Chapter 6 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
Chapter 6 Review Exercises
Chapter Review Exercises
Exponential Functions
- Determine whether the function[latex]\,y=156{\left(0.825\right)}^{t}\,[/latex]represents exponential growth, exponential decay, or neither. Explain
Show Solution
exponential decay; The growth factor,[latex]\,0.825,[/latex] is between[latex]\,0\,[/latex]and[latex]\,1.[/latex]
- The population of a herd of deer is represented by the function[latex]\,A\left(t\right)=205{\left(1.13\right)}^{t},\,[/latex]where[latex]\,t\,[/latex]is given in years. To the nearest whole number, what will the herd population be after[latex]\,6\,[/latex]years?
- Find an exponential equation that passes through the points[latex]\,\text{(2, 2}\text{.25)}\,[/latex]and[latex]\,\left(5,60.75\right).[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]y=0.25{\left(3\right)}^{x}[/latex]
- Determine whether (Figure) could represent a function that is linear, exponential, or neither. If it appears to be exponential, find a function that passes through the points.
| x | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| f(x) | 3 | 0.9 | 0.27 | 0.081 |
- A retirement account is opened with an initial deposit of $8,500 and earns[latex]\,8.12%\,[/latex]interest compounded monthly. What will the account be worth in[latex]\,20\,[/latex]years?
Show Solution
[latex]$42,888.18[/latex]
- Hsu-Mei wants to save $5,000 for a down payment on a car. To the nearest dollar, how much will she need to invest in an account now with[latex]\,7.5%\,[/latex]APR, compounded daily, in order to reach her goal in[latex]\,3\,[/latex]years?
- Does the equation[latex]\,y=2.294{e}^{-0.654t}\,[/latex]represent continuous growth, continuous decay, or neither? Explain.
Show Solution
continuous decay; the growth rate is negative.
- Suppose an investment account is opened with an initial deposit of[latex]\,\text{\$10,500}\,[/latex]earning[latex]\,6.25%\,[/latex]interest, compounded continuously. How much will the account be worth after[latex]\,25\,[/latex]years?
Graphs of Exponential Functions
- Graph the function[latex]\,f\left(x\right)=3.5{\left(2\right)}^{x}.\,[/latex]State the domain and range and give the y-intercept.
Show Solution
domain: all real numbers; range: all real numbers strictly greater than zero; y-intercept: (0, 3.5);
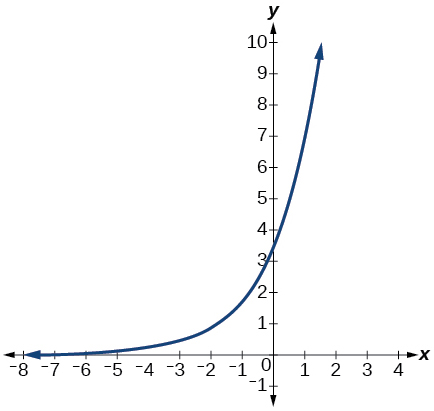
- Graph the function[latex]\,f\left(x\right)=4{\left(\frac{1}{8}\right)}^{x}\,[/latex]and its reflection about the y-axis on the same axes, and give the y-intercept.
- The graph of[latex]\,f\left(x\right)={6.5}^{x}\,[/latex]is reflected about the y-axis and stretched vertically by a factor of[latex]\,7.\,[/latex]What is the equation of the new function,[latex]\,g\left(x\right)?\,[/latex]State its y-intercept, domain, and range.
Show Solution
[latex]g\left(x\right)=7{\left(6.5\right)}^{-x};\,[/latex]y-intercept:[latex]\,\left(0,\text{ 7}\right);\,[/latex]Domain: all real numbers; Range: all real numbers greater than[latex]\,0.[/latex]
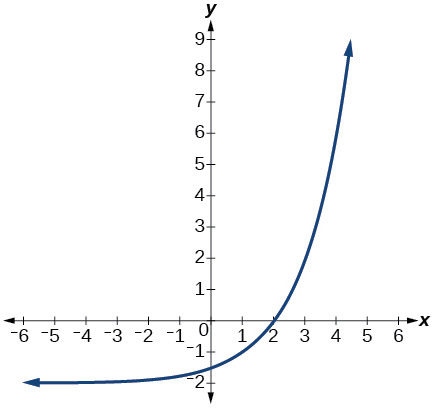
- The graph below shows transformations of the graph of[latex]\,f\left(x\right)={2}^{x}.\,[/latex]What is the equation for the transformation?
