148 Enthalpy
Paul Flowers; Edward J. Neth; William R. Robinson; Klaus Theopold; and Richard Langley
[latexpage]
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- State the first law of thermodynamics
- Define enthalpy and explain its classification as a state function
- Write and balance thermochemical equations
- Calculate enthalpy changes for various chemical reactions
- Explain Hess’s law and use it to compute reaction enthalpies
Thermochemistry is a branch of chemical thermodynamics, the science that deals with the relationships between heat, work, and other forms of energy in the context of chemical and physical processes. As we concentrate on thermochemistry in this chapter, we need to consider some widely used concepts of thermodynamics.
Substances act as reservoirs of energy, meaning that energy can be added to them or removed from them. Energy is stored in a substance when the kinetic energy of its atoms or molecules is raised. The greater kinetic energy may be in the form of increased translations (travel or straight-line motions), vibrations, or rotations of the atoms or molecules. When thermal energy is lost, the intensities of these motions decrease and the kinetic energy falls. The total of all possible kinds of energy present in a substance is called the internal energy (U), sometimes symbolized as E.
As a system undergoes a change, its internal energy can change, and energy can be transferred from the system to the surroundings, or from the surroundings to the system. Energy is transferred into a system when it absorbs heat (q) from the surroundings or when the surroundings do work (w) on the system. For example, energy is transferred into room-temperature metal wire if it is immersed in hot water (the wire absorbs heat from the water), or if you rapidly bend the wire back and forth (the wire becomes warmer because of the work done on it). Both processes increase the internal energy of the wire, which is reflected in an increase in the wire’s temperature. Conversely, energy is transferred out of a system when heat is lost from the system, or when the system does work on the surroundings.
The relationship between internal energy, heat, and work can be represented by the equation:
as shown in (Figure). This is one version of the first law of thermodynamics, and it shows that the internal energy of a system changes through heat flow into or out of the system (positive q is heat flow in; negative q is heat flow out) or work done on or by the system. The work, w, is positive if it is done on the system and negative if it is done by the system.
0”, “System,” and “Δ U 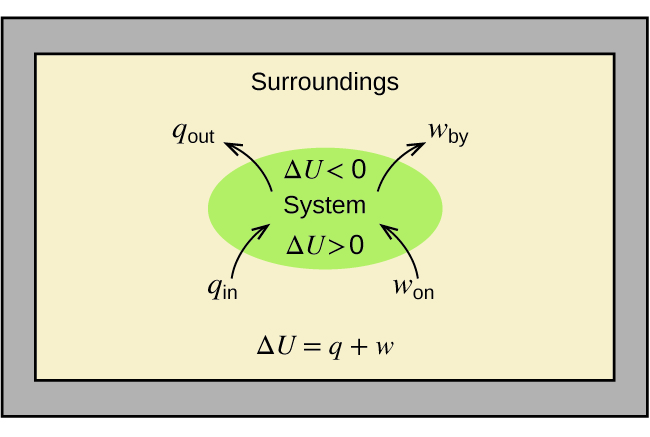 0”, “System,” and “Δ U
0”, “System,” and “Δ U
A type of work called expansion work (or pressure-volume work) occurs when a system pushes back the surroundings against a restraining pressure, or when the surroundings compress the system. An example of this occurs during the operation of an internal combustion engine. The reaction of gasoline and oxygen is exothermic. Some of this energy is given off as heat, and some does work pushing the piston in the cylinder. The substances involved in the reaction are the system, and the engine and the rest of the universe are the surroundings. The system loses energy by both heating and doing work on the surroundings, and its internal energy decreases. (The engine is able to keep the car moving because this process is repeated many times per second while the engine is running.) We will consider how to determine the amount of work involved in a chemical or physical change in the chapter on thermodynamics.
This view of an internal combustion engine illustrates the conversion of energy produced by the exothermic combustion reaction of a fuel such as gasoline into energy of motion.
