Proofs and Toolkit Functions
Appendix
Important Proofs and Derivations
Product Rule:
[latex]{\mathrm{log}}_{a}xy={\mathrm{log}}_{a}x+{\mathrm{log}}_{a}y[/latex]
Proof:
Let[latex]\,m={\mathrm{log}}_{a}x\,[/latex]and[latex]\,n={\mathrm{log}}_{a}y.[/latex]
Write in exponent form.
[latex]x={a}^{m}\,[/latex]and[latex]\,y={a}^{n}.[/latex]
Multiply.
[latex]xy={a}^{m}{a}^{n}={a}^{m+n}[/latex]
[latex]\begin{array}{ccc}\hfill {a}^{m+n}& =& xy\hfill \\ \hfill {\mathrm{log}}_{a}\left(xy\right)& =& m+n\hfill \\ & =& {\mathrm{log}}_{a}x+{\mathrm{log}}_{b}y\hfill \end{array}[/latex]
Change of Base Rule:
[latex]\begin{array}{l}\hfill \\ {\mathrm{log}}_{a}b=\frac{{\mathrm{log}}_{c}b}{{\mathrm{log}}_{c}a}\hfill \\ {\mathrm{log}}_{a}b=\frac{1}{{\mathrm{log}}_{b}a}\hfill \end{array}[/latex]
where[latex]\,x\,[/latex]and[latex]\,y\,[/latex]are positive, and[latex]\,a>0,a\ne 1.[/latex]
Proof:
Let[latex]\,x={\mathrm{log}}_{a}b.[/latex]
Write in exponent form.
[latex]{a}^{x}=b[/latex]
Take the[latex]\,{\mathrm{log}}_{c}\,[/latex]of both sides.
[latex]\begin{array}{ccc}\hfill {\mathrm{log}}_{c}{a}^{x}& =& {\mathrm{log}}_{c}b\hfill \\ \hfill x{\mathrm{log}}_{c}a& =& {\mathrm{log}}_{c}b\hfill \\ \hfill x& =& \frac{{\mathrm{log}}_{c}b}{{\mathrm{log}}_{c}a}\hfill \\ \hfill {\mathrm{log}}_{a}b& =& \frac{{\mathrm{log}}_{c}b}{{\mathrm{log}}_{a}b}\hfill \end{array}[/latex]
When[latex]\,c=b,[/latex]
[latex]{\mathrm{log}}_{a}b=\frac{{\mathrm{log}}_{b}b}{{\mathrm{log}}_{b}a}=\frac{1}{{\mathrm{log}}_{b}a}[/latex]
ToolKit Functions:
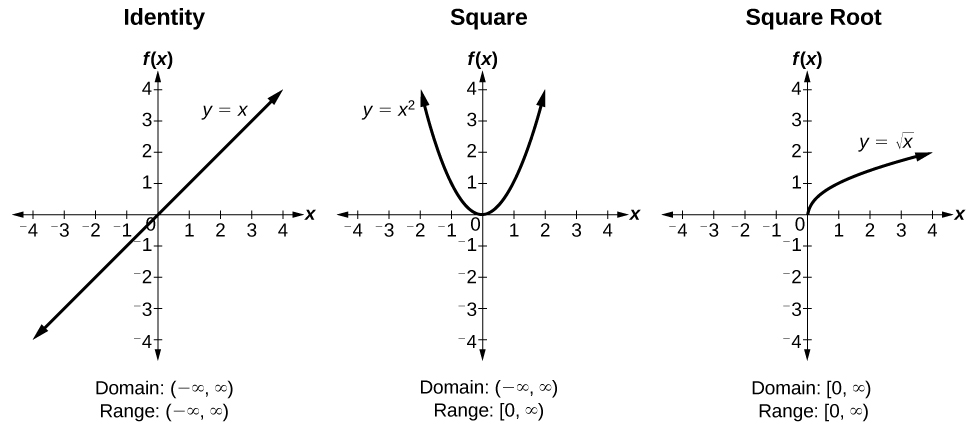
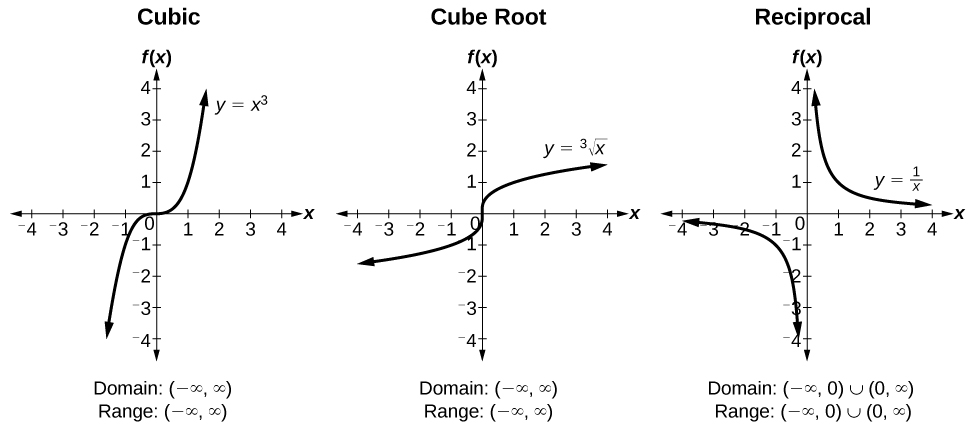
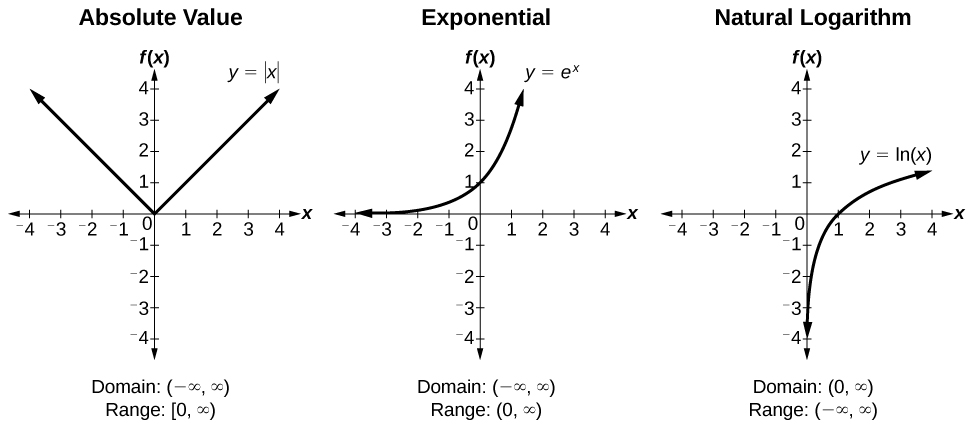
Media Attributions
- Toolkit Functions #1 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Toolkit Functions #2 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Toolkit Functions #3 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license

