Chapter 3 Functions
Chapter 3 Review Exercises
Functions and Function Notation
For the following exercises, determine whether the relation is a function.
- [latex]\left\{\left(a,b\right),\left(c,d\right),\left(e,d\right)\right\}[/latex]
Show Solution
function
- [latex]\left\{\left(5,2\right),\left(6,1\right),\left(6,2\right),\left(4,8\right)\right\}[/latex]
- [latex]{y}^{2}+4=x,\,[/latex]for[latex]\,x\,[/latex] the independent variable and [latex]\,y\,[/latex] the dependent variable
Show Solution
not a function
- Is the graph in Figure 1 a function?
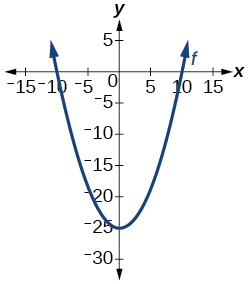
For the following exercises, evaluate the function at the indicated values:[latex]\,\,\,f\left(-3\right);\,\,f\left(2\right);\,\,\,f\left(-a\right);\,\,\,-f\left(a\right);\,\,\,f\left(a+h\right).[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=-2{x}^{2}+3x[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]f\left(-3\right)=-27;[/latex][latex]f\left(2\right)=-2;[/latex][latex]f\left(-a\right)=-2{a}^{2}-3a;[/latex]
[latex]-f\left(a\right)=2{a}^{2}-3a;[/latex][latex]f\left(a+h\right)=-2{a}^{2}+3a-4ah+3h-2{h}^{2}[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=2|3x-1|[/latex]
For the following exercises, determine whether the functions are one-to-one.
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=-3x+5[/latex]
Show Solution
one-to-one
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=|x-3|[/latex]
For the following exercises, use the vertical line test to determine if the relation whose graph is provided is a function.
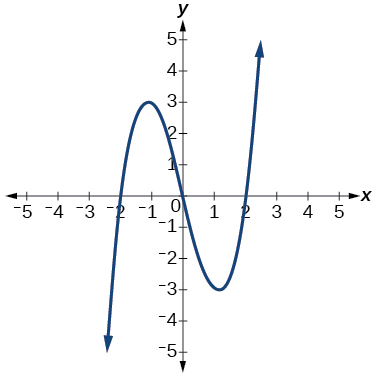
Show Solution
function
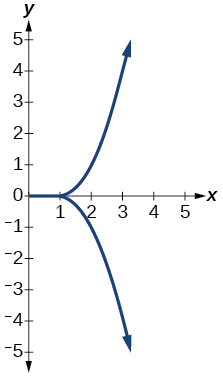
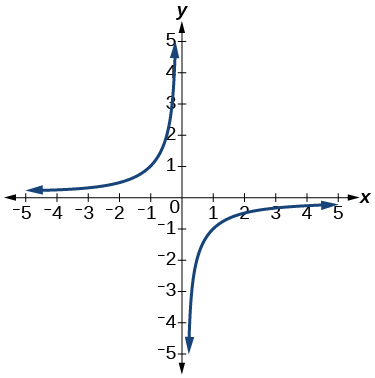
Show Solution
function
For the following exercises, graph the functions.
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=|x+1|[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(x\right)={x}^{2}-2[/latex]
Show Solution
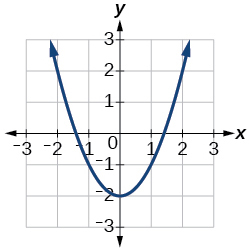
For the following exercises, use Figure 2 to approximate the values.

- [latex]f\left(2\right)[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(-2\right)[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]2[/latex]
- If [latex]\,f\left(x\right)=-2,\,[/latex] then solve for [latex]\,x.[/latex]
- If [latex]\,f\left(x\right)=1,\,[/latex] then solve for [latex]\,x.[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]x=-1.8\text{ }[/latex]or[latex]\text{ }x=1.8[/latex]
For the following exercises, use the function [latex]\,h\left(t\right)=-16{t}^{2}+80t\,[/latex] to find the values in simplest form.
