9 Introduction to Education

The contradiction, however, lies in the fact that the more necessary a college degree has become, the harder it has become to achieve it. The cost of getting a college degree has risen sharply since the mid-1980s, while government support in the form of Pell Grants has barely increased. The net result is that those who do graduate from college are likely to begin a career in debt. As of 2013, the average of a typical student’s loans amounted to around $29,000. Added to that is that employment opportunities have not met expectations. The Washington Post (Brad Plumer May 20, 2013) notes that in 2010, only 27 percent of college graduates had a job related to their major. The business publication Bloomberg News states that among twenty-two-year-old degree holders who found jobs in the past three years, more than half were in roles not even requiring a college diploma (Janet Lorin and Jeanna Smialek, June 5, 2014).
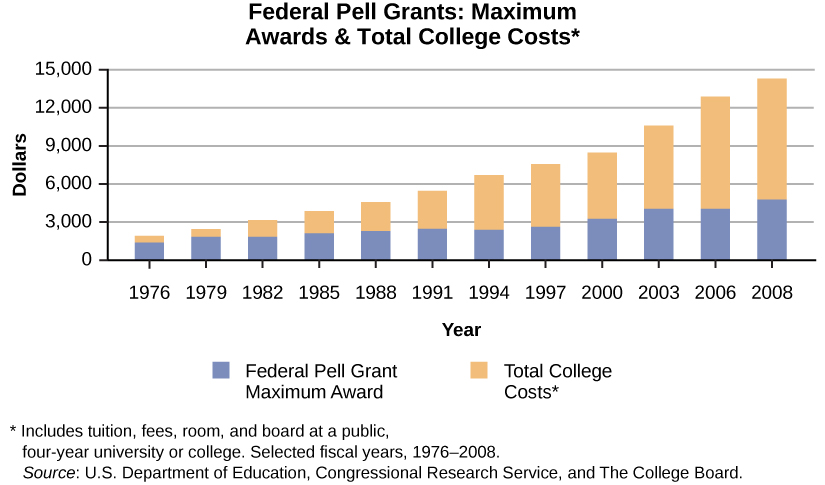
Is a college degree still worth it? All this is not to say that lifetime earnings among those with a college degree are not, on average, still much higher than for those without. But even with unemployment among degree-earners at a low of 3 percent, the increase in wages over the past decade has remained at a flat 1 percent. And the pay gap between those with a degree and those without has continued to increase because wages for the rest have fallen (David Leonhardt, New York Times, The Upshot, May 27, 2014).
But is college worth more than money?
Generally, the first two years of college are essentially a liberal arts experience. The student is exposed to a fairly broad range of topics, from mathematics and the physical sciences to history and literature, the social sciences, and music and art through introductory and survey-styled courses. It is in this period that the student’s world view is, it is hoped, expanded. Memorization of raw data still occurs, but if the system works, the student now looks at a larger world. Then, when he or she begins the process of specialization, it is with a much broader perspective than might be otherwise. This additional “cultural capital” can further enrich the life of the student, enhance his or her ability to work with experienced professionals, and build wisdom upon knowledge. Over two thousand years ago, Socrates said, “The unexamined life is not worth living.” The real value of an education, then, is to enhance our skill at self-examination.
9.1 Education around the World
Learning Objectives
- Identify differences in educational resources around the world
- Describe the concept of universal access to education

Education is a social institution through which a society’s children are taught basic academic knowledge, learning skills, and cultural norms. Every nation in the world is equipped with some form of educational system, though those systems vary greatly. The major factors that affect education systems are the resources and money that are utilized to support those systems in different nations. For instance, during the school years of 2020–2021, COVID-19 highlighted which school districts had the resources necessary to ensure students were able to continue receiving their education virtually. Unfortunately, many schools around the nation were not equipped; as a result, many students failed to obtain adequate education during that time, which caused more delays in their academic success.
As you might expect, a country’s wealth has much to do with the amount of money spent on education. Countries that do not have such basic amenities as running water are unable to support robust education systems or, in many cases, any formal schooling at all. The result of this worldwide educational inequality is a social concern for many countries, including the United States.
International differences in education systems are not solely a financial issue. The value placed on education, the amount of time devoted to it, and the distribution of education within a country also play a role in those differences. For example, students in South Korea spend 220 days a year in school, compared to the 180 days a year of their United States counterparts (Pellissier 2010). As of 2006, the United States ranked fifth among twenty-seven countries for college participation, but ranked sixteenth in the number of students who receive college degrees (National Center for Public Policy and Higher Education 2006). These statistics may be related to how much time is spent on education in the United States.
Then there is the issue of educational distribution within a nation. In December 2010, the results of a test called the Program for International Student Assessment (PISA), which is administered to fifteen-year-old students worldwide, were released. Those results showed that students in the United States had fallen from fifteenth to twenty-fifth in the rankings for science and math (National Public Radio 2010). Students at the top of the rankings hailed from Shanghai, Finland, Hong Kong, and Singapore.
Analysts determined that the nations and city-states at the top of the rankings had several things in common. For one, they had well-established standards for education with clear goals for all students. They also recruited teachers from the top 5 to 10 percent of university graduates each year, which is not the case for most countries (National Public Radio 2010).
Finally, there is the issue of social factors. One analyst from the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development, the organization that created the test, attributed 20 percent of performance differences and the United States’ low rankings to differences in social background. Researchers noted that educational resources, including money and quality teachers, are not distributed equitably in the United States. In the top-ranking countries, limited access to resources did not necessarily predict low performance. Analysts also noted what they described as “resilient students,” or those students who achieve at a higher level than one might expect given their social background. In Shanghai and Singapore, the proportion of resilient students is about 70 percent. In the United States, it is below 30 percent. These insights suggest that the United States’ educational system may be on a descending path that could detrimentally affect the country’s economy and its social landscape (National Public Radio 2010).
Big Picture
Education in Finland
With public education in the United States under such intense criticism, why is it that Singapore, South Korea, and especially Finland (which is culturally most similar to us) have such excellent public education? Over the course of thirty years, the country has pulled itself from among the lowest rankings by the Organization of Economic Cooperation (OEDC) to first in 2012, and remains, as of 2014, in the top five. Contrary to the rigid curriculum and long hours demanded of students in South Korea and Singapore, Finnish education often seems paradoxical to outside observers because it appears to break a lot of the rules we take for granted. It is common for children to enter school at seven years old, and children will have more recess and fewer hours in school than U.S. children—approximately 300 fewer hours. Their homework load is light when compared to all other industrialized nations (nearly 300 fewer hours per year in elementary school). There are no gifted programs, almost no private schools, and no high-stakes national standardized tests (Laukkanen 2008; LynNell Hancock 2011).
