Functions of the Endocrine System
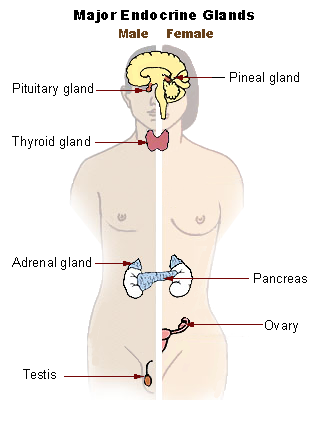
(Source Wikimedia Commons, National Cancer Institute, Public Domain)
The functions of the endocrine system are intricately connected to the body’s nutrition. This organ system is responsible for regulating appetite, nutrient absorption, nutrient storage, and nutrient usage, in addition to other functions, such as reproduction. The glands in the endocrine system are the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenals, thymus, pineal, pancreas, ovaries, and testes. The glands secrete hormones, which are biological molecules that regulate cellular processes in other target tissues, so they require transportation by the circulatory system. Adequate nutrition is critical for the functioning of all the glands in the endocrine system. A protein deficiency impairs gonadal hormone release, preventing reproduction. Athletic teenage girls with very little body fat often do not menstruate. Children who are malnourished usually do not produce enough growth hormone and fail to reach normal height for their age group.
Probably the most popularized connection between nutrition and the functions of the endocrine system is that unhealthy dietary patterns are linked to obesity and the development of Type 2 diabetes. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that 38.4 million Americans have diabetes as of 2024. This is 11.6 percent of the US population. Overweight or obesity is a significant risk factor, increasing the likelihood of Type 2 diabetes.[1]
What is the causal relationship between overnutrition and Type 2 diabetes? The prevailing theory is that the overconsumption of high-fat and high-sugar foods causes changes in muscle, fat, and liver cells that lead to a diminished response from the pancreatic hormone insulin. These cells are called “insulin-resistant.” Insulin is released after a meal and instructs the liver and other tissues to take up glucose and fatty acids that are circulating in the blood. When cells resist insulin, they do not take up enough glucose and fatty acids, so they remain at high concentrations in the blood. The chronic elevation of glucose and fatty acids in the blood also causes damage to other tissues over time. Hence, people who have Type 2 diabetes are at increased risk for cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and eye disease.
Career Connection
Do your part to slow the rising tide of obesity and Type 2 diabetes in this country. On the individual level, improve your own family’s diet; at the local community level, support the development of more nutritious school lunch programs; and at the national level, support your nation’s nutrition goals. Visit the CDC Diabetes Public Health Resource website (opens in a new window). It provides information on education resources, projects, and programs, and spotlights news on diabetes. For helpful information on obesity, visit the CDC’s About Obesity webpage (opens in a new window). The CDC also has web-based workplace resources, with the mission of designing worksites that prevent obesity. See the Workplace Health Promotion page (opens in a new window) of the CDC’s website for more details.
Learning Activities
Technology Note: The second edition of the Human Nutrition Open Educational Resource (OER) textbook features interactive learning activities. These activities are available in the web-based textbook and are not in downloadable versions (EPUB, Digital PDF, Print_PDF, or Open Document).
Learning activities may be used across various mobile devices; however, for the best user experience, it is strongly recommended that users complete these activities using a desktop or laptop computer.
- National Diabetes Statistics Report. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/php/data-research/. Updated May 15, 2024. Accessed August 12, 2025. ↵
The organ system composed of a collection of glands that produce and secrete hormones.
A chemical messenger in the body that is released into the blood from one specific location in the body and travels to another location, where it elicits a specific response.
A collection of cells that of the same or very similar type that come together to carry out a specific function.
A hormone secreted by the pancreas in response to elevated blood glucose levels to transport glucose into the muscle or fat cells.
A 6-carbon monosaccharide that is the major carbohydrate used to provide energy in the body.