Logarithmic Functions
- Rewrite[latex]\,{\mathrm{log}}_{17}\left(4913\right)=x\,[/latex]as an equivalent exponential equation.
Show Solution
[latex]{17}^{x}=4913[/latex]
- Rewrite[latex]\,\mathrm{ln}\left(s\right)=t\,[/latex]as an equivalent exponential equation.
- Rewrite[latex]\,{a}^{-\,\frac{2}{5}}=b\,[/latex]as an equivalent logarithmic equation.
Show Solution
[latex]{\mathrm{log}}_{a}b=-\frac{2}{5}[/latex]
- Rewrite [latex]\,{e}^{-3.5}=h\,[/latex] as an equivalent logarithmic equation.
- Solve for x if[latex]\,\,\,{\mathrm{log}}_{64}\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{3}\,[/latex]by converting to exponential form.
Show Solution
[latex]x={64}^{\frac{1}{3}}=4[/latex]
- Evaluate[latex]\,{\mathrm{log}}_{5}\left(\frac{1}{125}\right)\,[/latex]without using a calculator.
- Evaluate[latex]\,\mathrm{log}\left(\text{0}\text{.000001}\right)\,[/latex]without using a calculator.
Show Solution
[latex]\mathrm{log}\left(\text{0}\text{.000001}\right)=-6[/latex]
- Evaluate[latex]\,\mathrm{log}\left(4.005\right)\,[/latex]using a calculator. Round to the nearest thousandth.
- Evaluate[latex]\,\mathrm{ln}\left({e}^{-0.8648}\right)\,[/latex]without using a calculator.
Show Solution
[latex]\mathrm{ln}\left({e}^{-0.8648}\right)=-0.8648[/latex]
- Evaluate[latex]\,\mathrm{ln}\left(\sqrt[3]{18}\right)\,[/latex]using a calculator. Round to the nearest thousandth.
Graphs of Logarithmic Functions
- Graph the function[latex]\,g\left(x\right)=\mathrm{log}\left(7x+21\right)-4.[/latex]
Show Solution
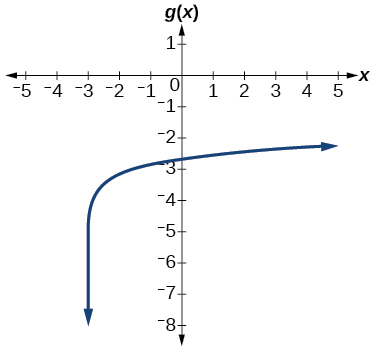
- Graph the function[latex]\,h\left(x\right)=2\mathrm{ln}\left(9-3x\right)+1.[/latex]
- State the domain, vertical asymptote, and end behavior of the function[latex]\,g\left(x\right)=\mathrm{ln}\left(4x+20\right)-17.[/latex]
Show Solution
Domain:[latex]\,x>-5;\,[/latex]Vertical asymptote:[latex]\,x=-5;\,[/latex]End behavior: as[latex]\,x\to -{5}^{+},f\left(x\right)\to -\infty \,[/latex]and as[latex]\,x\to \infty ,f\left(x\right)\to \infty .[/latex]
Logarithmic Properties
- Rewrite[latex]\,\mathrm{ln}\left(7r\cdot 11st\right)\,[/latex]in expanded form.
- Rewrite[latex]\,{\mathrm{log}}_{8}\left(x\right)+{\mathrm{log}}_{8}\left(5\right)+{\mathrm{log}}_{8}\left(y\right)+{\mathrm{log}}_{8}\left(13\right)\,[/latex]in compact form.
Show Solution
[latex]{\text{log}}_{8}\left(65xy\right)[/latex]
- Rewrite[latex]\,{\mathrm{log}}_{m}\left(\frac{67}{83}\right)\,[/latex]in expanded form.
- Rewrite[latex]\,\mathrm{ln}\left(z\right)-\mathrm{ln}\left(x\right)-\mathrm{ln}\left(y\right)\,[/latex]in compact form.
Show Solution
[latex]\mathrm{ln}\left(\frac{z}{xy}\right)[/latex]
- Rewrite[latex]\,\mathrm{ln}\left(\frac{1}{{x}^{5}}\right)\,[/latex]as a product.
- Rewrite[latex]\,-{\mathrm{log}}_{y}\left(\frac{1}{12}\right)\,[/latex]as a single logarithm.