Prioritization is different than in the United States. There is an emphasis on allocating resources for those who need them most, high standards, support for special needs students, qualified teachers taken from the top 10 percent of the nation’s graduates and who must earn a Master’s degree, evaluation of education, and balancing decentralization and centralization.
“We used to have a system which was really unequal,” stated the Finnish Education Chief in an interview. “My parents never had a real possibility to study and have a higher education. We decided in the 1960s that we would provide a free quality education to all. Even universities are free of charge. Equal means that we support everyone and we’re not going to waste anyone’s skills.” As for teachers, “We don’t test our teachers or ask them to prove their knowledge. But it’s true that we do invest in a lot of additional teacher training even after they become teachers” (Gross-Loh 2014).
Yet over the past decade Finland has consistently performed among the top nations on the PISA. Finland’s school children didn’t always excel. Finland built its excellent, efficient, and equitable educational system in a few decades from scratch, and the concept guiding almost every educational reform has been equity. The Finnish paradox is that by focusing on the bigger picture for all, Finland has succeeded at fostering the individual potential of most every child.
“We created a school system based on equality to make sure we can develop everyone’s potential. Now we can see how well it’s been working. Last year the OECD tested adults from twenty-four countries measuring the skill levels of adults aged sixteen to sixty-five on a survey called the PIAAC (Programme for International Assessment of Adult Competencies), which tests skills in literacy, numeracy, and problem solving in technology-rich environments. Finland scored at or near the top on all measures.”
Formal and Informal Education
As already mentioned, education is not solely concerned with the basic academic concepts that a student learns in the classroom. Societies also educate their children, outside of the school system, in matters of everyday practical living. These two types of learning are referred to as formal education and informal education.
Formal education describes the learning of academic facts and concepts through a formal curriculum. Arising from the tutelage of ancient Greek thinkers, centuries of scholars have examined topics through formalized methods of learning. Education in earlier times was only available to the higher classes; they had the means to access scholarly materials, plus the luxury of leisure time that could be used for learning. The Industrial Revolution and its accompanying social changes made education more accessible to the general population. Many families in the emerging middle class found new opportunities for schooling.
The modern U.S. educational system is the result of this progression. Today, basic education is considered a right and responsibility for all citizens. Expectations of this system focus on formal education, with curricula and testing designed to ensure that students learn the facts and concepts that society believes are basic knowledge.
In contrast, informal education describes learning about cultural values, norms, and expected behaviors by participating in a society. This type of learning occurs both through the formal education system and at home. Our earliest learning experiences generally happen via parents, relatives, and others in our community. Through informal education, we learn how to dress for different occasions, how to perform regular life routines like shopping for and preparing food, and how to keep our bodies clean.

Cultural transmission refers to the way people come to learn the values, beliefs, and social norms of their culture. Both informal and formal education include cultural transmission. For example, a student will learn about cultural aspects of modern history in a U.S. History classroom. In that same classroom, the student might learn the cultural norm for asking a classmate out on a date through passing notes and whispered conversations.
Access to Education
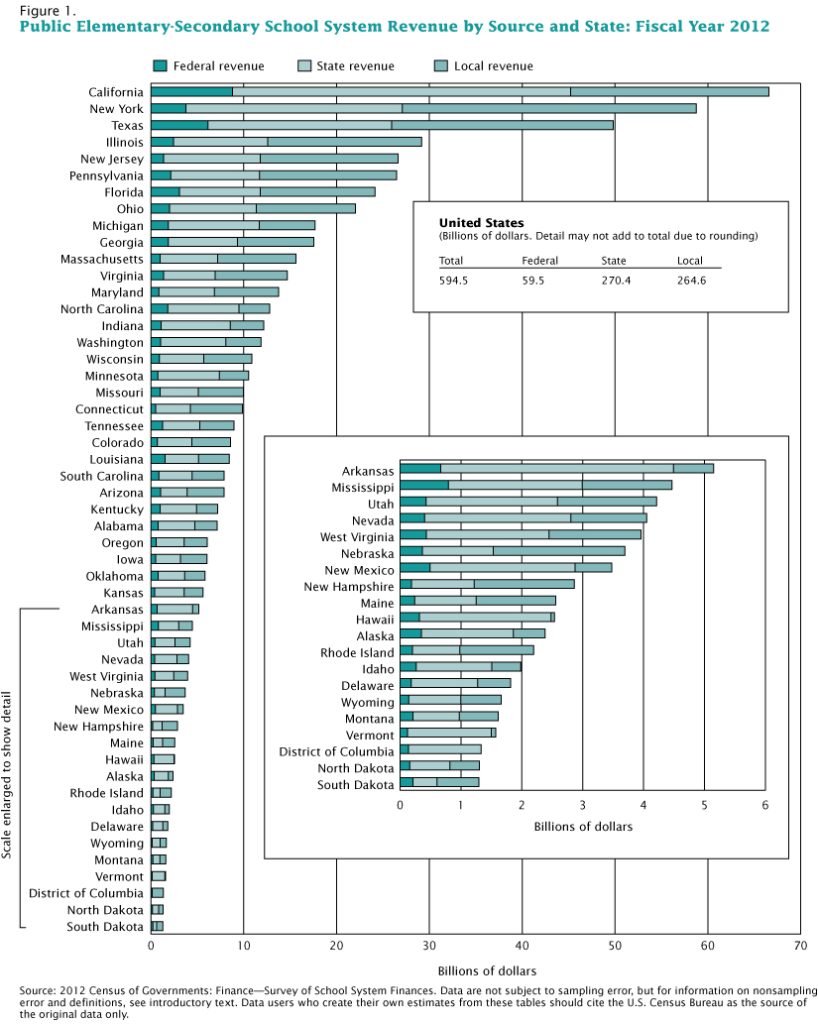
Another global concern in education is universal access. This term refers to people’s equal ability to participate in an education system. On a world level, access might be more difficult for certain groups based on class or gender (as was the case in the United States earlier in the nation’s history, a dynamic we still struggle to overcome). The modern idea of universal access arose in the United States as a concern for people with disabilities. In the United States, one way in which universal education is supported is through federal and state governments covering the cost of free public education. Of course, the way this plays out in terms of school budgets and taxes makes this an often-contested topic on the national, state, and community levels.
A precedent for universal access to education in the United States was set with the 1972 U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia’s decision in Mills v. Board of Education of the District of Columbia. This case was brought on behalf of seven school-age children with special needs who argued that the school board was denying their access to free public education. The school board maintained that the children’s “exceptional” needs, which included intellectual disabilities, precluded their right to be educated for free in a public school setting. The board argued that the cost of educating these children would be too expensive and that the children would therefore have to remain at home without access to education.
