Introduction
“I tell people all the time; you have to be in love with that pot. You have to put all your love in that pot. If you’re in a hurry, just eat your sandwich and go.”
-Chef Leah Chase

Learning Objectives
By the end of this chapter, you will be able to:
- Describe the body’s use, storage and balance of energy
- Describe factors that contribute to weight management
- Identify evidence-based nutritional recommendations
Energy is essential to life. Normal function of the human body requires a constant input and output of energy to maintain life. Various chemical components of food provide the input of energy to the body. The chemical breakdown of those chemicals provides the energy needed to carry out thousands of body functions that allow the body to perform daily functions and tasks such as breathing, walking up a flight of steps, and studying for a test.
Energy is classified as either potential or kinetic. Potential energy is stored energy, or energy waiting to happen. Kinetic energy is energy in motion. To illustrate this, think of an Olympic swimmer standing at the pool’s edge awaiting the sound of the whistle to begin the race. While he waits for the signal, he has potential energy. When the whistle sounds and he dives into the pool and begins to swim, his energy is kinetic (in motion).
In food and in components of the human body, potential energy resides in the chemical bonds of specific molecules such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and alcohol. This potential energy is converted into kinetic energy in the body that drives many body functions ranging from muscle and nerve function to driving the synthesis of body protein for growth. After potential energy is released to provide kinetic energy, it ultimately becomes thermal energy or heat. You can notice this when you exercise and your body heats up.
The Calorie Is a Unit of Energy
The amount of energy in nutrients or the amount of energy expended by the body can be quantified with a variety of units used to measure energy. In the US, the kilocalorie (kcal) is most commonly used and is often just referred to as a calorie. Strictly speaking, a kcal is 1000 calories. In nutrition, the term calories almost always refers to kcals. Sometimes the kcal is indicated by capitalizing calories as “Calories.” A kilocalorie is the amount of energy in the form of heat that is required to heat one kilogram of water one degree Celsius.
Most other countries use the kilojoule (kJ) as their standard unit of energy. The Joule is a measure of energy based on work accomplished – the energy needed to produce a specific amount of force. Since calories and Joules are both measures of energy, one can be converted to the other – 1 kcal = 4.18 kJ.
Estimating Caloric Content
The energy contained in energy-yielding nutrients differs because the energy-yielding nutrients are composed of different types of chemical bonds. The carbohydrate or protein in a food yields approximately 4 kilocalories per gram, whereas the triglycerides that compose the fat in a food yield 9 kilocalories per gram. A kilocalorie of energy performs one thousand times more work than a calorie. On the Nutrition Facts panel found on packaged food, the calories listed for a particular food are actually kilocalories.
Estimating the number of calories in commercially prepared food is fairly easy since the total number of calories in a serving of a particular food is listed on the Nutrition Facts panel. If you wanted to know the number of calories in the breakfast you consumed this morning just add up the number of calories in each food. For example, if you ate one serving of yogurt that contained 150 calories, on which you sprinkled half of a cup of low-fat granola cereal that contained 209 calories, and drank a glass of orange juice that contained 100 calories, the total number of calories you consumed at breakfast is 150 + 209 + 100 = 459 calories. If you do not have a Nutrition Facts panel for a certain food, such as a half cup of blueberries, and want to find out the amount of calories it contains, go to Food-a-pedia, a website maintained by the USDA. For more details on food composition data, go to the USDA Food Composition Databases page.
An Organism Requires Energy and Nutrient Input
Energy is required in order to build molecules into larger macromolecules (like proteins), and to turn macromolecules into organelles and cells, which then turn into tissues, organs, and organ systems, and finally into an organism. Proper nutrition provides the necessary nutrients to make the energy that supports life’s processes. Your body builds new macromolecules from the nutrients in food.