- [latex]\frac{h\left(2\right)-h\left(1\right)}{2-1}[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{h\left(a\right)-h\left(1\right)}{a-1}[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\frac{-64+80a-16{a}^{2}}{-1+a}=-16a+64[/latex]
Domain and Range
For the following exercises, find the domain of each function, expressing answers using interval notation.
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=\frac{2}{3x+2}[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=\frac{x-3}{{x}^{2}-4x-12}[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\left(-\infty ,-2\right)\cup \left(-2,6\right)\cup \left(6,\infty \right)[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=\frac{\sqrt{x-6}}{\sqrt{x-4}}[/latex]
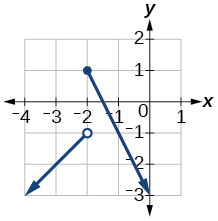
- Graph this piecewise function:[latex]f\left(x\right)=\bigg\{\begin{array}{l}x+1\text{ } \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ x<-2\\ -2x-3\text{ } \ \ \ x\ge -2\end{array}[/latex]
Show Solution
Rates of Change and Behavior of Graphs
For the following exercises, find the average rate of change of the functions from[latex]\,x=1\text{ to }x=2.[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=4x-3[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=10{x}^{2}+x[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]31[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=-\frac{2}{{x}^{2}}[/latex]
For the following exercises, use the graphs to determine the intervals on which the functions are increasing, decreasing, or constant.
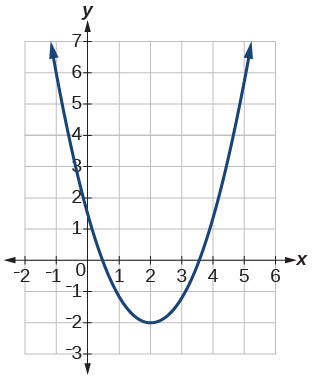
Show Solution
increasing[latex]\,\left(2,\infty \right);\,[/latex]
decreasing[latex]\,\left(-\infty ,2\right)[/latex]
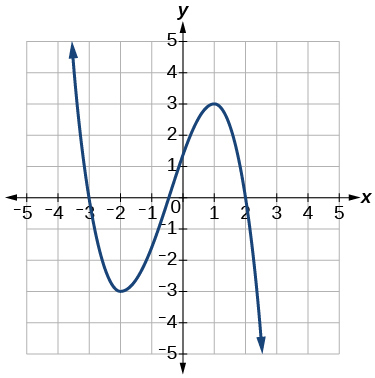
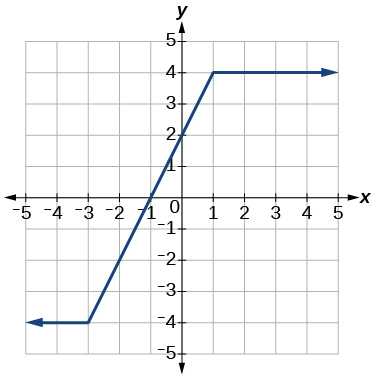
Show Solution
increasing[latex]\text{}\left(-3,1\right); \text{}[/latex]constant[latex]\,\left(-\infty ,-3\right)\cup \left(1,\infty \right)[/latex]
- Find the local minimum of the function graphed in Exercise 27.
- Find the local extrema for the function graphed in Exercise 28.
Show Solution
local minimum[latex]\,\left(-2,-3\right);\,[/latex]local maximum[latex]\,\left(1,3\right)[/latex]
- For the graph in Figure 3 below, the domain of the function is [latex]\,\left[-3,3\right].[/latex]The range is [latex]\,\left[-10,10\right].\,[/latex] Find the absolute minimum of the function on this interval.
- Find the absolute maximum of the function graphed in Figure 3.