This case was resolved in a hearing without any trial. The judge, Joseph Cornelius Waddy, upheld the students’ right to education, finding that they were to be given either public education services or private education paid for by the Washington, D.C., board of education. He noted that
Constitutional rights must be afforded citizens despite the greater expense involved … the District of Columbia’s interest in educating the excluded children clearly must outweigh its interest in preserving its financial resources. … The inadequacies of the District of Columbia Public School System whether occasioned by insufficient funding or administrative inefficiency, certainly cannot be permitted to bear more heavily on the “exceptional” or handicapped child than on the normal child (Mills v. Board of Education 1972).
Today, the optimal way to include students with disabilities in standard classrooms is still being researched and debated. “Inclusion” is a method that involves complete immersion in a standard classroom, whereas “mainstreaming” balances time in a special-needs classroom with standard classroom participation. There continues to be social debate surrounding how to implement the ideal of universal access to education.
9.2 Theoretical Perspectives on Education
Learning Objectives
- Define manifest and latent functions of education
- Explain and discuss how functionalism, conflict theory, feminism, and interactionism view issues of education
While it is clear that education plays an integral role in individuals’ lives as well as society as a whole, sociologists view that role from many diverse points of view. Functionalists believe that education equips people to perform different functional roles in society. Conflict theorists view education as a means of widening the gap in social inequality. Feminist theorists point to evidence that sexism in education continues to prevent women from achieving a full measure of social equality. Symbolic interactionists study the dynamics of the classroom, the interactions between students and teachers, and how those affect everyday life. In this section, you will learn about each of these perspectives.
Functionalism
Functionalists view education as one of the more important social institutions in a society. They contend that education contributes two kinds of functions: manifest (or primary) functions, which are the intended and visible functions of education; and latent (or secondary) functions, which are the hidden and unintended functions.
Manifest Functions
There are several major manifest functions associated with education. The first is socialization. Beginning in preschool and kindergarten, students are taught to practice various societal roles. The French sociologist Émile Durkheim (1858–1917), who established the academic discipline of sociology, characterized schools as “socialization agencies that teach children how to get along with others and prepare them for adult economic roles” (Durkheim 1898). Indeed, it seems that schools have taken on this responsibility in full.
This socialization also involves learning the rules and norms of the society as a whole. In the early days of compulsory education, students learned the dominant culture. Today, since the culture of the United States is increasingly diverse, students may learn a variety of cultural norms, not only that of the dominant culture.
School systems in the United States also transmit the core values of the nation through manifest functions like social control. One of the roles of schools is to teach students conformity to law and respect for authority. Obviously, such respect, given to teachers and administrators, will help a student navigate the school environment. This function also prepares students to enter the workplace and the world at large, where they will continue to be subject to people who have authority over them. Fulfillment of this function rests primarily with classroom teachers and instructors who are with students all day.

Education also provides one of the major methods used by people for upward social mobility. This function is referred to as social placement. College and graduate schools are viewed as vehicles for moving students closer to careers that will give them the financial freedom and security they seek. As a result, college students are often more motivated to study areas that they believe will be advantageous on the social ladder. A student might value business courses over a class in Victorian poetry because she sees business classes as a stronger vehicle for financial success.
Latent Functions
Education also fulfills latent functions. As you well know, much goes on in a school that has little to do with formal education. For example, you might notice an attractive fellow student when he gives a particularly interesting answer in class—catching up with him and making a date speaks to the latent function of courtship fulfilled by exposure to a peer group in the educational setting.
The educational setting introduces students to social networks that might last for years and can help people find jobs after their schooling is complete. Of course, with social media such as Facebook and LinkedIn, these networks are easier than ever to maintain. Another latent function is the ability to work with others in small groups, a skill that is transferable to a workplace and that might not be learned in a homeschool setting.
The educational system, especially as experienced on university campuses, has traditionally provided a place for students to learn about various social issues. There is ample opportunity for social and political advocacy, as well as the ability to develop tolerance for the many views represented on campus. In 2011, the Occupy Wall Street movement swept across college campuses all over the United States, leading to demonstrations in which diverse groups of students were unified with the purpose of changing the political climate of the country.
| Manifest Functions: Openly stated functions with intended goals | Latent Functions: Hidden, unstated functions with sometimes unintended consequences |
|---|---|
| Socialization | Courtship |
| Transmission of culture | Social networks |
| Social control | Group work |
| Social placement | Creation of generation gap |
| Cultural innovation | Political and social integration |
Functionalists recognize other ways that schools educate and enculturate students. One of the most important U.S. values students in the United States learn is that of individualism—the valuing of the individual over the value of groups or society as a whole. In countries such as Japan and China, where the good of the group is valued over the rights of the individual, students do not learn as they do in the United States that the highest rewards go to the “best” individual in academics as well as athletics. One of the roles of schools in the United States is fostering self-esteem; conversely, schools in Japan focus on fostering social esteem—the honoring of the group over the individual.
In the United States, schools also fill the role of preparing students for competition in life. Obviously, athletics foster a competitive nature, but even in the classroom students compete against one another academically. Schools additionally fill the role of teaching patriotism. Students recite the Pledge of Allegiance each morning and take history classes where they learn about national heroes and the nation’s past.

Another role of schools, according to functionalist theory, is that of sorting, or classifying students based on academic merit or potential. The most capable students are identified early in schools through testing and classroom achievements. Such students are placed in accelerated programs in anticipation of successful college attendance.
Functionalists also contend that school, particularly in recent years, is taking over some of the functions that were traditionally undertaken by family. Society relies on schools to teach about human sexuality as well as basic skills such as budgeting and job applications—topics that at one time were addressed by the family.
Conflict Theory
Conflict theorists do not believe that public schools reduce social inequality. Rather, they believe that the educational system reinforces and perpetuates social inequalities that arise from differences in class, gender, race, and ethnicity. Where functionalists see education as serving a beneficial role, conflict theorists view it more negatively. To them, educational systems preserve the status quo and push people of lower status into obedience.

The fulfillment of one’s education is closely linked to social class. Students of low socioeconomic status are generally not afforded the same opportunities as students of higher status, no matter how great their academic ability or desire to learn. Picture a student from a working-class home who wants to do well in school. On a Monday, he’s assigned a paper that’s due Friday. On Monday evening, he has to babysit his younger sister while his divorced mother works. Tuesday and Wednesday, he works stocking shelves after school until 10:00 p.m. By Thursday, the only day he might have available to work on that assignment, he’s so exhausted he can’t bring himself to start the paper. His mother, though she’d like to help him, is so tired herself that she isn’t able to give him the encouragement or support he needs. And since English is her second language, she has difficulty with some of his educational materials. They also lack a computer and printer at home, which most of his classmates have, so they have to rely on the public library or school system for access to technology. As this story shows, many students from working-class families have to contend with helping out at home, contributing financially to the family, poor study environments, and a lack of support from their families. This is a difficult match with education systems that adhere to a traditional curriculum that is more easily understood and completed by students of higher social classes.
