Chapter 3 Functions
Chapter 3 Practice Test
For the following exercises, determine whether each of the following relations is a function.
- [latex]y=2x+8[/latex]
Show Solution
The relation is a function.
- [latex]\left\{\left(2,1\right),\left(3,2\right),\left(-1,1\right),\left(0,-2\right)\right\}[/latex]
For the following exercises, evaluate the function[latex]\,f\left(x\right)=-3{x}^{2}+2x\,[/latex] at the given input.
- [latex]f\left(-2\right)[/latex]
Show Solution
−16
- [latex]\,f\left(a\right)\,[/latex]
- Show that the function [latex]\,f\left(x\right)=-2{\left(x-1\right)}^{2}+3\,[/latex] is not one-to-one.
Show Solution
The graph is a parabola and the graph fails the horizontal line test.
- Write the domain of the function [latex]\,f\left(x\right)=\sqrt{3-x}\,[/latex] in interval notation.
- Given[latex]\,f\left(x\right)=2{x}^{2}-5x,\,[/latex] find [latex]f\left(a+1\right)-f\left(1\right)\,[/latex] in simplest form.
Show Solution
[latex]2{a}^{2}-a[/latex]
- Graph the function [latex]f(x) = \bigg\{\begin{array}{l} x +1 \text{ } \ \ \ -2< x<3\\ -x \text{ } \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ x\ge 3\end{array}[/latex].
- Find the average rate of change of the function [latex]\,f\left(x\right)=3-2{x}^{2}+x\,[/latex] by finding[latex]\,\frac{f\left(b\right)-f\left(a\right)}{b-a}\,[/latex] in simplest form.
Show Solution
[latex]-2\left(a+b\right)+1[/latex]
For the following exercises, use the functions [latex]\,f\left(x\right)=3-2{x}^{2}+x\text{ and }g\left(x\right)=\sqrt{x}\,[/latex] to find the composite functions.
- [latex]\left(g\circ f\right)\left(x\right)[/latex]
- [latex]\left(g\circ f\right)\left(1\right)[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\sqrt{2}[/latex]
- Express[latex]\,H\left(x\right)=\sqrt[3]{5{x}^{2}-3x}\,[/latex]as a composition of two functions,[latex]\,f\,[/latex]and[latex]\,g,\,[/latex]where[latex]\,\left(f\circ g\right)\left(x\right)=H\left(x\right).[/latex]
For the following exercises, graph the functions by translating, stretching, and/or compressing a toolkit function.
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=\sqrt{x+6}-1[/latex]
Show Solution
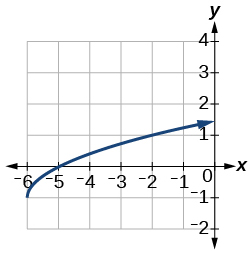
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{x+2}-1[/latex]
For the following exercises, determine whether the functions are even, odd, or neither.
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=-\frac{5}{{x}^{2}}+9{x}^{6}[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\text{even}[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=-\frac{5}{{x}^{3}}+9{x}^{5}[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{x}[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\text{odd}[/latex]
- Graph the absolute value function[latex]\,f\left(x\right)=-2|x-1|+3.[/latex]
For the following exercises, find the inverse of the function.
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=3x-5[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]{f}^{-1}\left(x\right)=\frac{x+5}{3}[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=\frac{4}{x+7}[/latex]
For the following exercises, use the graph of [latex]\,g\,[/latex]shown in Figure below.
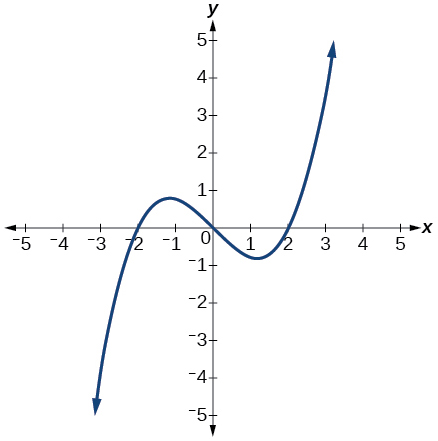
- On what intervals is the function increasing?
Show Solution
[latex]\left(-\infty ,-1.1\right)\text{ and }\left(1.1,\infty \right)[/latex]
- On what intervals is the function decreasing?
- Approximate the local minimum of the function. Express the answer as an ordered pair.
Show Solution
[latex]\left(1.1,-0.9\right)[/latex]
- Approximate the local maximum of the function. Express the answer as an ordered pair.
For the following exercises, use the graph of the piecewise function shown in the Figure below.
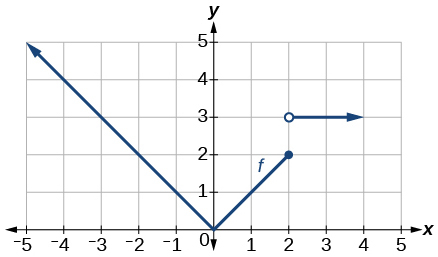
- Find[latex]\,f\left(2\right).[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]f\left(2\right)=2[/latex]
- Find[latex]\,f\left(-2\right).[/latex]
- Write an equation for the piecewise function.
Show Solution
[latex]f\left(x\right)=\bigg\{\begin{array}{l} | x | \text{ } \ \ \ \ \ x<2\\ 3 \text{ } \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ x\ge 2\end{array}[/latex]
For the following exercises, use the values listed in Table 1.
| [latex]x[/latex] | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| [latex]F(x)[/latex] | 1 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 17 |
- Find[latex]\,F\left(6\right).[/latex]
- Solve the equation[latex]\,F\left(x\right)=5.[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]x=2[/latex]
- Is the graph increasing or decreasing on its domain?
- Is the function represented by the graph one-to-one?
Show Solution
yes
- Find[latex]\,{F}^{-1}\left(15\right).[/latex]
- Given[latex]\,f\left(x\right)=-2x+11,\,[/latex]find[latex]\,{f}^{-1}\left(x\right).[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]{f}^{-1}\left(x\right)=-\frac{x-11}{2}[/latex]
Media Attributions
- Ch-3-Practice-Test-13 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Practice-Test-20 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Practice-Test-24 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license

