Engagement in a Democracy
Lumen Learning and OpenStax
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Explain the importance of citizen engagement in a democracy
- Describe the main ways Americans can influence and become engaged in government
- Discuss factors that may affect people’s willingness to become engaged in government
Participation in government matters. Although people may not get all that they want, they can achieve many goals and improve their lives through civic engagement. According to the pluralist theory, government cannot function without active participation by at least some citizens. Even if we believe the elite make political decisions, participation in government through the act of voting can change who the members of the elite are.
WHY GET INVOLVED?
Are fewer people today active in politics than in the past? Political scientist Robert Putnam has argued that civic engagement is declining; although many Americans may report belonging to groups, these groups are usually large, impersonal ones with thousands of members. People who join groups such as Amnesty International or Greenpeace may share certain values and ideals with other members of the group, but they do not actually interact with these other members. These organizations are different from the types of groups Americans used to belong to, like church groups or bowling leagues. Although people are still interested in volunteering and working for the public good, they are more interested in either working individually or joining large organizations where they have little opportunity to interact with others. Putnam considers a number of explanations for this decline in small group membership, including increased participation by women in the workforce, a decrease in the number of marriages and an increase in divorces, and the effect of technological developments, such as the internet, that separate people by allowing them to feel connected to others without having to spend time in their presence.[1]
Putnam argues that a decline in social capital—“the collective value of all ‘social networks’ [those whom people know] and the inclinations that arise from these networks to do things for each other”—accompanies this decline in membership in small, interactive groups.[2] Included in social capital are such things as networks of individuals, a sense that one is part of an entity larger than oneself, concern for the collective good and a willingness to help others, and the ability to trust others and to work with them to find solutions to problems. This, in turn, has hurt people’s willingness and ability to engage in representative government. If Putnam is correct, this trend is unfortunate, because becoming active in government and community organizations is important for many reasons.
Some have countered Putnam’s thesis and argue that participation is in better shape than what he portrays. Everett Ladd shows many positive trends in social involvement in American communities that serve to soften some of the declines identified by Putnam. For example, while bowling league participation is down, soccer league participation has proliferated.[3] April Clark examines and analyzes a wide variety of social capital data trends and disputes the original thesis of erosion.[4] Others have suggested that technology has increased connectedness, an idea that Putnam himself has critiqued as not as deep as in-person connections.[5] In the decades since Putnam has levied his argument that people are becoming less civic engaged, a rise in the intensity of polarization in politics has been observed, and the argument has been made that political engagement has become a substitute for much of the previous civic engagement in the organization of civil society. A national view of all political issues has pervaded many local political issues leading to the simultaneous intensification and disengagement in civil society, perhaps reinforcing the erosion of social capital.
LINK TO LEARNING
Civic engagement can increase the power of ordinary people to influence government actions. Even those without money or connections to important people can influence the policies that affect their lives and change the direction taken by government. U.S. history is filled with examples of people actively challenging the power of elites, gaining rights for themselves, and protecting their interests. For example, slavery was once legal in the United States and large sectors of the U.S. economy were dependent on this forced labor. Slavery was outlawed and enslaved people were granted citizenship because of the actions of abolitionists. Although some abolitionists were wealthy White men, most were ordinary people, including men and women of both races. White women and African Americans were able to actively assist in the campaign to end slavery despite the fact that, with few exceptions, they were unable to vote. Similarly, the right to vote once belonged solely to White men until the Fifteenth Amendment gave the vote to African American men. The Nineteenth Amendment extended the vote to include women, and the Voting Rights Act of 1965 made exercising the right to vote a reality for Black men and women in the South. None of this would have happened, however, without the efforts of people who marched in protest, participated in boycotts, delivered speeches, wrote letters to politicians, and sometimes risked arrest in order to be heard. The tactics used to influence the government and effect change by abolitionists and members of the women’s rights and African American civil rights movements are still used by many activists today.

