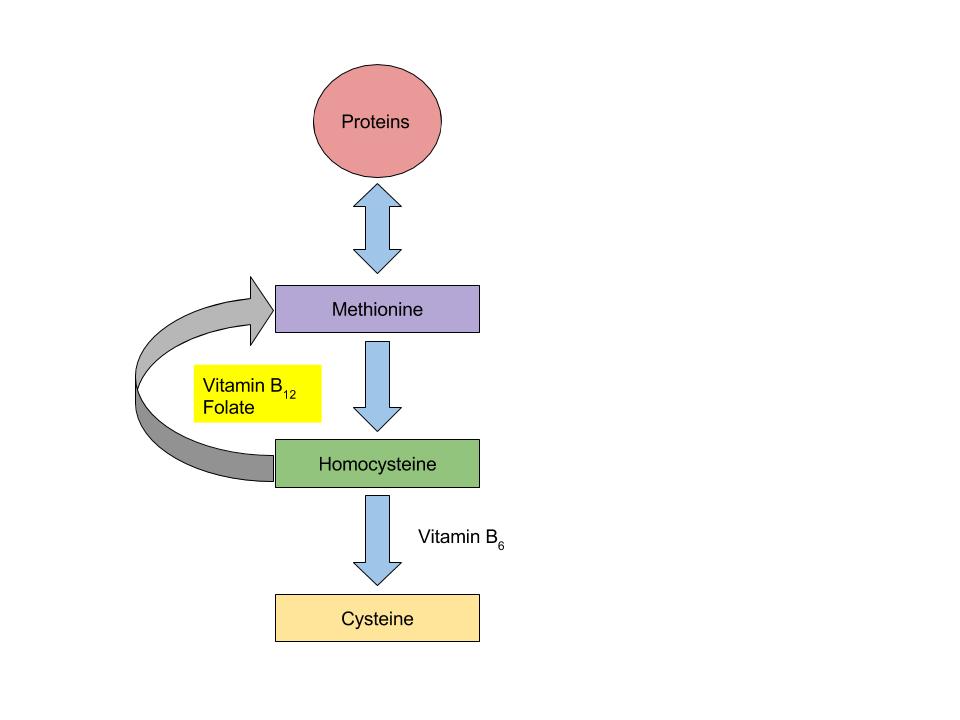
(Source: University of Hawaii @ Manoa, Allison Calabrese, CC-BY)
Vitamin B12 and folate play key roles in converting homocysteine to the amino acid methionine. High levels of homocysteine in the blood increase the risk for heart disease. Low levels of vitamin B12, folate, or vitamin B6 will increase homocysteine levels, therefore increasing the risk of heart disease.
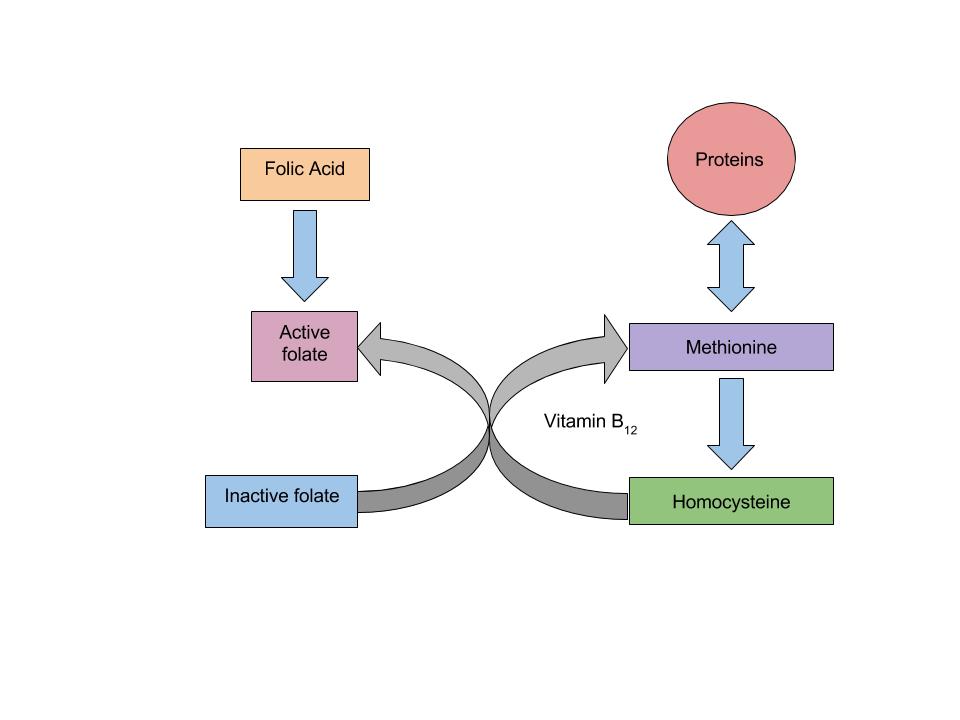
(Source: University of Hawaii @ Manoa, Allison Calabrese, CC-BY)
When there is a deficiency in vitamin B12 , inactive folate (from food) cannot be converted to active folate and used in the body to synthesize DNA. Folic Acid however (that comes from supplements or fortified foods) is available to be used as active folate in the body without vitamin B12 . Therefore, if there is a deficiency in vitamin B12, macrocytic anemia may occur. With the fortification of foods incorporated into people’s diets, an individual’s risk of developing macrocytic anemia is decreased.
Dietary Reference Intakes
The RDAs and ULs for different age groups for Vitamin B12 are listed in Table 9.27 “Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin B12“.[22]
| Age Group | RDA Males and Females mcg/day |
|---|---|
| Infants (0–6 months) | 0.4* |
| Infants (7–12 months) | 0.5* |
| Children (1–3 years) | 0.9 |
| Children (4–8 years) | 1.2 |
| Children (9–13 years) | 1.8 |
| Adolescents (14–18 years) | 2.4 |