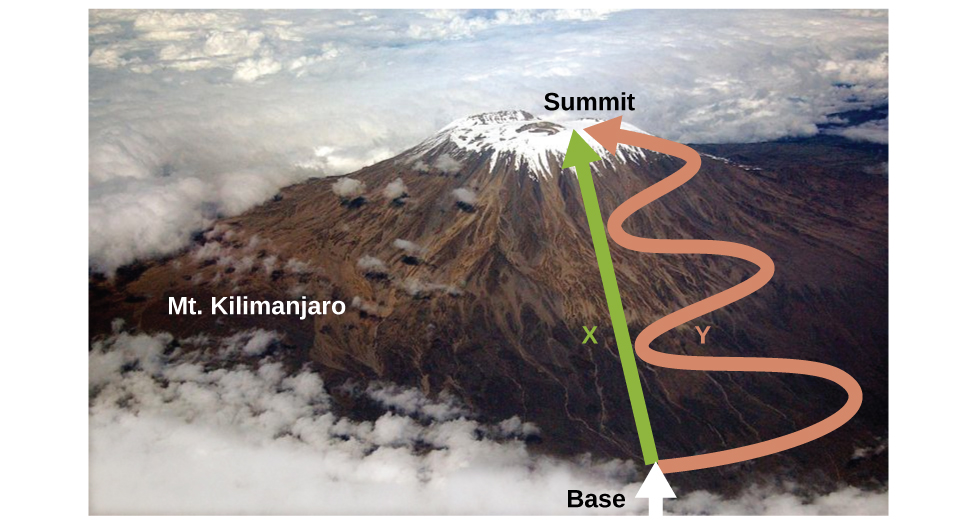
As discussed, the relationship between internal energy, heat, and work can be represented as ΔU = q + w. Internal energy is an example of a state function (or state variable), whereas heat and work are not state functions. The value of a state function depends only on the state that a system is in, and not on how that state is reached. If a quantity is not a state function, then its value does depend on how the state is reached. An example of a state function is altitude or elevation. If you stand on the summit of Mt. Kilimanjaro, you are at an altitude of 5895 m, and it does not matter whether you hiked there or parachuted there. The distance you traveled to the top of Kilimanjaro, however, is not a state function. You could climb to the summit by a direct route or by a more roundabout, circuitous path ((Figure)). The distances traveled would differ (distance is not a state function) but the elevation reached would be the same (altitude is a state function).
Chemists ordinarily use a property known as enthalpy (H) to describe the thermodynamics of chemical and physical processes. Enthalpy is defined as the sum of a system’s internal energy (U) and the mathematical product of its pressure (P) and volume (V):
Enthalpy is also a state function. Enthalpy values for specific substances cannot be measured directly; only enthalpy changes for chemical or physical processes can be determined. For processes that take place at constant pressure (a common condition for many chemical and physical changes), the enthalpy change (ΔH) is:
The mathematical product PΔV represents work (w), namely, expansion or pressure-volume work as noted. By their definitions, the arithmetic signs of ΔV and w will always be opposite:
Substituting this equation and the definition of internal energy into the enthalpy-change equation yields:
where qp is the heat of reaction under conditions of constant pressure.
And so, if a chemical or physical process is carried out at constant pressure with the only work done caused by expansion or contraction, then the heat flow (qp) and enthalpy change (ΔH) for the process are equal.
The heat given off when you operate a Bunsen burner is equal to the enthalpy change of the methane combustion reaction that takes place, since it occurs at the essentially constant pressure of the atmosphere. On the other hand, the heat produced by a reaction measured in a bomb calorimeter ((Figure)) is not equal to ΔH because the closed, constant-volume metal container prevents the pressure from remaining constant (it may increase or decrease if the reaction yields increased or decreased amounts of gaseous species). Chemists usually perform experiments under normal atmospheric conditions, at constant external pressure with q = ΔH, which makes enthalpy the most convenient choice for determining heat changes for chemical reactions.
The following conventions apply when using ΔH:
-
A negative value of an enthalpy change, ΔH < 0, indicates an exothermic reaction; a positive value, ΔH > 0, indicates an endothermic reaction. If the direction of a chemical equation is reversed, the arithmetic sign of its ΔH is changed (a process that is endothermic in one direction is exothermic in the opposite direction).