The rights gained by these activists and others have dramatically improved the quality of life for many in the United States. Civil rights legislation did not focus solely on the right to vote or to hold public office; it also integrated schools and public accommodations, prohibited discrimination in housing and employment, and increased access to higher education. Activists for women’s rights fought for, and won, greater reproductive freedom for women, better wages, and access to credit. Only a few decades ago, homosexuality was considered a mental disorder, and intercourse between consenting adults of the same sex was illegal in many states. Although legal discrimination against LGBTQ people still remains, consensual intercourse between gay and lesbian adults is no longer illegal anywhere in the United States, same-sex couples have the right to legally marry, and LGBTQ people are better protected against employment discrimination.
Activism can improve people’s lives in less dramatic ways as well. Working to make cities clean up vacant lots, destroy or rehabilitate abandoned buildings, build more parks and playgrounds, pass ordinances requiring people to curb their dogs, and ban late-night noise greatly affects people’s quality of life. The actions of individual Americans can make their own lives better and improve their neighbors’ lives as well.
Representative democracy cannot work effectively without the participation of informed citizens, however. Engaged citizens familiarize themselves with the most important issues confronting the country and with the plans different candidates have for dealing with those issues. Then they vote for the candidates they believe will be best suited to the job, and they may join others to raise funds or campaign for those they support. They inform their representatives of how they feel about important issues. Through these efforts and others, engaged citizens let their representatives know what they want and thus influence policy. Only then can government actions accurately reflect the interests and concerns of the majority. Even people who believe the elite rule government should recognize that it is easier for them to do so if ordinary people make no effort to participate in public life.
PATHWAYS TO ENGAGEMENT
People can become civically engaged in many ways, either as individuals or as members of groups. Some forms of individual engagement require very little effort. One of the simplest ways is to stay informed about debates and events in the community, in the state, and in the nation. Awareness is the first step toward engagement. News is available from a variety of reputable sources, such as newspapers like the New York Times; national news shows, including those offered by the Public Broadcasting Service and National Public Radio; and reputable internet sites.
LINK TO LEARNING
Visit Avaaz and Change.org for more information on current political issues.
Another form of individual engagement is to write or email political representatives. Filing a complaint with the city council is another avenue of engagement. City officials cannot fix problems if they do not know anything is wrong to begin with. Responding to public opinion polls, actively contributing to a political blog, or starting a new blog are all examples of different ways to be involved. It is also inescapable that social media engagement has exploded over the last ten years. Moreover, with the self-selection of friend groups and feeds online, bias is mobilized, and we see increasing complaints about fake news.
One of the most basic ways to engage with government as an individual is to vote. Individual votes do matter. City council members, mayors, state legislators, governors, and members of Congress are all chosen by popular vote. Although the president of the United States is not chosen directly by popular vote but by a group called the Electoral College, the votes of individuals in their home states determine how the Electoral College ultimately votes. Registering to vote beforehand is necessary in most states, but it is usually a simple process, and many states allow registration online. (We discuss voter registration and voter turnout in more depth in a later chapter.)

Voting, however, is not the only form of political engagement in which people may participate. Individuals can engage by attending political rallies, donating money to campaigns, and signing petitions. Starting a petition of one’s own is relatively easy, and some websites that encourage people to become involved in political activism provide petitions that can be circulated through email. Taking part in a poll or survey is another simple way to make your voice heard.
MILESTONE
Votes for Eighteen-Year-Olds
Young Americans are often reluctant to become involved in traditional forms of political activity. They may believe politicians are not interested in what they have to say, or they may feel their votes do not matter. However, this attitude has not always prevailed. Indeed, today’s college students can vote because of the activism of college students in the 1960s. Most states at that time required citizens to be twenty-one years of age before they could vote in national elections. This angered many young people, especially young men who could be drafted to fight the war in Vietnam. They argued that it was unfair to deny eighteen-year-olds the right to vote for the people who had the power to send them to war. As a result, the Twenty-Sixth Amendment, which lowered the voting age in national elections to eighteen, was ratified by the states and went into effect in 1971.
Are you engaged in or at least informed about actions of the federal or local government? Are you registered to vote? How would you feel if you were not allowed to vote until age twenty-one?
