5 Scientific Thinking
Learning Objectives
- Describe the principles of the scientific method and explain its importance in conducting and interpreting research.
- Differentiate laws from theories and explain how research hypotheses are developed and tested.
- Identify the role of the research hypothesis in psychological research.
Psychologists aren’t the only people who seek to understand human behavior and solve social problems. Philosophers, religious leaders, and politicians, among others, also strive to provide explanations for human behavior. But psychologists believe that research is the best tool for understanding human beings and their relationships with others. Rather than accepting the claim of a philosopher that people do (or do not) have free will, a psychologist would collect data to empirically test whether or not people are able to actively control their own behavior. Rather than accepting a politician’s contention that creating (or abandoning) a new center for mental health will improve the lives of individuals in the inner city, a psychologist would empirically assess the effects of receiving mental health treatment on the quality of life of the recipients. The statements made by psychologists are empirical, which means they are based on systematic collection and analysis of data.
The Scientific Method
All scientists (whether they are physicists, chemists, biologists, sociologists, or psychologists) are engaged in the basic processes of collecting data and drawing conclusions about those data. The methods used by scientists have developed over many years and provide a common framework for developing, organizing, and sharing information. The scientific method is the set of assumptions, rules, and procedures scientists use to conduct research.
In addition to requiring that science be empirical, the scientific method demands that the procedures used be objective, or free from the personal bias or emotions of the scientist. The scientific method describes how scientists collect and analyze data, how they draw conclusions from data, and how they share data with others. These rules increase objectivity by placing data under the scrutiny of other scientists and even the public at large. Because data are reported objectively, other scientists know exactly how the scientist collected and analyzed the data. This means that they do not have to rely only on the scientist’s own interpretation of the data; they may draw their own, potentially different, conclusions.
The scientific method is an iterative process. The scientific process often starts with making a hypothesis (which is also an educated guess). Then, research studies are designed to test the hypothesis. The results obtained from experiments then inform the researchers how behaviors may be predicted or explained. This is a recurring process in which the results then loop back to modify the hypothesis if necessary. With an updated hypothesis, researchers then continue to employ the scientific process to conduct experiments.