Show Solution
[latex]{\text{log}}_{y}\left(12\right)[/latex]
- Use properties of logarithms to expand[latex]\,\mathrm{log}\left(\frac{{r}^{2}{s}^{11}}{{t}^{14}}\right).[/latex]
- Use properties of logarithms to expand[latex]\,\mathrm{ln}\left(2b\sqrt{\frac{b+1}{b-1}}\right).[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\mathrm{ln}\left(2\right)+\mathrm{ln}\left(b\right)+\frac{\mathrm{ln}\left(b+1\right)-\mathrm{ln}\left(b-1\right)}{2}[/latex]
- Condense the expression[latex]\,5\mathrm{ln}\left(b\right)+\mathrm{ln}\left(c\right)+\frac{\mathrm{ln}\left(4-a\right)}{2}\,[/latex]to a single logarithm.
- Condense the expression[latex]\,3{\mathrm{log}}_{7}v+6{\mathrm{log}}_{7}w-\frac{{\mathrm{log}}_{7}u}{3}\,[/latex]to a single logarithm.
Show Solution
[latex]{\mathrm{log}}_{7}\left(\frac{{v}^{3}{w}^{6}}{\sqrt[3]{u}}\right)[/latex]
- Rewrite[latex]\,{\mathrm{log}}_{3}\left(12.75\right)\,[/latex]to base[latex]\,e.[/latex]
- Rewrite[latex]\,{5}^{12x-17}=125\,[/latex]as a logarithm. Then apply the change of base formula to solve for[latex]\,x\,[/latex]using the common log. Round to the nearest thousandth.
Show Solution
[latex]x=\frac{\frac{\mathrm{log}\left(125\right)}{\mathrm{log}\left(5\right)}+17}{12}=\frac{5}{3}[/latex]
Exponential and Logarithmic Equations
- Solve[latex]\,{216}^{3x}\cdot {216}^{x}={36}^{3x+2}\,[/latex]by rewriting each side with a common base.
- Solve[latex]\,\frac{125}{{\left(\frac{1}{625}\right)}^{-x-3}}={5}^{3}\,[/latex]by rewriting each side with a common base.
Show Solution
[latex]x=-3[/latex]
- Use logarithms to find the exact solution for[latex]\,7\cdot {17}^{-9x}-7=49.\,[/latex]If there is no solution, write no solution.
- Use logarithms to find the exact solution for[latex]\,3{e}^{6n-2}+1=-60.\,[/latex]If there is no solution, write no solution.
Show Solution
no solution
- Find the exact solution for[latex]\,5{e}^{3x}-4=6\,[/latex]. If there is no solution, write no solution.
- Find the exact solution for[latex]\,2{e}^{5x-2}-9=-56.\,[/latex]If there is no solution, write no solution.
Show Solution
no solution
- Find the exact solution for[latex]\,{5}^{2x-3}={7}^{x+1}.\,[/latex]If there is no solution, write no solution.
- Find the exact solution for[latex]\,{e}^{2x}-{e}^{x}-110=0.\,[/latex]If there is no solution, write no solution.
Show Solution
[latex]x=\mathrm{ln}\left(11\right)[/latex]
- Use the definition of a logarithm to solve.[latex]\,-5{\mathrm{log}}_{7}\left(10n\right)=5.[/latex]
- 47. Use the definition of a logarithm to find the exact solution for[latex]\,9+6\mathrm{ln}\left(a+3\right)=33.[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]a={e}^{4}-3[/latex]
- Use the one-to-one property of logarithms to find an exact solution for[latex]\,{\mathrm{log}}_{8}\left(7\right)+{\mathrm{log}}_{8}\left(-4x\right)={\mathrm{log}}_{8}\left(5\right).\,[/latex]If there is no solution, write no solution.
- Use the one-to-one property of logarithms to find an exact solution for[latex]\,\mathrm{ln}\left(5\right)+\mathrm{ln}\left(5{x}^{2}-5\right)=\mathrm{ln}\left(56\right).\,[/latex]If there is no solution, write no solution.
Show Solution
[latex]x=±\frac{9}{5}[/latex]
- The formula for measuring sound intensity in decibels[latex]\,D\,[/latex]is defined by the equation[latex]\,D=10\mathrm{log}\left(\frac{I}{{I}_{0}}\right),[/latex] where[latex]\,I\,[/latex]is the intensity of the sound in watts per square meter and[latex]\,{I}_{0}={10}^{-12}\,[/latex]is the lowest level of sound that the average person can hear. How many decibels are emitted from a large orchestra with a sound intensity of[latex]\,6.3\cdot {10}^{-3}\,[/latex]watts per square meter?