Some people prefer to work with groups when participating in political activities or performing service to the community. Group activities can be as simple as hosting a book club or discussion group to talk about politics. Coffee Party USA provides an online forum for people from a variety of political perspectives to discuss issues that are of concern to them. People who wish to be more active often work for political campaigns. Engaging in fundraising efforts, handing out bumper stickers and campaign buttons, helping people register to vote, and driving voters to the polls on Election Day are all important activities that anyone can engage in. Individual citizens can also join interest groups that promote the causes they favor.
GET CONNECTED!
Getting Involved
In many ways, the pluralists were right. There is plenty of room for average citizens to become active in government, whether it is through a city council subcommittee or another type of local organization. Civic organizations always need volunteers, sometimes for only a short while and sometimes for much longer.
For example, Common Cause is a non-partisan organization that seeks to hold government accountable for its actions. It calls for campaign finance reform and paper verification of votes registered on electronic voting machines. Voters would then receive proof that the machine recorded their actual vote. This would help to detect faulty machines that were inaccurately tabulating votes or election fraud. Therefore, one could be sure that election results were reliable and that the winning candidate had in fact received the votes counted in their favor. Common Cause has also advocated that the Electoral College be done away with and that presidential elections be decided solely on the basis of the popular vote.
Follow-up activity: Choose one of the following websites to connect with organizations and interest groups in need of help:
- Common Cause;
- Friends of the Earth which mobilizes people to protect the natural environment;
- The Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget which seeks to inform the public on issues with fiscal impact and favors smaller budget deficits; or
- Conservative Leaders for Education which supports local control and increased parent choice in education.

Political activity is not the only form of engagement, and many people today seek other opportunities to become involved. This is particularly true of young Americans. Although young people today often shy away from participating in traditional political activities, they do express deep concern for their communities and seek out volunteer opportunities.[6] Although they may not realize it, becoming active in the community and engaging in a wide variety of community-based volunteer efforts are important forms of civic engagement and help government do its job. The demands on government are great, and funds do not always exist to enable it to undertake all the projects it may deem necessary. Even when there are sufficient funds, politicians have differing ideas regarding how much government should do and what areas it should be active in. Volunteers and community organizations help fill the gaps. Examples of community action include tending a community garden, building a house for Habitat for Humanity, cleaning up trash in a vacant lot, volunteering to deliver meals to the elderly, and tutoring children in after-school programs.

Some people prefer even more active and direct forms of engagement such as protest marches and demonstrations, including civil disobedience. Such tactics were used successfully in the African American civil rights movement of the 1950s and 1960s and remain effective today. Likewise, the sit-ins (and sleep-ins and pray-ins) staged by Black civil rights activists, which they employed successfully to desegregate lunch counters, motels, and churches, have been adopted today by movements such as Black Lives Matter and Occupy Wall Street. Other tactics, such as boycotting businesses whose policies the activists disapproved of, are also still common. Along with boycotts, there are now “buycotts,” in which consumers purchase goods and services from companies that give extensively to charity, help the communities in which they are located, or take steps to protect the environment.
LINK TO LEARNING
INSIDER PERSPECTIVE
Ritchie Torres
In 2013, at the age of twenty-five, Ritchie Torres became the youngest member of the New York City Council and the first gay council member to represent the Bronx. Torres became interested in social justice early in his life. He was raised in poverty in the Bronx by his mother and a stepfather who left the family when Torres was twelve. The mold in his family’s public housing apartment caused him to suffer from asthma as a child, and he spent time in the hospital on more than one occasion because of it. His mother’s complaints to the New York City Housing Authority were largely ignored. In high school, Torres decided to become a lawyer, participated in mock trials, and met a young and aspiring local politician named James Vacca. After graduation, he volunteered to campaign for Vacca in his run for a seat on the City Council. After Vacca was elected, he hired Torres to serve as his housing director to reach out to the community on Vacca’s behalf. While doing so, Torres took pictures of the poor conditions in public housing and collected complaints from residents. In 2013, Torres ran for a seat on the City Council himself and won. In November 2020, Torres was elected to the U.S. House of Representatives to represent New York’s 15th congressional district. He and Mondaire Jones, who represents NY 17, are the first openly gay Black men elected to Congress. He remains committed to improving housing for the poor.[7]

Why don’t more young people run for local office as Torres did? What changes might they affect in their communities if they were elected to government positions?