-
Chemists use a thermochemical equation to represent the changes in both matter and energy. In a thermochemical equation, the enthalpy change of a reaction is shown as a ΔH value following the equation for the reaction. This ΔH value indicates the amount of heat associated with the reaction involving the number of moles of reactants and products as shown in the chemical equation. For example, consider this equation:
\({\text{H}}_{2}\left(g\right)+\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}\frac{1}{2}{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\phantom{\rule{2em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}\text{H}=-286\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\)This equation indicates that when 1 mole of hydrogen gas and \(\frac{1}{2}\) mole of oxygen gas at some temperature and pressure change to 1 mole of liquid water at the same temperature and pressure, 286 kJ of heat are released to the surroundings. If the coefficients of the chemical equation are multiplied by some factor, the enthalpy change must be multiplied by that same factor (ΔH is an extensive property):
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{(two-fold increase in amounts)}\\ 2{\text{H}}_{2}\left(g\right)+{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}2{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}\text{H}=2\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}×\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\left(-286\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\right)=-572\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\\ \left(\text{two-fold decrease in amounts}\right)\\ \frac{1}{2}{\text{H}}_{2}\left(g\right)+\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}\frac{1}{4}{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\frac{1}{2}{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}\text{H}=\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\frac{1}{2}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}×\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\left(-286\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\right)=-143\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\end{array}\) -
The enthalpy change of a reaction depends on the physical states of the reactants and products, so these must be shown. For example, when 1 mole of hydrogen gas and \(\frac{1}{2}\) mole of oxygen gas change to 1 mole of liquid water at the same temperature and pressure, 286 kJ of heat are released. If gaseous water forms, only 242 kJ of heat are released.
\({\text{H}}_{2}\left(g\right)+\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}\frac{1}{2}\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}\text{H}=-242\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\)
Writing Thermochemical EquationsWhen 0.0500 mol of HCl(aq) reacts with 0.0500 mol of NaOH(aq) to form 0.0500 mol of NaCl(aq), 2.9 kJ of heat are produced. Write a balanced thermochemical equation for the reaction of one mole of HCl.?
Solution For the reaction of 0.0500 mol acid (HCl), q = −2.9 kJ. The reactants are provided in stoichiometric amounts (same molar ratio as in the balanced equation), and so the amount of acid may be used to calculate a molar enthalpy change. Since ΔH is an extensive property, it is proportional to the amount of acid neutralized:
The thermochemical equation is then
Check Your Learning When 1.34 g Zn(s) reacts with 60.0 mL of 0.750 M HCl(aq), 3.14 kJ of heat are produced. Determine the enthalpy change per mole of zinc reacting for the reaction:
ΔH = −153 kJ
Be sure to take both stoichiometry and limiting reactants into account when determining the ΔH for a chemical reaction.
Writing Thermochemical Equations A gummy bear contains 2.67 g sucrose, C12H22O11. When it reacts with 7.19 g potassium chlorate, KClO3, 43.7 kJ of heat are produced. Write a thermochemical equation for the reaction of one mole of sucrose:
Solution Unlike the previous example exercise, this one does not involve the reaction of stoichiometric amounts of reactants, and so the limiting reactant must be identified (it limits the yield of the reaction and the amount of thermal energy produced or consumed).
The provided amounts of the two reactants are
The provided molar ratio of perchlorate-to-sucrose is then
The balanced equation indicates 8 mol KClO3 are required for reaction with 1 mol C12H22O11. Since the provided amount of KClO3 is less than the stoichiometric amount, it is the limiting reactant and may be used to compute the enthalpy change:
Because the equation, as written, represents the reaction of 8 mol KClO3, the enthalpy change is
The enthalpy change for this reaction is −5960 kJ, and the thermochemical equation is:
Check Your Learning When 1.42 g of iron reacts with 1.80 g of chlorine, 3.22 g of FeCl2(s) and 8.60 kJ of heat is produced. What is the enthalpy change for the reaction when 1 mole of FeCl2(s) is produced?
ΔH = −338 kJ
Enthalpy changes are typically tabulated for reactions in which both the reactants and products are at the same conditions. A standard state is a commonly accepted set of conditions used as a reference point for the determination of properties under other different conditions. For chemists, the IUPAC standard state refers to materials under a pressure of 1 bar and solutions at 1 M, and does not specify a temperature. Many thermochemical tables list values with a standard state of 1 atm. Because the ΔH of a reaction changes very little with such small changes in pressure (1 bar = 0.987 atm), ΔH values (except for the most precisely measured values) are essentially the same under both sets of standard conditions. We will include a superscripted “o” in the enthalpy change symbol to designate standard state. Since the usual (but not technically standard) temperature is 298.15 K, this temperature will be assumed unless some other temperature is specified. Thus, the symbol \(\left(\text{Δ}H\text{°}\right)\) is used to indicate an enthalpy change for a process occurring under these conditions. (The symbol ΔH is used to indicate an enthalpy change for a reaction occurring under nonstandard conditions.)