Figure 2.1 The scientific process employed by psychologists
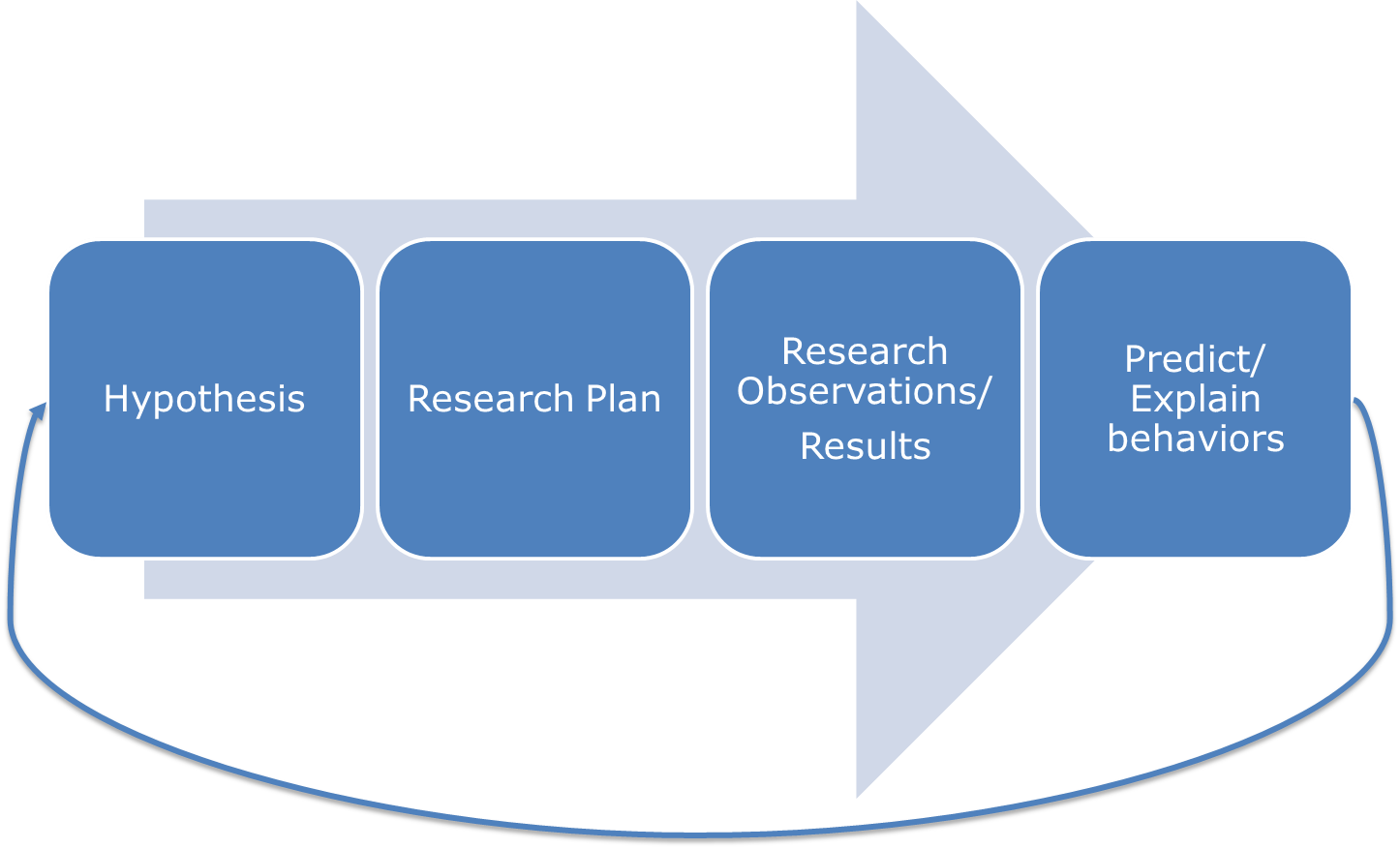
Most new research is designed to replicate—that is, to repeat, add to, or modify—previous research findings. The scientific method therefore results in an accumulation of scientific knowledge through the reporting of research and the addition to and modifications of these reported findings by other scientists.
Laws and Theories as Organizing Principles
One goal of research is to organize information into meaningful statements that can be applied in many situations. Principles that are so general as to apply to all situations in a given domain of inquiry are known as laws. There are well-known laws in the physical sciences, such as the law of gravity and the laws of thermodynamics, and there are some universally accepted laws in psychology, such as the law of effect and Weber’s law. But because laws are very general principles and their validity has already been well established, they are themselves rarely directly subjected to scientific testing.
The next step down from laws in the hierarchy of organizing principles is theory. A theory is an integrated set of principles that explains and predicts many, but not all, observed relationships within a given domain of inquiry. One example of an important theory in psychology is the stage theory of cognitive development proposed by the Swiss psychologist Jean Piaget. The theory states that children pass through a series of cognitive stages as they grow, each of which must be mastered in succession before movement to the next cognitive stage can occur. This is an extremely useful theory in human development because it can be applied to many different content areas and can be tested in many different ways.
Good theories have four important characteristics. First, good theories are general, meaning they summarize many different outcomes. Second, they are parsimonious, meaning they provide the simplest possible account of those outcomes. The stage theory of cognitive development meets both of these requirements. It can account for developmental changes in behavior across a wide variety of domains, and yet it does so parsimoniously—by hypothesizing a simple set of cognitive stages. Third, good theories provide ideas for future research. The stage theory of cognitive development has been applied not only to learning about cognitive skills but also to the study of children’s moral (Kohlberg, 1966) and gender (Ruble & Martin, 1998) development.