Such a situation leads to social class reproduction, extensively studied by French sociologist Pierre Bourdieu. He researched how cultural capital, or cultural knowledge that serves (metaphorically) as currency that helps us navigate a culture, alters the experiences and opportunities available to French students from different social classes. Members of the upper and middle classes have more cultural capital than do families of lower-class status. As a result, the educational system maintains a cycle in which the dominant culture’s values are rewarded. Instruction and tests cater to the dominant culture and leave others struggling to identify with values and competencies outside their social class. For example, there has been a great deal of discussion over what standardized tests such as the SAT truly measure. Many argue that the tests group students by cultural ability rather than by natural intelligence.
The cycle of rewarding those who possess cultural capital is found in formal educational curricula as well as in the hidden curriculum, which refers to the type of nonacademic knowledge that students learn through informal learning and cultural transmission. This hidden curriculum reinforces the positions of those with higher cultural capital and serves to bestow status unequally.
Conflict theorists point to tracking, a formalized sorting system that places students on “tracks” (advanced versus low achievers) that perpetuate inequalities. While educators may believe that students do better in tracked classes because they are with students of similar ability and may have access to more individual attention from teachers, conflict theorists feel that tracking leads to self-fulfilling prophecies in which students live up (or down) to teacher and societal expectations (Education Week 2004).
To conflict theorists, schools play the role of training working-class students to accept and retain their position as lower members of society. They argue that this role is fulfilled through the disparity of resources available to students in richer and poorer neighborhoods as well as through testing (Lauen and Tyson 2008).
IQ tests have been attacked for being biased—for testing cultural knowledge rather than actual intelligence. For example, a test item may ask students what instruments belong in an orchestra. To correctly answer this question requires certain cultural knowledge—knowledge most often held by more affluent people who typically have more exposure to orchestral music. Though experts in testing claim that bias has been eliminated from tests, conflict theorists maintain that this is impossible. These tests, to conflict theorists, are another way in which education does not provide opportunities, but instead maintains an established configuration of power.
Feminist Theory
Feminist theory aims to understand the mechanisms and roots of gender inequality in education, as well as their societal repercussions. Like many other institutions of society, educational systems are characterized by unequal treatment and opportunity for women. Almost two-thirds of the world’s 862 million illiterate people are women, and the illiteracy rate among women is expected to increase in many regions, especially in several African and Asian countries (UNESCO 2005; World Bank 2007).
Women in the United States have been relatively late, historically speaking, to be granted entry to the public university system. In fact, it wasn’t until the establishment of Title IX of the Education Amendments in 1972 that discriminating on the basis of sex in U.S. education programs became illegal. In the United States, there is also a post-education gender disparity between what male and female college graduates earn. A study released in May 2011 showed that, among men and women who graduated from college between 2006 and 2010, men out-earned women by an average of more than $5,000 each year. First-year job earnings for men averaged $33,150; for women, the average was $28,000 (Godofsky, Zukin, and van Horn 2011). Similar trends are seen among salaries of professionals in virtually all industries.
When women face limited opportunities for education, their capacity to achieve equal rights, including financial independence, is limited. Feminist theory seeks to promote women’s rights to equal education (and its resultant benefits) across the world.
Sociology in the Real World
Grade Inflation: When Is an A Really a C?
Consider a large-city newspaper publisher. Ten years ago, when culling résumés for an entry-level copywriter, they were well assured that if they selected a grad with a GPA of 3.7 or higher, they’d have someone with the writing skills to contribute to the workplace on day one. But over the last few years, they’ve noticed that A-level students don’t have the competency evident in the past. More and more, they find themselves in the position of educating new hires in abilities that, in the past, had been mastered during their education.
This story illustrates a growing concern referred to as grade inflation—a term used to describe the observation that the correspondence between letter grades and the achievements they reflect has been changing (in a downward direction) over time. Put simply, what used to be considered C-level, or average, now often earns a student a B or even an A.
Why is this happening? Research on this emerging issue is ongoing, so no one is quite sure yet. Some cite the alleged shift toward a culture that rewards effort instead of product, i.e., the amount of work a student puts in raises the grade, even if the resulting product is poor quality. Another oft-cited contributor is the pressure many of today’s instructors feel to earn positive course evaluations from their students—records that can tie into teacher compensation, award of tenure, or the future career of a young grad teaching entry-level courses. The fact that these reviews are commonly posted online exacerbates this pressure.
Other studies don’t agree that grade inflation exists at all. In any case, the issue is hotly debated, with many being called upon to conduct research to help us better understand and respond to this trend (National Public Radio 2004; Mansfield 2005).
Symbolic Interactionism
Symbolic interactionism sees education as one way that labeling theory is seen in action. A symbolic interactionist might say that this labeling has a direct correlation to those who are in power and those who are labeled. For example, low standardized test scores or poor performance in a particular class often lead to a student who is labeled as a low achiever. Such labels are difficult to “shake off,” which can create a self-fulfilling prophecy (Merton 1968).
In his book High School Confidential, Jeremy Iversen details his experience as a Stanford graduate posing as a student at a California high school. One of the problems he identifies in his research is that of teachers applying labels that students are never able to lose. One teacher told him, without knowing he was a bright graduate of a top university, that he would never amount to anything (Iversen 2006). Iversen obviously didn’t take this teacher’s false assessment to heart. But when an actual seventeen-year-old student hears this from a person with authority over her, it’s no wonder that the student might begin to “live down to” that label.
The labeling with which symbolic interactionists concern themselves extends to the very degrees that symbolize completion of education. Credentialism embodies the emphasis on certificates or degrees to show that a person has a certain skill, has attained a certain level of education, or has met certain job qualifications. These certificates or degrees serve as symbols of what a person has achieved and allow the labeling of that individual.
Indeed, as these examples show, labeling theory can significantly impact a student’s schooling. This is easily seen in the educational setting, as teachers and more powerful social groups within the school dole out labels that are adopted by the entire school population.
9.3 Issues in Education
Learning Objectives
- Identify and discuss historical and contemporary issues in education
As schools strive to fill a variety of roles in their students’ lives, many issues and challenges arise. Students walk a minefield of bullying, violence in schools, the results of declining funding, plus other problems that affect their education. When Americans are asked about their opinion of public education on the Gallup poll each year, reviews are mixed at best (Saad 2008). Schools are no longer merely a place for learning and socializing. With the landmark Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka ruling in 1954, schools became a repository of much political and legal action that is at the heart of several issues in education.
Equal Education
Until the 1954 Brown v. Board of Education ruling, schools had operated under the precedent set by Plessy v. Ferguson in 1896, which allowed racial segregation in schools and private businesses (the case dealt specifically with railroads) and introduced the much maligned phrase “separate but equal” into the U.S. lexicon. The 1954 Brown v. Board decision overruled this, declaring that state laws that had established separate schools for black and white students were, in fact, unequal and unconstitutional.