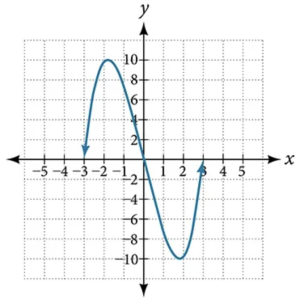
Show Solution
[latex]\,\left(-1.8,10\right)\,[/latex]
Composition of Functions
For the following exercises, find [latex]\,\left(f\circ g\right)\left(x\right)\,[/latex] and [latex]\,\left(g\circ f\right)\left(x\right)\,[/latex] for each pair of functions.
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=4-x,\,g\left(x\right)=-4x[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=3x+2,\,g\left(x\right)=5-6x[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\left(f\circ g\right)\left(x\right)=17-18x;\,\left(g\circ f\right)\left(x\right)=-7-18x[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(x\right)={x}^{2}+2x,\,g\left(x\right)=5x+1[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=\sqrt{x+2},\text{ }g\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{x}[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\left(f\circ g\right)\left(x\right)=\sqrt{\frac{1}{x}+2};\,\left(g\circ f\right)\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{x+2}}[/latex]
- [latex]\,f\left(x\right)=\frac{x+3}{2},\text{ }g\left(x\right)=\sqrt{1-x}\,[/latex]
For the following exercises, find [latex]\,\left(f\circ g\right)\,[/latex] and the domain for [latex]\,\left(f\circ g\right)\left(x\right)\,[/latex]for each pair of functions.
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=\frac{x+1}{x+4},\text{ }g\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{x}[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\left(f\circ g\right)\left(x\right)=\frac{1+x}{1+4x}, x\ne 0, x\ne -\frac{1}{4}[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{x+3},\text{ }g\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{x-9}[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{x},\text{ }g\left(x\right)=\sqrt{x}[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\left(f\circ g\right)\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{x}},\,x>0[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{{x}^{2}-1},\text{ }g\left(x\right)=\sqrt{x+1}[/latex]
For the following exercises, express each function[latex]\,H\,[/latex] as a composition of two functions [latex]\,f\,[/latex]and[latex]\,g\,[/latex] where [latex]\,H\left(x\right)=\left(f\circ g\right)\left(x\right).[/latex]
- [latex]H\left(x\right)=\sqrt{\frac{2x-1}{3x+4}}[/latex]
Show Solution
sample:[latex]\,g\left(x\right)=\frac{2x-1}{3x+4};\,f\left(x\right)=\sqrt{x}[/latex]
- [latex]H\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{{\left(3{x}^{2}-4\right)}^{-3}}[/latex]
Transformation of Functions
For the following exercises, sketch a graph of the given function.
- [latex]f\left(x\right)={\left(x-3\right)}^{2}[/latex]
Show Solution
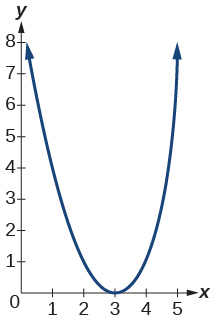
- [latex]f\left(x\right)={\left(x+4\right)}^{3}[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=\sqrt{x}+5[/latex]
Show Solution
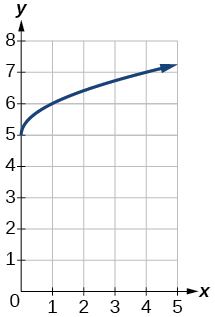
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=-{x}^{3}[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=\sqrt[3]{-x}[/latex]
Show Solution
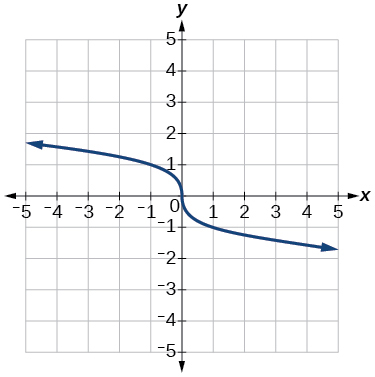
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=5\sqrt{-x}-4[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=4\left[|x-2|-6\right][/latex]
Show Solution
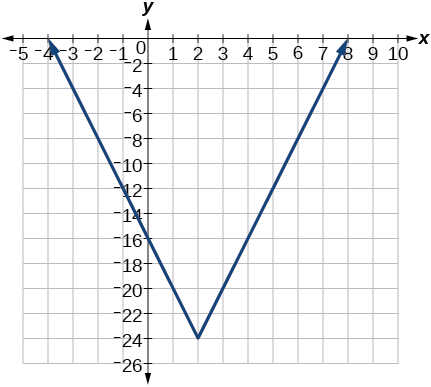
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=-{\left(x+2\right)}^{2}-1[/latex]
For the following exercises, sketch the graph of the function [latex]\,g\,[/latex] if the graph of the function [latex]\,f\,[/latex] is shown in Figure 4.