Finally, good theories are falsifiable (Popper, 1959), which means the variables of interest can be adequately measured and the relationships between the variables that are predicted by the theory can be shown through research to be incorrect. The stage theory of cognitive development is falsifiable because the stages of cognitive reasoning can be measured and because if research discovers, for instance, that children learn new tasks before they have reached the cognitive stage hypothesized to be required for that task, then the theory will be shown to be incorrect.
No single theory is able to account for all behavior in all cases. Rather, theories are each limited in that they make accurate predictions in some situations or for some people but not in other situations or for other people. As a result, there is a constant exchange between theory and data: Existing theories are modified on the basis of collected data, and the newly modified theories then make new predictions that are tested by new data, and so forth. When a better theory is found, it will replace the old one. This is part of the accumulation of scientific knowledge.
The Research Hypothesis
Theories are usually framed too broadly to be tested in a single experiment. Therefore, scientists use a more precise statement of the presumed relationship among specific parts of a theory—a research hypothesis—as the basis for their research. A research hypothesis is a specific and falsifiable prediction about the relationship between or among two or more variables, where a variable is any attribute that can assume different values among different people or across different times or places. The research hypothesis states the existence of a relationship between the variables of interest and the specific direction of that relationship. For instance, the research hypothesis “Using marijuana will reduce learning” predicts that there is a relationship between a variable “using marijuana” and another variable called “learning.” Similarly, in the research hypothesis “participating in psychotherapy will reduce anxiety,” the variables that are expected to be related are “participating in psychotherapy” and “level of anxiety.”
When stated in an abstract manner, the ideas that form the basis of a research hypothesis are known as conceptual variables. Conceptual variables are abstract ideas that form the basis of research hypotheses. Sometimes the conceptual variables are rather simple—for instance, “age,” “gender,” or “weight.” In other cases, the conceptual variables represent more complex ideas, such as “anxiety,” “cognitive development,” “learning,” “self-esteem,” or “sexism.”
The first step in testing a research hypothesis involves turning the conceptual variables into measured variables, which are variables consisting of numbers that represent the conceptual variables. For instance, the conceptual variable “participating in psychotherapy” could be represented as the measured variable “number of psychotherapy hours the patient has accrued,” and the conceptual variable “using marijuana” could be assessed by having the research participants rate, on a scale from 1 to 10, how often they use marijuana or by administering a blood test that measures the presence of the chemicals in marijuana.
Psychologists use the term operational definition to refer to a precise statement of how a conceptual variable is turned into a measured variable. The relationship between conceptual and measured variables in a research hypothesis is diagrammed in Figure 2.2 “Diagram of a Research Hypothesis.” The conceptual variables are represented within circles at the top of the figure, and the measured variables are represented within squares at the bottom. The two vertical arrows, which lead from the conceptual variables to the measured variables, represent the operational definitions of the two variables. The arrows indicate the expectation that changes in the conceptual variables (psychotherapy and anxiety in this example) will cause changes in the corresponding measured variables. The measured variables are then used to draw inferences about the conceptual variables.