| Adults (> 19 years) | 2.4 |
| *denotes Adequate Intake |
Dietary Sources
Vitamin B12 is found naturally in animal products such as fish, meat, poultry, eggs, and milk products. Although vitamin B12 is not generally present in plant foods, fortified breakfast cereals are also a good source of vitamin B12. For the vitamin B12 content of various foods, see Table 9.28 “Vitamin B12 Content of Various Foods”.[23]
| Food | Serving | Vitamin B12 (mcg) | Percent Daily Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clams | 3 oz. | 84.1 | 1,402 |
| Salmon | 3 oz. | 4.8 | 80 |
| Tuna, canned | 3 oz. | 2.5 | 42 |
| Breakfast cereals, fortified | 1 serving | 1.5 | 25 |
| Beef, top sirloin | 3 oz. | 1.4 | 23 |
| Milk, lowfat | 8 fl oz. | 1.2 | 18 |
| Yogurt, lowfat | 8 oz. | 1.1 | 18 |
| Cheese, swiss | 1 oz. | 0.9 | 15 |
| Egg | 1 large | 0.6 | 10 |
Choline Functions and Health Benefits
Choline is a water-soluble substance that is not classified as a vitamin because it can be synthesized by the body. However, the synthesis of choline is limited, and therefore it is recognized as an essential nutrient. Choline is needed to perform functions such as the synthesis of neurotransmitter acetylcholine, the synthesis of phospholipids used to make cell membranes, lipid transport, and homocysteine metabolism. A choline deficiency may lead to interfered brain development in the fetus during pregnancy, and in adults cause fatty liver and muscle damage.