While the ruling paved the way toward civil rights, it was also met with contention in many communities. In Arkansas in 1957, the governor mobilized the state National Guard to prevent black students from entering Little Rock Central High School. President Eisenhower, in response, sent members of the 101st Airborne Division from Kentucky to uphold the students’ right to enter the school. In 1963, almost ten years after the ruling, Governor George Wallace of Alabama used his own body to block two black students from entering the auditorium at the University of Alabama to enroll in the school. Wallace’s desperate attempt to uphold his policy of “segregation now, segregation tomorrow, segregation forever,” stated during his 1963 inauguration (PBS 2000) became known as the “Stand in the Schoolhouse Door.” He refused to grant entry to the students until a general from the Alabama National Guard arrived on President Kennedy’s order.

Presently, students of all races and ethnicities are permitted into schools, but there remains a troubling gap in the equality of education they receive. The long-term socially embedded effects of racism—and other discrimination and disadvantage—have left a residual mark of inequality in the nation’s education system. Students from wealthy families and those of lower socioeconomic status do not receive the same opportunities.
Today’s public schools, at least in theory, are positioned to help remedy those gaps. Predicated on the notion of universal access, this system is mandated to accept and retain all students regardless of race, religion, social class, and the like. Moreover, public schools are held accountable to equitable per-student spending (Resnick 2004). Private schools, usually only accessible to students from high-income families, and schools in more affluent areas generally enjoy access to greater resources and better opportunities. In fact, some of the key predictors for student performance include socioeconomic status and family background. Children from families of lower socioeconomic status often enter school with learning deficits they struggle to overcome throughout their educational tenure. These patterns, uncovered in the landmark Coleman Report of 1966, are still highly relevant today, as sociologists still generally agree that there is a great divide in the performance of white students from affluent backgrounds and their nonwhite, less affluent, counterparts (Coleman 1966).
Head Start
The findings in the Coleman Report were so powerful that they brought about two major changes to education in the United States. The federal Head Start program, which is still active and successful today, was developed to give low-income students an opportunity to make up the preschool deficit discussed in Coleman’s findings. The program provides academic-centered preschool to students of low socioeconomic status.
Busing
The second major change brought about after the release of the Coleman Report was less successful than the Head Start program and has been the subject of a great deal of controversy. With the goal of further desegregating education, courts across the United States ordered some school districts to begin a program that became known as “busing.” This program involved bringing students to schools outside their neighborhoods (and therefore schools they would not normally have the opportunity to attend) to bring racial diversity into balance. This practice was met with a great deal of public resistance from people on both sides dissatisfied with white students traveling to inner city schools and minority students being transported to schools in the suburbs.
No Child Left Behind
In 2001, the Bush administration passed the No Child Left Behind Act, which requires states to test students in designated grades. The results of those tests determine eligibility to receive federal funding. Schools that do not meet the standards set by the Act run the risk of having their funding cut. Sociologists and teachers alike have contended that the impact of the No Child Left Behind Act is far more negative than positive, arguing that a “one size fits all” concept cannot apply to education.
Teaching to the Test
The funding tie-in of the No Child Left Behind Act has led to the social phenomenon commonly called “teaching to the test,” which describes when a curriculum focuses on equipping students to succeed on standardized tests, to the detriment of broader educational goals and concepts of learning. At issue are two approaches to classroom education: the notion that teachers impart knowledge that students are obligated to absorb, versus the concept of student-centered learning that seeks to teach children not facts but problem-solving abilities and learning skills. Both types of learning have been valued in the U.S. school system. The former, to critics of “teaching to the test,” only equips students to regurgitate facts, while the latter, to proponents of the other camp, fosters lifelong learning and transferable work skills.
Bilingual Education
New issues of inequality have entered the national conversation in recent years with the issue of bilingual education, which attempts to give equal opportunity to minority students through offering instruction in languages other than English. Though it is actually an old issue (bilingual education was federally mandated in 1968), it remains one of hot debate. Supporters of bilingual education argue that all students deserve equal opportunities in education—opportunities some students cannot access without instruction in their first language. On the other side, those who oppose bilingual education often point to the need for English fluency in everyday life and in the professional world.
Common Core
“The Common Core is a set of high-quality academic standards in mathematics and English language arts/literacy (ELA). These learning goals outline what a student should know and be able to do at the end of each grade.” Included in the list of standards is that they be evidence-based, clear, understandable, consistent, aligned with college and career expectations, include the application of knowledge through higher-order thinking skills, and are informed by other top-performing countries (The Common Core State Standards Initiative 2014).
The primary controversy over the Common Core State Standards, or simply the Common Core, from the standpoint of teachers, parents and students, and even administrators, is not so much the standards themselves, but the assessment process and the high stakes involved. Both the national teacher’s unions in the United States initially agreed to them, at least on principle. But both have since become strong voices of criticism. Given a public education system that is primarily funded by local property taxes, rather than by state and federal funds distributed to all schools equally, we see a wide disparity of funding per student throughout the country, with the result that students in schools funded by well-to-do communities are clearly better off than those who are not, sometimes only a few miles away.
What gets measured?
Much has been said about the quality, usefulness, and even accuracy of many of the standardized tests. Math questions have been found to be misleading and poorly phrased; for instance, “Tyler made 36 total snowfalls with is a multiple of how triangular snowflakes he made. How many triangular snowflakes could he have made?”
Some of the essays had questions that made little sense to the students. One notable test question in 2014 that dominated the Internet for a time was about “The Hare and the Pineapple.” This was a parody on the well-known Aesop fable of the race between the hare and the tortoise that appeared on a standardized test for New York’s eighth-grade exam, with the tortoise changed into a talking pineapple. With the pineapple clearly unable to participate in a race and the hare winning, “the animals ate the pineapple.” “Moral: Pineapples don’t have sleeves.”
At the end of the story, questions for the student included, “Which animal spoke the wisest words?” and “Why did the animals eat the talking fruit?”
Charter Schools
Charter schools are self-governing public schools that have signed agreements with state governments to improve students when poor performance is revealed on tests required by the No Child Left Behind Act. While such schools receive public money, they are not subject to the same rules that apply to regular public schools. In return, they make agreements to achieve specific results. Charter schools, as part of the public education system, are free to attend, and are accessible via lottery when there are more students seeking enrollment than there are spots available at the school. Some charter schools specialize in certain fields, such as the arts or science, while others are more generalized.