Nutrient and Energy Flow
Energy is stored in a nutrient’s chemical bonds. Energy comes from sunlight, which plants capture and, via photosynthesis, use it to transform carbon dioxide in the air into the molecule glucose. When the glucose bonds are broken, energy is released. Bacteria, plants, and animals (including humans) harvest the energy in glucose via a biological process called cellular respiration. In this process oxygen is required and the chemical energy of glucose is gradually released in a series of chemical reactions. Some of this energy is trapped in the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and some is lost as heat. ATP can be used when needed to drive chemical reactions in cells that require an input of energy. Cellular respiration requires oxygen (aerobic) and it is provided as a byproduct of photosynthesis. The byproducts of cellular respiration are carbon dioxide (CO2) and water, which plants use to conduct photosynthesis again. Thus, carbon is constantly cycling between plants and animals.
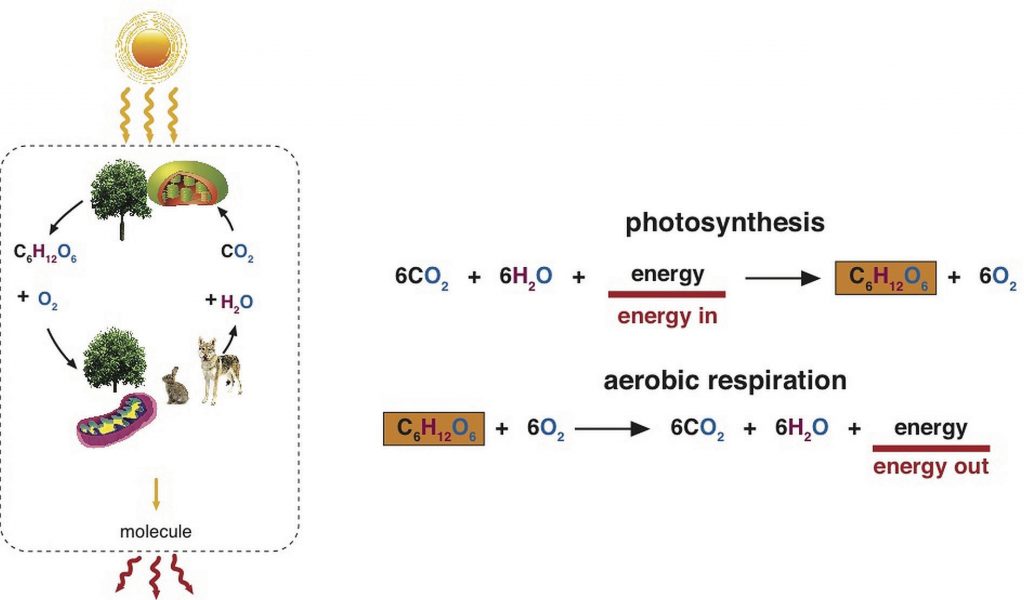
(Source: University of Hawaii @ Manoa, CC-BY-NC-SA)
Plants harvest energy from the sun and capture it in the molecule glucose. Humans harvest the energy in glucose and capture it into the molecule ATP.
Food Quality
One measurement of food quality is the amount of nutrients it contains relative to the amount of energy it provides. High-quality foods are nutrient dense, meaning they contain lots of nutrients relative to the amount of calories they provide. Nutrient-dense foods are the opposite of “empty-calorie” foods such as carbonated sugary soft drinks, which provide many calories and very little, if any, other nutrients. Food quality is additionally associated with its taste, texture, appearance, microbial content, and how much consumers like it.
Learning Activities
Technology Note: The second edition of the Human Nutrition Open Educational Resource (OER) textbook features interactive learning activities. These activities are available in the web-based textbook and not available in the downloadable versions (EPUB, Digital PDF, Print_PDF, or Open Document).
Learning activities may be used across various mobile devices, however, for the best user experience it is strongly recommended that users complete these activities using a desktop or laptop computer.
The energy that systems contain because of the position of their parts.
The energy things possess because they are moving.
The standard unit of energy used in nutrition; the amount of heat required to raise temperature of 1 kg water 1℃ .
A fundamental unit of energy, equal to 4.1855 joule; 1000 calories equals 1 kcal.
A portion of a food label that provides information about the overall nutritional composition of a food and how it fits in the overall diet.
A group of organs that work together to perform different functions.
A complete living system capable of conducting all of life’s biological processes.
A substance in food that can provide energy, contribute to body structure, and/or regulate body processes.
A 6-carbon monosaccharide that is the major carbohydrate used to provide energy in the body.