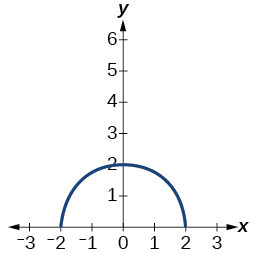
- [latex]g\left(x\right)=f\left(x-1\right)[/latex]
Show Solution
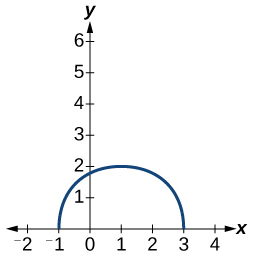
- [latex]g\left(x\right)=3f\left(x\right)[/latex]
For the following exercises, write the equation for the standard function represented by each of the graphs below.
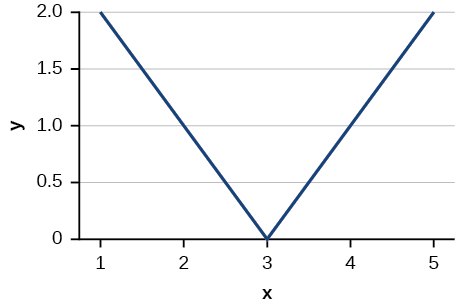
Show Solution
[latex]f\left(x\right)=|x-3|[/latex]
For the following exercises, determine whether each function below is even, odd, or neither.
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=3{x}^{4}[/latex]
Show Solution
even
- [latex]g\left(x\right)=\sqrt{x}[/latex]
- [latex]h\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{x}+3x[/latex]
Show Solution
odd
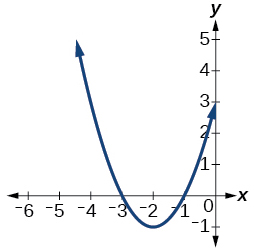
For the following exercises, analyze the graph and determine whether the graphed function is even, odd, or neither.
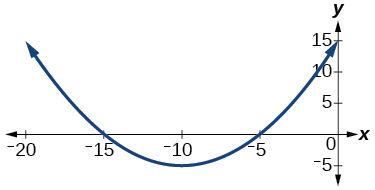
Show Solution
even
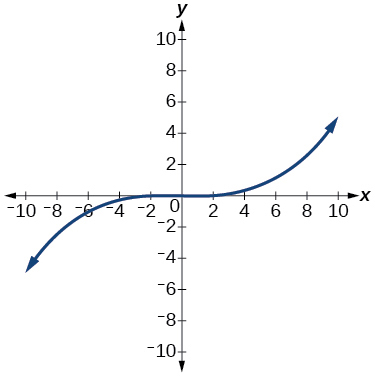
Absolute Value Functions
For the following exercises, write an equation for the transformation of[latex]\,f\left(x\right)=|x|.[/latex]
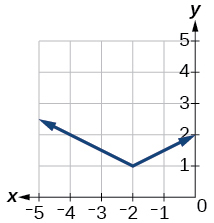
Show Solution
[latex]f\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{2}|x+2|+1[/latex]
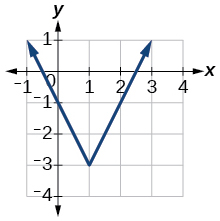
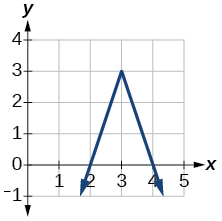
Show Solution
[latex]f\left(x\right)=-3|x-3|+3[/latex]
For the following exercises, graph the absolute value function.