FACTORS OF ENGAGEMENT
Many Americans engage in political activity on a regular basis. A survey conducted in 2018 revealed that almost 70 percent of American adults had participated in some type of political action in the past five years. These activities included largely non-personal activities that did not require a great deal of interaction with others, such as signing petitions, expressing opinions on social media, contacting elected representatives, or contributing money to campaigns. During the same period, approximately 30 percent of people attended a local government meeting or a political rally or event, while 16 percent worked or volunteered for a campaign.[8]
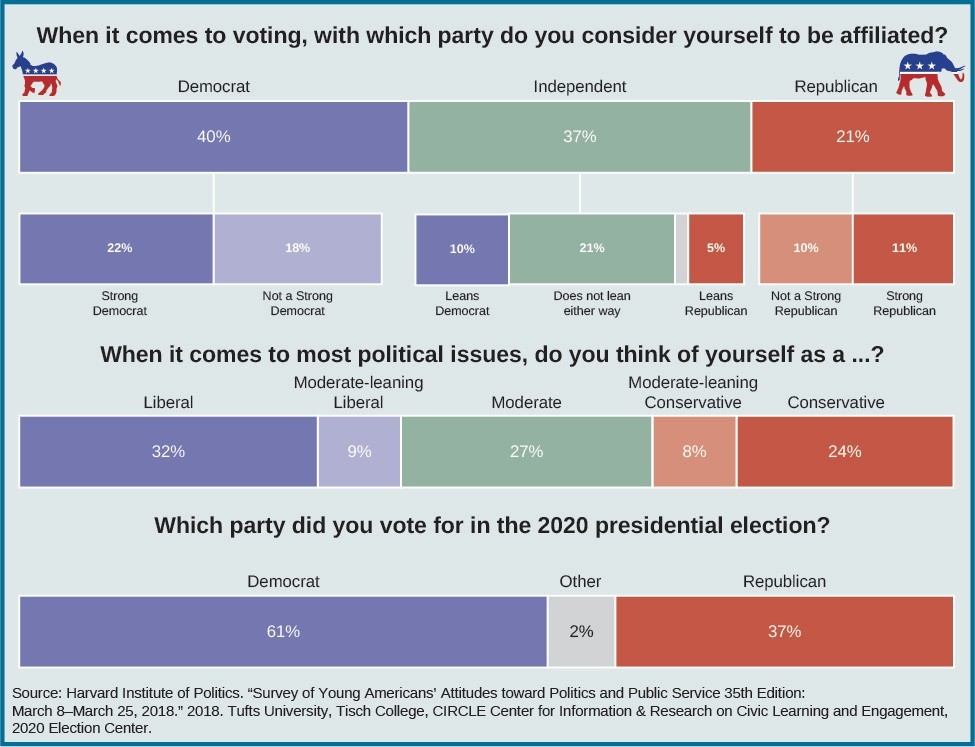
Americans aged 18–29 were less likely to become involved in traditional forms of political activity than older Americans. A 2018 poll of more than two thousand young adults by Harvard University’s Institute of Politics revealed that only 24 percent claimed to be politically engaged, and fewer than 35 percent said that they had voted in a primary. Only 9 percent said that they had gone to a political demonstration, rally, or march.[9] However, in the 2018 midterm elections, an estimated 31 percent of Americans under thirty turned out to vote, the highest level of young adult engagement in decades.[10] In 2020, Harvard’s polling showed significant interest in the 2020 presidential campaign and intent to vote. Post-election analysis by Tuft University’s Center for Information and Research on Civic Learning & Engagement (CIRCLE) showed a record youth turnout of 53 percent, which was greater even than the historic turnout in the 2008 contest. The young vote swung heavily toward Biden in swing states. And, yet, young voters again participated at lower rates than did other age groups.[11]
Why are younger Americans less likely to become involved in traditional political organizations? One answer may be that as American politics become more partisan in nature, young people turn away. Committed partisanship, which is the tendency to identify with and to support (often blindly) a particular political party, alienates some Americans who feel that elected representatives should vote in support of the nation’s best interests instead of voting in the way their party wishes them to. When elected officials ignore all factors other than their party’s position on a particular issue, some voters become disheartened while others may become polarized. However, a recent study reveals that it is a distrust of the opposing party and not an ideological commitment to their own party that is at the heart of most partisanship among voters.[12]
Young Americans are particularly likely to be put off by partisan politics. More Americans under the age of thirty now identify themselves as Independents instead of Democrats or Republicans. Instead of identifying with a particular political party, young Americans are increasingly concerned about specific issues, such as same-sex marriage.[13] People whose votes are determined based on single issues are unlikely to vote according to party affiliation.