Sociology in the Real World
Money as Motivation in Charter Schools
Public school teachers typically find stability, comprehensive benefits packages, and long-term job security. In 2011, one charter school in New York City set out to learn if teachers would give up those protections if it meant an opportunity to make much more money than the typical teacher’s salary. The Equity Project is a privately run charter school that offered teachers positions paying $125,000 per year (more than twice the average salary for teachers). The school’s founder and principal, Zeke Vanderhoek, explained that this allows him to attract the best and brightest teachers to his school—to decide whom he hires and how much they are paid—and build a school where “every teacher is a great teacher” (CBS News 2011). He sees attracting top teachers as a direct road to student achievement. A nationwide talent search resulted in the submission of thousands of applications. The final round of interviews consisted of a day-long trial run. The school looks for teachers who can show evidence of student growth and achievement. They also must be highly engaging.
The majority of students at the school are African American and Hispanic, from poor families, and reading below grade level. The school faces the challenge faced by schools all over the United States: getting poor, disadvantaged students to perform at the same level as their more affluent counterparts. Vanderhoek believes his team of dream teachers can help students close their learning gaps by several grade levels within one year.
This is not an affluent school. It is publicly funded and classes are held in trailers. Most of the school’s budget goes into the teachers’ salaries. There are no reading or math aides; those roles are filled by the regular classroom teachers.
The experiment may be working. Students who were asked how they feel about their education at The Equity Project said that their teachers care if they succeed and give them the attention they need to achieve at high levels. They cite the feeling that their teachers believe in them as a major reason for liking school for the first time.
Of course, with the high salary comes high risk. Most public schools offer contracts to teachers. Those contracts guarantee job security. But The Equity Project is an at-will employer. Those who don’t meet the standards set by the school will lose their jobs. Vanderhoek does not believe in teacher tenure, which he feels gives teachers “a job for life no matter how they perform” (CBS News 2011). With a teaching staff of roughly fifteen, he terminated two teachers after the first year. In comparison, in New York City as a whole, only seven teachers out of 55,000 with tenure have been terminated for poor performance.
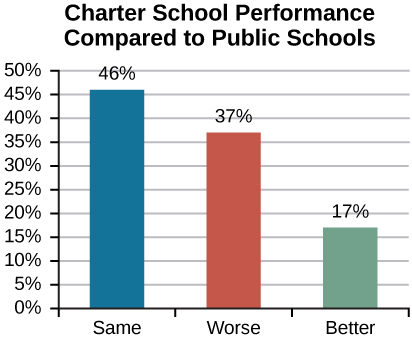
One of those two teachers who was let go said she was relieved, citing eighty- to ninety-hour work weeks and a decline in the quality of her family life. Meanwhile, there is some question as to whether the model is working. On one hand, there are individual success stories, such as a student whose reading skills increased two grade levels in a single year. On the other, there is the fact that on the state math and reading exams taken by all fifth graders, the Equity Project students remained out-scored by other district schools (CBS News 2011). Do charter schools actually work? A Stanford CREDO study in 2009 found “there is a wide variance in the quality of the nation’s several thousand charter schools with, in the aggregate, students in charter schools not faring as well as students in traditional public schools” (CREDO 2009).
Teacher Training
Schools face an issue of teacher effectiveness, in that most high school teachers perceive students as being prepared for college, while most college professors do not see those same students as prepared for the rigors of collegiate study. Some feel that this is due to teachers being unprepared to teach. Many teachers in the United States teach subject matter that is outside their own field of study. This is not the case in many European and Asian countries. Only eight percent of United States fourth-grade math teachers majored or minored in math, compared with 48 percent in Singapore. Further, students in disadvantaged American schools are 77 percent more likely to be educated by a teacher who didn’t specialize in the subject matter than students who attend schools in affluent neighborhoods (Holt, McGrath, and Seastrom 2006).
Social Promotion
Social promotion is another issue identified by sociologists. This is the concept of passing students to the next grade regardless of their meeting standards for that grade. Critics of this practice argue that students should never move to the next grade if they have not mastered the skills required to “graduate” from the previous grade. Proponents of the practice question what a school is to do with a student who is three to four years older than other students in his or her grade, saying this creates more issues than the practice of social promotion.
Affirmative Action
Affirmative action has been a subject of debate, primarily as it relates to the admittance of college students. Opponents suggest that, under affirmative action, minority students are given greater weighted priorities for admittance. Supporters of affirmative action point to the way in which it grants opportunities to students who are traditionally done a disservice in the college admission process.
Rising Student Loan Debt
In a growing concern, the amount of college loan debt that students are taking on is creating a new social challenge. As of 2010, the debts of students with student loans averaged $25,250 upon graduation, leaving students hard-pressed to repay their education while earning entry-level wages, even at the professional level (Lewin 2011). With the increase in unemployment since the 2008 recession, jobs are scarce and make this burden more pronounced. As recent grads find themselves unable to meet their financial obligations, all of society is affected.
Homeschooling
Homeschooling refers to children being educated in their own homes, typically by a parent, instead of in a traditional public or private school system. Proponents of this type of education argue that it provides an outstanding opportunity for student-centered learning while circumventing problems that plague today’s education system. Opponents counter that homeschooled children miss out on the opportunity for social development that occurs in standard classroom environments and school settings.
Proponents say that parents know their own children better than anyone else and are thus best equipped to teach them. Those on the other side of the debate assert that childhood education is a complex task and requires the degree teachers spend four years earning. After all, they argue, a parent may know her child’s body better than anyone, yet she seeks out a doctor for her child’s medical treatment. Just as a doctor is a trained medical expert, teachers are trained education experts.
The National Center for Education Statistics shows that the quality of the national education system isn’t the only major concern of homeschoolers. While nearly half cite their reason for homeschooling as the belief that they can give their child a better education than the school system can, just under 40 percent choose homeschooling for “religious reasons” (NCES 2008).
To date, researchers have not found consensus in studies evaluating the success, or lack thereof, of homeschooling.
Key Terms
- credentialism
- the emphasis on certificates or degrees to show that a person has a certain skill, has attained a certain level of education, or has met certain job qualifications
- cultural capital
- cultural knowledge that serves (metaphorically) as currency to help one navigate a culture
- cultural transmission
- the way people come to learn the values, beliefs, and social norms of their culture
- education
- a social institution through which a society’s children are taught basic academic knowledge, learning skills, and cultural norms
- formal education
- the learning of academic facts and concepts
- grade inflation
- the idea that the achievement level associated with an A today is notably lower than the achievement level associated with A-level work a few decades ago
- Head Start program
- a federal program that provides academically focused preschool to students of low socioeconomic status
- hidden curriculum
- the type of nonacademic knowledge that people learn through informal learning and cultural transmission
- informal education
- education that involves learning about cultural values, norms, and expected behaviors through participation in a society
- No Child Left Behind Act
- an act that requires states to test students in prescribed grades, with the results of those tests determining eligibility to receive federal funding
- social placement
- the use of education to improve one’s social standing
- sorting
- classifying students based on academic merit or potential
- tracking
- a formalized sorting system that places students on “tracks” (advanced, low achievers) that perpetuate inequalities
- universal access
- the equal ability of all people to participate in an education system
Section Summary
9.1 Education around the World
Educational systems around the world have many differences, though the same factors—including resources and money—affect every educational system. Educational distribution is a major issue in many nations, including in the United States, where the amount of money spent per student varies greatly by state. Education happens through both formal and informal systems; both foster cultural transmission. Universal access to education is a worldwide concern.