- The population of a city is modeled by the equation[latex]\,P\left(t\right)=256,114{e}^{0.25t}\,[/latex]where[latex]\,t\,[/latex]is measured in years. If the city continues to grow at this rate, how many years will it take for the population to reach one million?
Show Solution
about[latex]\,5.45\,[/latex]years
- Find the inverse function[latex]\,{f}^{-1}\,[/latex]for the exponential function[latex]\,f\left(x\right)=2\cdot {e}^{x+1}-5.[/latex]
- Find the inverse function[latex]\,{f}^{-1}\,[/latex]for the logarithmic function[latex]\,f\left(x\right)=0.25\cdot {\mathrm{log}}_{2}\left({x}^{3}+1\right).[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]{f}^{-1}\left(x\right)=\sqrt[3]{{2}^{4x}-1}[/latex]
Exponential and Logarithmic Models
For the following exercises, use this scenario: A doctor prescribes[latex]\,300\,[/latex]milligrams of a therapeutic drug that decays by about[latex]\,17%\,[/latex]each hour.
- To the nearest minute, what is the half-life of the drug?
- Write an exponential model representing the amount of the drug remaining in the patient’s system after[latex]\,t\,[/latex]hours. Then use the formula to find the amount of the drug that would remain in the patient’s system after[latex]\,24\,[/latex]hours. Round to the nearest hundredth of a gram.
Show Solution
[latex]f\left(t\right)=300{\left(0.83\right)}^{t};f\left(24\right)\approx 3.43\text{ }\text{ }g[/latex]
For the following exercises, use this scenario: A soup with an internal temperature of[latex]\,\text{350°}\,[/latex]Fahrenheit was taken off the stove to cool in a[latex]\,\text{71°F}\,[/latex]room. After fifteen minutes, the internal temperature of the soup was[latex]\,\text{175°F}\text{.}[/latex]
- Use Newton’s Law of Cooling to write a formula that models this situation.
- How many minutes will it take the soup to cool to[latex]\,\text{85°F?}[/latex]
Show Solution
about[latex]\,45\,[/latex]minutes
For the following exercises, use this scenario: The equation[latex]\,N\left(t\right)=\frac{1200}{1+199{e}^{-0.625t}}\,[/latex]models the number of people in a school who have heard a rumor after[latex]\,t\,[/latex]days.
- How many people started the rumor?
- To the nearest tenth, how many days will it be before the rumor spreads to half the carrying capacity?
Show Solution
about[latex]\,8.5\,[/latex]days
- What is the carrying capacity?
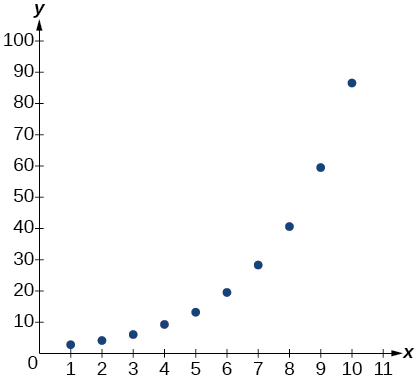
For the following exercises, enter the data from each table into a graphing calculator and graph the resulting scatter plots. Determine whether the data from the table would likely represent a function that is linear, exponential, or logarithmic.
| x | f(x) |
| 1 | 3.05 |
| 2 | 4.42 |
| 3 | 6.4 |
| 4 | 9.28 |
| 5 | 13.46 |
| 6 | 19.52 |
| 7 | 28.3 |
| 8 | 41.04 |
| 9 | 50.5 |
| 10 | 86.28 |
Show Solution
exponential
| x | f(x) |
| 0.5 | 18.05 |
| 1 | 17 |
| 3 | 15.33 |
| 5 | 14.55 |
| 7 | 14.04 |
| 10 | 13.5 |
| 12 | 13.22 |
| 13 | 13.1 |
| 15 | 12.88 |
| 17 | 12.69 |
| 20 | 12.45 |
- Find a formula for an exponential equation that goes through the points[latex]\,\left(-2,100\right)\,[/latex]and[latex]\,\left(0,4\right).\,[/latex]Then express the formula as an equivalent equation with base e.
Show Solution
[latex]y=4{\left(0.2\right)}^{x};\,[/latex][latex]y=4{e}^{\text{-1}\text{.609438}x}[/latex]
Media Attributions
- Ch 6 Review 9 © OpenStax College Algebra and Trigonometry is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch 6 Review 12 © OpenStax College Algebra and Trigonometry is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch 6 Review 23 © OpenStax College Algebra and Trigonometry is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch 6 Review 61 © OpenStax College Algebra and Trigonometry is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license