The other factor involved in low youth voter turnout in the past was that younger Americans did not feel that candidates generally tackle issues relevant to their lives. When younger voters cannot relate to the issues put forth in a campaign, such as entitlements for seniors, they lose interest. This dynamic changed somewhat in 2016 as Democratic candidate Bernie Sanders made college costs an issue, even promising free college tuition for undergraduates at public institutions. Senator Sanders enjoyed intense support on college campuses across the United States. After his nomination campaign failed, this young voter enthusiasm faded. Despite the fact that Democratic nominee Hillary Clinton eventually took up the free tuition issue, young people did not flock to her as well as they had to Sanders. In the general election, won by Republican nominee Donald Trump, turnout was down and Clinton received a smaller proportion of the youth vote than President Obama had in 2012.[14] In 2020, youth again felt connected with candidates, and that compelled participation throughout the election year. Sanders again galvanized interest, as did Biden and Harris during the general election phase. Student loan debt was a key campaign issue.
While some Americans disapprove of partisanship in general, others are put off by the ideology—established beliefs and ideals that help shape political policy—of one of the major parties. This is especially true among the young. While ideological polarization has occurred on both sides of the political spectrum, as some members of the Republican Party have become more ideologically conservative (e.g., opposing same-sex marriage, legalization of certain drugs, immigration reform, gun control, separation of church and state, and access to abortion), those young people who do identify with one of the major parties have in recent years tended to favor the Democratic Party.[15] Of the Americans under age thirty who were surveyed by Harvard in 2015, more tended to hold a favorable opinion of Democrats in Congress than of Republicans, and in the 2020 election, 61 percent of younger voters voted for the Democratic ticket. Even those young Americans who identify themselves as Republicans are more liberal on certain issues, such as being supportive of same-sex marriage and immigration reform, than are older Republicans. The young Republicans also may be more willing to see similarities between themselves and Democrats.[16] Once again, support for the views of a particular party does not necessarily mean that someone will vote for members of that party.
Other factors may keep even those college students who do wish to vote away from the polls. Because many young Americans attend colleges and universities outside of their home states, they may find it difficult to register to vote. In places where a state-issued ID is required, students may not have one or may be denied one if they cannot prove that they paid in-state tuition rates.[17]
The likelihood that people will become active in politics also depends not only on age but on such factors as wealth and education. In 2020, as was the case in past elections, the percentage of people who reported that they were regular voters grew as levels of income and education increased.[18][19] Political involvement also depends on how strongly people feel about current political issues. Unfortunately, public opinion polls, which politicians may rely on when formulating policy or deciding how to vote on issues, capture only people’s latent preferences or beliefs. Latent preferences are not deeply held and do not remain the same over time. They may not even represent a person’s true feelings, since they may be formed on the spot when someone is asked a question about which he or she has no real opinion. Indeed, voting itself may reflect merely a latent preference because even people who do not feel strongly about a particular political candidate or issue vote. On the other hand, intense preferences are based on strong feelings regarding an issue that someone adheres to over time. People with intense preferences tend to become more engaged in politics; they are more likely to donate time and money to campaigns or to attend political rallies. The more money that one has and the more highly educated one is, the more likely that he or she will form intense preferences and take political action.[20]