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=|x-5|[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=-|x-3|[/latex]
Show Solution
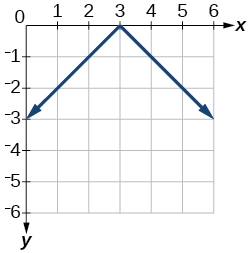
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=|2x-4|[/latex]
Inverse Functions
For the following exercises, find[latex]\text{ }{f}^{-1}\left(x\right)\text{ }[/latex]for each function.
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=9+10x[/latex]
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=\frac{x}{x+2}[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]{f}^{-1}\left(x\right)=\frac{-2x}{x-1}[/latex]
For the following exercise, find a domain on which the function[latex]\text{ }f\text{ }[/latex]is one-to-one and non-decreasing. Write the domain in interval notation. Then find the inverse of[latex]\text{ }f\text{ }[/latex]restricted to that domain.
- [latex]f\left(x\right)={x}^{2}+1[/latex]
- Given [latex]f\left(x\right)={x}^{3}-5[/latex] and [latex]g\left(x\right)=\sqrt[3]{x+5}:[/latex]
- Find [latex]f\left(g\left(x\right)\right)[/latex] and [latex]g\left(f\left(x\right)\right).[/latex]
- What does the answer tell us about the relationship between [latex]f\left(x\right)[/latex] and [latex]g\left(x\right)?[/latex]
Show Solution
- [latex]f\left(g\left(x\right)\right)=x[/latex] and [latex]g\left(f\left(x\right)\right)=x.[/latex]
- This tells us that [latex]f[/latex] and [latex]g[/latex] are inverse functions
For the following exercises, use a graphing utility to determine whether each function is one-to-one.
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{x}[/latex]
Show Solution
The function is one-to-one.
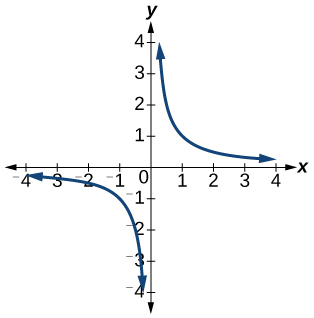
- [latex]f\left(x\right)=-3{x}^{2}+x[/latex]
Show Solution
The function is not one-to-one.
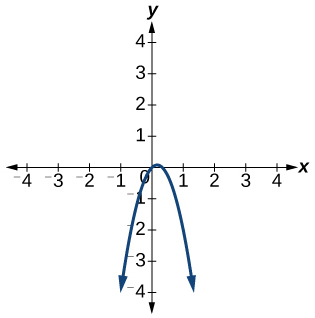
- If [latex]f\left(5\right)=2,[/latex] find [latex]{f}^{-1}\left(2\right).[/latex]
Show Solution
- If [latex]f\left(1\right)=4,[/latex] find [latex]{f}^{-1}\left(4\right).[/latex]
Media Attributions
- Ch-3-Review # 4 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review#9 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review# 10 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review# 11 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review# 13 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review# 23 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review# 27 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review# 28 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review# 29 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch 3 Review # 33 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review# 45 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review# 47 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review# 49 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch 3 Review # 51 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review# 53 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review# 53 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch 3 Review # 55 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review# 56 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review# 60 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review# 61 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review# 62 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review# 63 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review# 64 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review# 65 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review# 67 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review# 73 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Ch-3-Review# 74 © OpenStax Algebra and Trigonometry, 2e is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license