Dietary Reference Intakes
There is insufficient data on choline, so the FNB has developed AIs for all ages in order to prevent fatty liver disease. The AI and UL for different age groups for choline are listed in Table 9.29 “Dietary Reference Intakes for Choline”.[24]
| Age Group | AI Males and Females mg/day) | UL |
|---|---|---|
| Infants (0–6 months) | 125 | – |
| Infants (7–12 months) | 150 | – |
| Children (1–3 years) | 200 | 1000 |
| Children (4–8 years) | 250 | 1000 |
| Children (9–13 years) | 375 | 2000 |
| Adolescents (14–18 years) | 550 (males), 400 (females) | 3000 |
| Adults (> 19 years) | 550 (males), 425 (females) | 3500 |
Dietary Sources
Choline can be found in a variety of foods. The main dietary sources of choline in the United States consist primarily of animal-based products. For the Choline content of various foods, see Table 9.30 “Choline Content of Various Foods”.[25]
| Food | Serving | Choline (mg) | Percent Daily Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Egg | 1 large | 147 | 27 |
| Soybeans | ½ cup | 107 | 19 |
| Chicken breast | 3 oz. | 72 | 13 |
| Mushrooms, shiitake | ½ c. | 58 | 11 |
| Potatoes | 1 large | 57 | 10 |
| Kidney beans | ½ c. | 45 | 8 |
| Peanuts | ¼ c. | 24 | 4 |
| Brown rice | 1 c. | 19 | 3 |
Summary of Water-Soluble Vitamins
| Vitamin | Sources | Recommended Intake for adults |
Major Functions | Deficiency diseases and symptoms |
Groups at risk of deficiency |
Toxicity | UL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) | Orange juice, grapefruit juice, strawberries, tomato, sweet red pepper | 75-90 mg/day | Antioxidant, collagen synthesis, hormone, and neurotransmitter synthesis | Scurvy, bleeding gums, joint pain, poor wound healing, | Smokers, alcoholics, and the elderly | Kidney stones, GI distress, diarrhea | 2000 mg/day |
| Thiamin (B1) | Pork, enriched and whole grains, fish, legumes | 1.1-1.2 mg/day | Coenzyme: assists in glucose metabolism, RNA, DNA, and ATP synthesis | Beriberi: fatigue, confusion, movement impairment, swelling, heart failure | Alcoholics, older adults, and eating disorders | None reported | ND |
| Riboflavin (B2) | Beef liver, enriched breakfast cereals, yogurt, steak, mushrooms, almonds, eggs | 1.1-1.3 mg/day | Coenzyme: assists in glucose, fat, and carbohydrate metabolism, electron carrier; other B vitamins are dependent on it. | Ariboflavinosis: dry scaly skin, mouth inflammation and sores, sore throat, itchy eyes, light sensitivity | None | None reported | ND |
| Niacin (B3) |
Meat, poultry, fish, peanuts, enriched grains | 14-16 NE/day | Coenzyme: assists in glucose, fat, and protein metabolism, and is an electron carrier | Pellagra: diarrhea, dermatitis, dementia, death | Alcoholics | Nausea, rash, tingling extremities | 35 mg/day from fortified foods and supplements |
| Pantothenic Acid (B5) |
Sunflower seeds, fish, dairy products, widespread in foods | 5 mg/day | Coenzyme: assists in glucose, fat, and protein metabolism, cholesterol, and neurotransmitter synthesis | Muscle numbness and pain, fatigue, irritability | Alcoholics | Fatigue, rash | ND |
| B6 (Pyridoxine) | Meat, poultry, fish, legumes, nuts | 1.3-1.7 mg/day | Coenzyme; assists in amino-acid synthesis, glycogenolysis, neurotransmitter, and hemoglobin synthesis | Muscle weakness, dermatitis, mouth sores, fatigue, and confusion | Alcoholics | Nerve damage | 100 mg/day |
| Biotin | Egg yolks, fish, pork, nuts, and seeds | 30 mcg/day | Coenzyme; assists in glucose, fat, and protein metabolism, amino-acid synthesis | Muscle weakness, dermatitis, fatigue, hair loss | Those consuming raw egg whites | None reported | ND |
| Folate | Leafy green vegetables, enriched grains, and orange juice | 400 mcg/day | Coenzyme; amino acid synthesis, RNA, DNA, and red blood cell synthesis | Diarrhea, mouth sores, confusion, anemia, neural-tube defects | Pregnant women, alcoholics | Masks B12 deficiency | 1000 mcg/day from fortified foods and supplements |
| B12 (cobalamin) | Meats, poultry, fish | 2.4 mcg/day | Coenzyme; fat and protein catabolism, folate function, red-blood-cell synthesis | Muscle weakness, sore tongue, anemia, nerve damage, neural-tube defects | Vegans, elderly | None reported | ND |
| Choline | Egg yolk, wheat, meat, fish, and synthesis in the body | 425-550 mg/day | Synthesis of neurotransmitters and cell membranes, lipid transport | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, muscle damage, and interfered brain development in a fetus | None | Liver damage, excessive sweating, hypotension | 3500 mg/day |
Learning Activities
Technology Note: The second edition of the Human Nutrition Open Educational Resource (OER) textbook features interactive learning activities. These activities are available in the web-based textbook and are not in downloadable versions (EPUB, Digital PDF, Print_PDF, or Open Document).