9.2 Theoretical Perspectives on Education
The major sociological theories offer insight into how we understand education. Functionalists view education as an important social institution that contributes both manifest and latent functions. Functionalists see education as serving the needs of society by preparing students for later roles, or functions, in society. Conflict theorists see schools as a means for perpetuating class, racial-ethnic, and gender inequalities. In the same vein, feminist theory focuses specifically on the mechanisms and roots of gender inequality in education. The theory of symbolic interactionism focuses on education as a means for labeling individuals.
9.3 Issues in Education
As schools continue to fill many roles in the lives of students, challenges arise. Historical issues include the racial desegregation of schools, marked by the 1954 Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka ruling. In today’s diverse educational landscape, socioeconomic status and diversity remain at the heart of issues in education, with programs such as the Head Start program attempting to give students equal footing. Other educational issues that impact society include charter schools, teaching to the test, student loan debt, and homeschooling.
One hot topic is the Common Core State Standards, or the Common Core. The primary controversy over the Common Core, from the standpoint of teachers, parents, students, and even administrators, is not so much the standards themselves but the assessment process and the high stakes involved.
Section Quizzes
9.1 Education around the World
1. What are the major factors that affect education systems throughout the world?
- Resources and money
- Student interest
- Teacher interest
- Transportation
2. What do nations that are top-ranked in science and math have in common?
- They are all in Asia.
- They recruit top teachers.
- They spend more money per student.
- They use cutting-edge technology in classrooms.
3. Informal education _________________.
- describes when students teach their peers
- refers to the learning of cultural norms
- only takes place at home
- relies on a planned instructional process
4. Learning from classmates that most students buy lunch on Fridays is an example of ________.
- cultural transmission
- educational access
- formal education
- informal education
5. The 1972 case Mills v. Board of Education of the District of Columbia set a precedent for __________.
- access to education
- average spending on students
- desegregation of schools
- teacher salary
9.2 Theoretical Perspectives on Education
6. Which of the following is not a manifest function of education?
- Cultural innovation
- Courtship
- Social placement
- Socialization
7. Because she plans on achieving success in marketing, Tammie is taking courses on managing social media. This is an example of ________.
- cultural innovation
- social control
- social placement
- socialization
8. Which theory of education focuses on the ways in which education maintains the status quo?
- Conflict theory
- Feminist theory
- Functionalist theory
- Symbolic interactionism
9. Which theory of education focuses on the labels acquired through the educational process?
- Conflict theory
- Feminist theory
- Functionalist theory
- Symbolic interactionism
10. What term describes the assignment of students to specific education programs and classes on the basis of test scores, previous grades, or perceived ability?
- Hidden curriculum
- Labeling
- Self-fulfilling prophecy
- Tracking
11. Functionalist theory sees education as serving the needs of _________.
- families
- society
- the individual
- all of the above
12. Rewarding students for meeting deadlines and respecting authority figures is an example of ________.
- a latent function
- a manifest function
- informal education
- transmission of moral education
13. What term describes the separation of students based on merit?
- Cultural transmission
- Social control
- Sorting
- Hidden curriculum
14. Conflict theorists see sorting as a way to ________.
- challenge gifted students
- perpetuate divisions of socioeconomic status
- help students who need additional support
- teach respect for authority
15. Conflict theorists see IQ tests as being biased. Why?
- They are scored in a way that is subject to human error.
- They do not give children with learning disabilities a fair chance to demonstrate their true intelligence.
- They don’t involve enough test items to cover multiple intelligences.
- They reward affluent students with questions that assume knowledge associated with upper-class culture.
9.3 Issues in Education
16. Plessy v. Ferguson set the precedent that _____________.
- racial segregation in schools was allowed
- separate schools for black and white students were unconstitutional
- students do not have a right to free speech in public schools
- students have a right to free speech in public schools
17. Public schools must guarantee that ___________.
- all students graduate from high school
- all students receive an equal education
- per-student spending is equitable
- the amount spent on each student is equal to that spent regionally
18. Key predictors for student success include ____________.
- how many school-age siblings the student has
- socioeconomic status and family background
- the age of the student when she or he enters kindergarten
- how many students attend the school
19. Allowing a student to move to the next grade regardless of whether or not they have met the requirements for that grade is called ____________.
- affirmative action
- social control
- social promotion
- socialization
Short Answer
9.1 Education around the World
9.2 Theoretical Perspectives on Education
9.3 Issues in Education
Further Research
9.1 Education around the World
Though it’s a struggle, education is continually being improved in the developing world. To learn how educational programs are being fostered worldwide, explore the Education section of the Center for Global Development’s website: http://openstax.org/l/center_global_development
9.2 Theoretical Perspectives on Education
Can tracking actually improve learning? This 2009 article from Education Next explores the debate with evidence from Kenya. http://openstax.org/l/education_next
The National Center for Fair & Open Testing (FairTest) is committed to ending the bias and other flaws seen in standardized testing. Their mission is to ensure that students, teachers, and schools are evaluated fairly. You can learn more about their mission, as well as the latest in news on test bias and fairness, at their website: http://openstax.org/l/fair_test
9.3 Issues in Education
Whether or not students in public schools are entitled to free speech is a subject of much debate. In the public school system, there can be a clash between the need for a safe learning environment and the guarantee of free speech granted to U.S. citizens. You can learn more about this complicated issue at the Center for Public Education. http://openstax.org/l/center_public_education
References
Introduction to Education
Leonhardt, David. 2014. “Is College Worth It? Clearly, New Data Say.” The New York Times. Retrieved December 12, 2014. (http://www.nytimes.com/2014/05/27/upshot/is-college-worth-it-clearly-new-data-say.html?_r=0&abt=0002&abg=1).
Lorin, Janet, and Jeanna Smialek. 2014. “College Graduates Struggle to Find Employment Worth a Degree.” Bloomberg. Retrieved December 12, 2014. (http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2014-06-05/college-graduates-struggle-to-find-employment-worth-a-degree.html).
New Oxford English Dictionary. “contradiction.” New Oxford English Dictionary. Retrieved December 12, 2014. (http://www.oxforddictionaries.com/us/definition/american_english/contradiction?searchDictCode=all).
Plumer, Brad. 2013. “Only 27 percent of college graduates have a job related to their major.” The Washington Post. Retrieved December 12, 2014. (http://www.washingtonpost.com/blogs/wonkblog/wp/2013/05/20/only-27-percent-of-college-grads-have-a-job-related-to-their-major/).