CHAPTER REVIEW
- Robert D. Putnam. 2001. Bowling Alone: The Collapse and Revival of American Community. New York: Simon & Schuster, 75. ↵
- ———. 1995. "Bowling Alone: America’s Declining Social Capital," Journal of Democracy 6: 66–67, 69; "About Social Capital," https://www.hks.harvard.edu/programs/saguaro/about-social-capital (May 2, 2016). ↵
- Everett Ladd. The Ladd Report. http://movies2.nytimes.com/books/first/l/ladd-report.html ↵
- April Clark. "Rethinking the Decline in Social Capital." American Politics Research. April 29, 2014. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/1532673X14531071 ↵
- Emily Badger. "The Terrible Loneliness of Growing Up Poor in Robert Putnam's America." The Washington Post. March 6, 2015. https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/wonk/wp/2015/03/06/the-terrible-loneliness-of-growing-up-poor-in-robert-putnams-america/?noredirect=on&utm_term=.32998051b18a ↵
- Jared Keller. 4 May 2015. "Young Americans are Opting Out of Politics, but Not Because They’re Cynical," http://www.psmag.com/politics-and-law/young-people-are-not-so-politically-inclined. ↵
- Winston Ross, "Ritchie Torres: Gay, Hispanic and Powerful," Newsweek, 25 January 2015. ↵
- Pew Research Center. 26 April 2018. "Political Engagement, Knowledge, and the Midterms." http://www.people-press.org/2018/04/26/10-political-engagement-knowledge-and-the-midterms/. ↵
- Harvard Kennedy School Institute of Politics. 17 October 2018. Survey of Young Americans’ Attitudes toward Politics and Public Service. https://iop.harvard.edu/sites/default/files/content/Harvard-IOP-Fall-2018-poll-toplines.pdf. ↵
- Center for Information and Research on Civic Learning and Engagement (CIRCLE). 7 November 2018. "Young People Dramatically Increase Their Turnout to 31%, Shape 2018 Midterm Elections." CIRCLE. https://civicyouth.org/young-people-dramatically-increase-their-turnout-31-percent-shape-2018-midterm-elections/. ↵
- Harvard Institute of Politics. "Survey of Young Americans' Attitudes toward Politics and Public Service 35th Edition: March 8–March 25, 2018." 2018; Center for Information and Research on Civic Learning and Engagement. "Election Week 2020: Young People Increase Turnout, Lead Biden to Victory." 25 November 2020. https://circle.tufts.edu/latest-research/election-week-2020. ↵
- Marc Hetherington and Thomas Rudolph, "Why Don’t Americans Trust the Government?" The Washington Post, 30 January 2014. ↵
- Keller, "Young Americans are Opting Out." ↵
- Tami Luhby and Jennifer Agiesta. 8 November 2016. "Exit Polls: Clinton Fails to Energize African-Americans, Latinos and the Young, http://www.cnn.com/2016/11/08/politics/first-exit-polls-2016/. ↵
- Harvard Institute of Politics, "No Front-Runner among Prospective Republican Candidates," http://iop.harvard.edu/no-front-runner-among-prospective-republican-candidates-hillary-clinton-control-democratic-primary (May 2, 2016). ↵
- Jocelyn Kiley and Michael Dimock. 25 September 2014. "The GOP’s Millennial Problem Runs Deep," http://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2014/09/25/the-gops-millennial-problem-runs-deep/. ↵
- "Keeping Students from the Polls," New York Times, 26 December 2011. ↵
- 18 October 2006. “Who Votes, Who Doesn’t, and Why,” http://www.people-press.org/2006/10/18/who-votes-who-doesnt-and-why/. ↵
- "What Affects Voter Turnout Rates," Fair Vote, https://www.fairvote.org/what_affects_voter_turnout_rates (June 1, 2021). ↵
- Jonathan M. Ladd. 11 September 2015. "Don’t Worry about Special Interests," https://www.vox.com/mischiefs-of-faction/2015/9/11/9279615/economic-inequality-special-interests. ↵
connections with others and the willingness to interact and aid them
strong support, or even blind allegiance, for a particular political party
the beliefs and ideals that help to shape political opinion and eventually policy
beliefs and preferences people are not deeply committed to and that change over time
beliefs and preferences based on strong feelings regarding an issue that someone adheres to over time