Learning activities may be used across various mobile devices; however, for the best user experience, it is strongly recommended that users complete these activities using a desktop or laptop computer.
- Mente, A., et al. (2009). A Systematic Review of the Evidence Supporting a Causal Link between Dietary Factors and Coronary Heart Disease. Archives of Internal Medicine, 169 (7): 659–69. http://archinte.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/full/169/7/659. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Myint, P.K., et al. (2008). Plasma Vitamin C Concentrations Predict Risk of Incident Stroke Over 10 Years in 20,649 Participants of the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer, Norfolk Prospective Population Study. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 87 (1), 64–69. http://www.ajcn.org/content/87/1/64.long. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Douglas RM, et al. (2004). Vitamin C for Preventing and Treating the Common Cold. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Oct 18 2004, (4): CD000980. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15495002?dopt=Abstract. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Dietary Supplement Fact Sheet: Vitamin C. National Institutes of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. http://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminC-QuickFacts/. Updated March 22, 2021. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Dietary Supplement Fact Sheet: Vitamin C. National Institutes of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. http://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminC-QuickFacts/. Updated March 22, 2021. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Sir Frederick Gowland Hopkins. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/biography/Frederick-Gowland-Hopkins. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Fact Sheets for Health Professionals: Thiamin. National Institute of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Thiamin-HealthProfessional/. Updated Feburary 9, 2023. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Health Professional Fact Sheet: Thiamin. National Institutes of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Thiamin-HealthProfessional/ . Updated February 9, 2023 . Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Health Professional Fact Sheet: Thiamin. National Institutes of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Thiamin-HealthProfessional/ . Updated February 9, 2023 . Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Fact Sheet for Health Professionals, Riboflavin. National Institute of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Riboflavin-HealthProfessional/. Updated May 11, 2022. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Fact Sheet for Health Professionals, Riboflavin. National Institute of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Riboflavin-HealthProfessional/. Updated May 11, 2022. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Micronutrient Information Center: Niacin. Oregon State University, Linus Pauling Institute. http://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/vitamins/niacin. Updated in August 10, 2018. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Micronutrient Information Center: Niacin. Oregon State University, Linus Pauling Institute. http://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/vitamins/niacin. Updated in August 10, 2018. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Micronutrient Information Center: Pantothenic Acid. Oregon State University, Linus Pauling Institute. https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/vitamins/pantothenic-acid. Updated in April 2023. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Micronutrient Information Center: Pantothenic Acid. Oregon State University, Linus Pauling Institute. https://lpi.oregonstate.edu/mic/vitamins/pantothenic-acid. Updated in April 2023. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Fact Sheet for Health Professionals: Biotin. National Institute of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Biotin-HealthProfessional/. Updated January 10, 2022. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Fact Sheet for Health Professionals: Biotin. National Institute of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Biotin-HealthProfessional/. Updated January 10, 2022. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Dietary Supplement Fact Sheet: Vitamin B6. National Institute of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB6-HealthProfessional/. Updates June 16, 2023. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Dietary Supplement Fact Sheet: Vitamin B6. National Institute of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB6-HealthProfessional/. Updates June 16, 2023. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Dietary Supplement Fact Sheet: Folate. National Institute of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Folate-HealthProfessional/. Updated November 30, 2022. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Dietary Supplement Fact Sheet: Folate. National Institute of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Folate-HealthProfessional/. Updated November 30, 2022. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Dietary Fact Sheet: Vitamin B12. National Institute of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB12-HealthProfessional/. Updated July 2, 2025. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Dietary Fact Sheet: Vitamin B12. National Institute of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminB12-HealthProfessional/. Updated July 2, 2025. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Fact Sheet for Health Professionals: Choline. National Institute of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Choline-HealthProfessional/. Updated June 2, 2022. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
- Fact Sheet for Health Professionals: Choline. National Institute of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Choline-HealthProfessional/. Updated June 2, 2022. Accessed August 13, 2025. ↵
A substance that dissolves in water. This may include minerals, sugars, B vitamins and vitamin C.