Simon, R David. 1995. Social Problems and the Sociological Imagination: A Paradigm for Analysis. New York: McGraw-Hill Education.
9.1 Education around the World
Darling-Hammond, Linda. 2010. “What We Can Learn from Finland’s Successful School Reform.” NEA Today Magazine. Retrieved December 12, 2014. (http://www.nea.org/home/40991.htm).
Durkheim, Émile. 1898 [1956]. Education and Sociology. New York: Free Press.
Gross-Loh, Christine. 2014. “Finnish Education Chief: ‘We Created a School System Based on Equality.'” The Atlantic. Retrieved December 12, 2014. (http://www.theatlantic.com/education/archive/2014/03/finnish-education-chief-we-created-a-school-system-based-on-equality/284427/?single_page=true).
Mills v. Board of Education, 348 DC 866 (1972).
National Center for Public Policy and Higher Education. 2006. Measuring UP: The National Report Card on Higher Education. Retrieved December 9, 2011 (http://www.eric.ed.gov/PDFS/ED493360.pdf).
National Public Radio. 2010. “Study Confirms U.S. Falling Behind in Education.” All Things Considered, December 10. Retrieved December 9, 2011 (https://www.npr.org/2010/12/07/131884477/Study-Confirms-U-S-Falling-Behind-In-Education).
Pellissier, Hank. 2010. “High Test Scores, Higher Expectations, and Presidential Hype.” Great Schools. Retrieved January 17, 2012 (http://www.greatschools.org/students/academic-skills/2427-South-Korean-schools.gs).
Rampell, Catherine. 2009. “Of All States, New York’s Schools Spend Most Money Per Pupil.” Economix. Retrieved December 15, 2011 (http://economix.blogs.nytimes.com/2009/07/27/of-all-states-new-york-schools-spend-most-money-per-pupil/).
U.S. Census Bureau. 2014. “Public Education Finances 2012.” Retrieved December 12, 2014. (http://www2.census.gov/govs/school/12f33pub.pdf).
World Bank. 2011. “Education in Afghanistan.” Retrieved December 14, 2011 (http://go.worldbank.org/80UMV47QB0).
9.2 Theoretical Perspectives on Education
Education Week. 2004. “Tracking.” Education Week, August 4. Retrieved February 24, 2012 (http://www.edweek.org/ew/issues/tracking/).
Godofsky, Jessica, Cliff Zukin, and Carl Van Horn. 2011. Unfulfilled Expectations: Recent College Graduates Struggle in a Troubled Economy. New Brunswick, NJ: Rutgers University.
Iversen, Jeremy. 2006. High School Confidential. New York: Atria.
Lauen, Douglas Lee and Karolyn Tyson. 2008. “Perspectives from the Disciplines: Sociological Contribution to Education Policy Research and Debate.” AREA Handbook on Education Policy Research. Retrieved February 24, 2012.
National Public Radio. 2004. “Princeton Takes Steps to Fight ‘Grade Inflation.’” Day to Day, April 28.
Mansfield, Harvey C. 2001. “Grade Inflation: It’s Time to Face the Facts.” The Chronicle of Higher Education 47(30): B24.
Merton, Robert K. 1968. Social Theory and Social Structure. New York: Free Press.
UNESCO. 2005. Towards Knowledge Societies: UNESCO World Report. Paris: UNESCO Publishing.
World Bank. 2007. World Development Report. Washington, DC: World Bank.
9.3 Issues in Education
CBS News. 2011. “NYC Charter School’s $125,000 Experiment.” CBS, March 10. Retrieved December 14, 2011 (http://www.cbsnews.com/stories/2011/03/10/60minutes/main20041733.shtml).
Chapman, Ben, and Rachel Monahan. 2012. “Talking Pineapple Question on State Exam Stumps…Everyone!” Retrieved December 12, 2014. (http://www.nydailynews.com/new-york/talking-pineapple-question-state-exam-stumps-article-1.1064657).
Coleman, James S. 1966. Equality of Educational Opportunity Study. Washington, DC: United States Department of Health, Education, and Welfare.
The Common Core State Standards Initiative. 2014. “About the Standards.” Retrieved December 12, 2014. (http://www.corestandards.org/about-the-standards/).
CREDO, Stanford University. “Multiple Choice: Charter School Performance in 16 States,” published in 2009. Accessed on December 31, 2014 (http://credo.stanford.edu/reports/MULTIPLE_CHOICE_CREDO.pdf).
Holt, Emily W., Daniel J. McGrath, and Marily M. Seastrom. 2006. “Qualifications of Public Secondary School History Teachers, 1999–2001.” Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics.
Lewin, Tamar. 2011. “College Graduates Debt Burden Grew, Yet Again, in 2010.” The New York Times, November 2. Retrieved January 17, 2012 (http://www.nytimes.com/2011/11/03/education/average-student-loan-debt-grew-by-5-percent-in-2010.html).
Morse et al. v. Frederick, 439 F. 3d 1114 (2007).
National Center for Education Statistics. 2008. “1.5 Million Homeschooled Students in the United States in 2007.” Retrieved January 17, 2012 (http://nces.ed.gov/pubs2009/2009030.pdf).
PBS. 2000. Wallace Quotes. Retrieved December 15, 2011 (http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/amex/wallace/sfeature/quotes.html).
Resnick, Michael A. 2004. “Public Education—An American Imperative: Why Public Schools Are Vital to the Well-Being of Our Nation.” Policy Research Brief. Alexandria, VA: National School Boards Association.
Saad, Lydia. 2008. “U.S. Education System Garners Split Reviews.” Gallup. Retrieved January 17, 2012 (http://www.gallup.com/poll/109945/us-education-system-garners-split-reviews.aspx).
Media Attributions
- Introduction-to-Sociology-1655759772_Page_329_Image_0001 © Kevin Dooley/flickr is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Introduction-to-Sociology-1655759772_Page_330_Image_0001 © OpenStax is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Introduction-to-Sociology-1655759772_Page_331_Image_0001 is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Introduction-to-Sociology-1655759772_Page_334_Image_0001 © eyeliam/flickr is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Introduction-to-Sociology-1655759772_Page_335_Image_0001 © Census of Governments: Survey of School System Finances 2012 is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Introduction-to-Sociology-1655759772_Page_337_Image_0001 © Tulane Public Relations/flickr is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Introduction-to-Sociology-1655759772_Page_339_Image_0001 © Jeff Turner/flickr is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Introduction-to-Sociology-1655759772_Page_339_Image_0002 © Thomas Ricker/flickr is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- Introduction-to-Sociology-1655759772_Page_344_Image_0001 © U.S. Army is licensed under a Public Domain license
- Introduction-to-Sociology-1655759772_Page_347_Image_0001