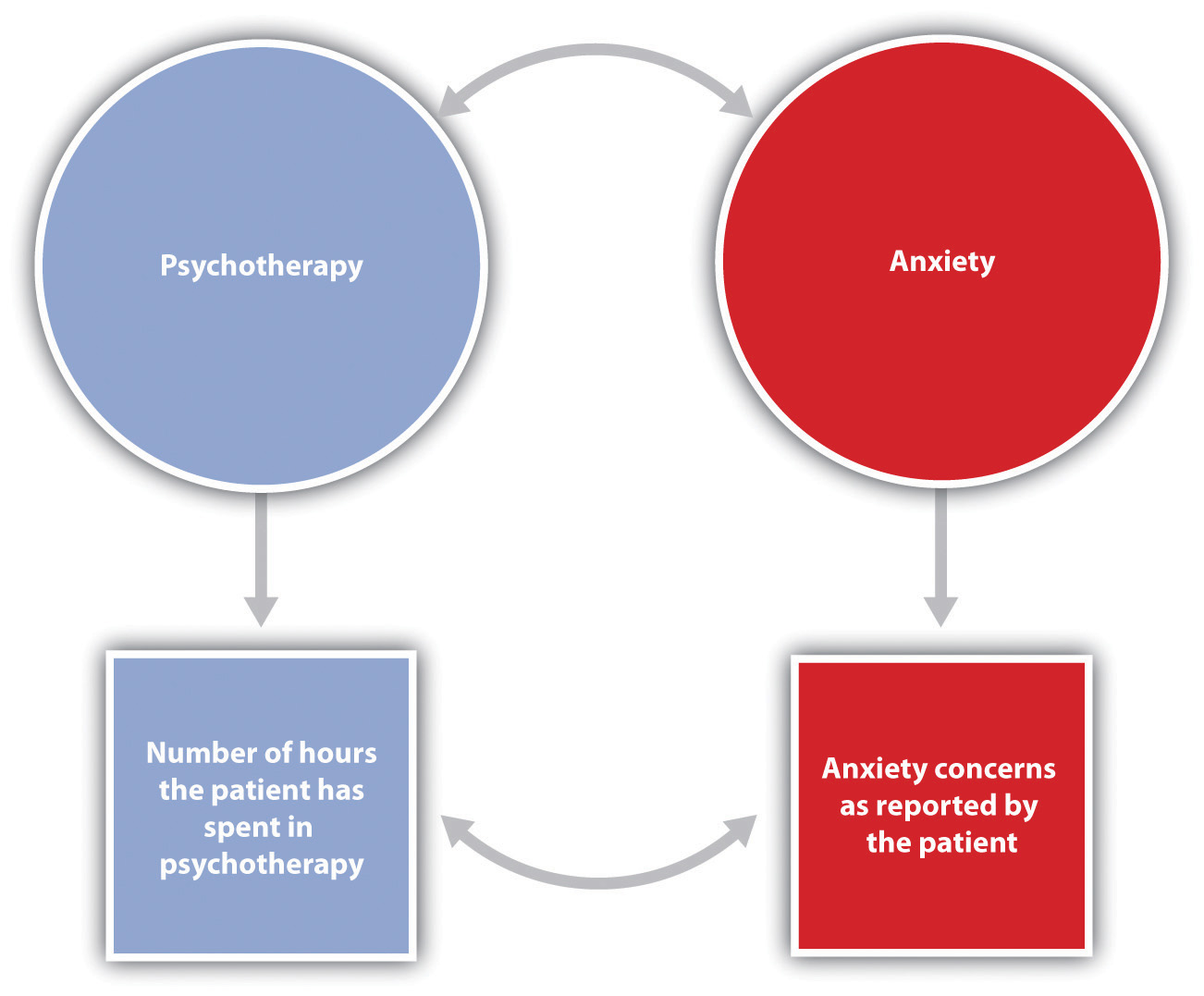
Table 2.1, “Examples of the Operational Definitions of Conceptual Variables That Have Been Used in Psychological Research,” lists some potential operational definitions of conceptual variables that have been used in psychological research. As you read through this list, note that in contrast to the abstract conceptual variables, the measured variables are very specific. This specificity is important for two reasons. First, more specific definitions mean that there is less danger that the collected data will be misunderstood by others. Second, specific definitions will enable future researchers to replicate the research.
Table 2.1 Examples of the Operational Definitions of Conceptual Variables That Have Been Used in Psychological Research
| Conceptual variable | Operational definitions |
|---|---|
| Aggression |
|
| Interpersonal attraction |
|
| Employee satisfaction |
|
| Decision-making skills |
|
| Depression |
|
the set of assumptions, rules, and procedures scientists use to conduct research
free from the personal bias or emotions of the scientist