The entire biochemical activities of an organism.
Chemical groups that bind to enzymes and assist in enzymatic catalysis.
Chemicals required for enzymes to perform their acts of catalysts.
The branch of metabolism that involves the breakdown of compounds in the body, including the reactions that release energy from foods.
The branch of metabolism that synthesizes body compounds and promotes tissue growth.
A water soluble vitamin that is needed for the maintenance of collagen.
Negatively charged particles found within the nuclei of atoms.
Compounds that inhibit the oxidation of other substances.
A highly reactive atom or molecule that causes oxidative damage.
A fat-soluble vitamin that functions as an antioxidant in the body.
A strong, fibrous protein that functions as an extracellular structural element in connective tissue.
A disease caused by a vitamin C deficiency characterized by bleeding gums, tooth loss, joint pain, bleeding into the skin and mucous membrane, and fatigue.
The level of nutrient intake that should be used as a goal when no RDA exists. This value is an approximation of the nutrient intake that sustains health.
(Tolerable Upper Intake Level) The maximum daily nutrient intake levels that are likely to pose health risks to almost all individuals in a given gender and life-stage group.
(Recommended Dietary Allowance) The levels of intake of essential nutrients that is based off of scientific knowledge, and it judged by the Food and Nutrition Board to be adequate to meet the known nutrient needs for all healthy people.
A chemical released from one end of a nerve cell that travels across the gap (synapse) between one cell and the next to either stimulate or inhibit its transmission of a nerve impulse. Neurotransmitters are the chemicals responsible for transmitting nerve signals between nerve cells.
The thiamin deficiency disorder characterized by muscle weakness, loss of appetite, nerve degeneration, and sometimes edema.
A molecule made from the fermentation of carbohydrates from plant products.
Essential nutrients that are needed by the body in small amounts. These include vitamins and minerals.
A B vitamin that is needed for energy metabolism.
Organic compounds that are needed in small amounts in the diet to support and regulate the chemical reactions and processes needed for growth, reproduction, and the maintenance of health.
A B vitamin that is needed for the synthesis of DNA and the metabolism of some amino acids.
A pair of organs that aid in filtering waste and water out of the blood while also maintaining chemical balance in our bodies.
A B vitamin that is needed for energy metabolism.
A disease caused by niacin deficiency, characterized by inflammation of the skin, diarrhea, and eventually mental incapacity.
The deterioration of an individual’s mental state that results in impaired memory, thinking, and judgement.
(Niacin Equivalent) The units used to express the niacin content of a food. 60 mg of tryptophan = 1 mg niacin.
The amount of a dietary nutrient that is absorbed and utilized by the body.
One of the B vitamins needed for energy metabolism.
A class of nutrients containing carbon, hydrogen, a little oxygen, and some other atoms. Commonly known as fats that include fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, and sterols.
Best-known sterol because of its role in heart disease but is also an important molecule in cell membrane structure
signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse
(Adequate Intake) The level of nutrient intake that should be used as a goal when no RDA exists. This value is an approximation of the nutrient intake that sustains health.
A B vitamin that is needed for energy metabolism.
An amino acid that can be synthesized by the human body in sufficient quantities to meet the body’s needs.
An iron-containing protein found in red blood cells that bind and transports oxygen throughout the body.
A form of anemia (also known as megaloblastic anemia) that is characterized by large red blood cells that continue to grow because they do not lose their nucleus when they should.
The organ system that includes the brain and spinal cord responsible for sensing changes in the external environment and creating a reaction to them.
A form of folate that is easily digestible and used in dietary supplements and fortified foods.
One of the B vitamins that is only found in animal products.
The mucoprotein molecule secreted by the gastric mucosal cells and required for the absorption of vitamin B12 into the body.
A form of macrocytic anemia resulting from vitamin B12 deficiency due to a lack of intrinsic factor.
An essential nutrient, needed for the synthesis of the phospholipids, the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, lipid transport and also homocysteine metabolism.
The accumulation of fat in the liver. An early sign of excess alcohol consumption.