The enthalpy changes for many types of chemical and physical processes are available in the reference literature, including those for combustion reactions, phase transitions, and formation reactions. As we discuss these quantities, it is important to pay attention to the extensive nature of enthalpy and enthalpy changes. Since the enthalpy change for a given reaction is proportional to the amounts of substances involved, it may be reported on that basis (i.e., as the ΔH for specific amounts of reactants). However, we often find it more useful to divide one extensive property (ΔH) by another (amount of substance), and report a per-amount intensive value of ΔH, often “normalized” to a per-mole basis. (Note that this is similar to determining the intensive property specific heat from the extensive property heat capacity, as seen previously.)
Standard Enthalpy of Combustion
Standard enthalpy of combustion\(\left(\text{Δ}{H}_{C}^{\text{°}}\right)\) is the enthalpy change when 1 mole of a substance burns (combines vigorously with oxygen) under standard state conditions; it is sometimes called “heat of combustion.” For example, the enthalpy of combustion of ethanol, −1366.8 kJ/mol, is the amount of heat produced when one mole of ethanol undergoes complete combustion at 25 °C and 1 atmosphere pressure, yielding products also at 25 °C and 1 atm.
Enthalpies of combustion for many substances have been measured; a few of these are listed in (Figure). Many readily available substances with large enthalpies of combustion are used as fuels, including hydrogen, carbon (as coal or charcoal), and hydrocarbons (compounds containing only hydrogen and carbon), such as methane, propane, and the major components of gasoline.
| Standard Molar Enthalpies of Combustion | ||
|---|---|---|
| Substance | Combustion Reaction | Enthalpy of Combustion, \(\text{Δ}{H}_{c}^{°}\)\(\left(\frac{\text{kJ}}{\text{mol}}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{at}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}25\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{°C}\right)\) |
| carbon | \(\text{C}\left(s\right)+{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{CO}}_{2}\left(g\right)\) | −393.5 |
| hydrogen | \({\text{H}}_{2}\left(g\right)+\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}\frac{1}{2}\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\) | −285.8 |
| magnesium | \(\text{Mg}\left(s\right)+\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}\frac{1}{2}\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{MgO}\left(s\right)\) | −601.6 |
| sulfur | \(\text{S}\left(s\right)+{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{SO}}_{2}\left(g\right)\) | −296.8 |
| carbon monoxide | \(\text{CO}\left(g\right)+\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}\frac{1}{2}\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{CO}}_{2}\left(g\right)\) | −283.0 |
| methane | \({\text{CH}}_{4}\left(g\right)+2{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{CO}}_{2}\left(g\right)+2{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\) | −890.8 |
| acetylene | \({\text{C}}_{2}{\text{H}}_{2}\left(g\right)+\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}\frac{5}{2}\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}2{\text{CO}}_{2}\left(g\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\) | −1301.1 |
| ethanol | \({\text{C}}_{2}{\text{H}}_{5}\text{OH}\left(l\right)+3{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{2CO}}_{2}\left(g\right)+3{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\) | −1366.8 |
| methanol | \({\text{CH}}_{3}\text{OH}\left(l\right)+\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}\frac{3}{2}\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{CO}}_{2}\left(g\right)+2{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\) | −726.1 |
| isooctane | \({\text{C}}_{8}{\text{H}}_{18}\left(l\right)+\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}\frac{25}{2}\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}8{\text{CO}}_{2}\left(g\right)+9{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\) | −5461 |
Using Enthalpy of Combustion As (Figure) suggests, the combustion of gasoline is a highly exothermic process. Let us determine the approximate amount of heat produced by burning 1.00 L of gasoline, assuming the enthalpy of combustion of gasoline is the same as that of isooctane, a common component of gasoline. The density of isooctane is 0.692 g/mL.

Solution Starting with a known amount (1.00 L of isooctane), we can perform conversions between units until we arrive at the desired amount of heat or energy. The enthalpy of combustion of isooctane provides one of the necessary conversions. (Figure) gives this value as −5460 kJ per 1 mole of isooctane (C8H18).
Using these data,
The combustion of 1.00 L of isooctane produces 33,100 kJ of heat. (This amount of energy is enough to melt 99.2 kg, or about 218 lbs, of ice.)
Note: If you do this calculation one step at a time, you would find:
Check Your Learning How much heat is produced by the combustion of 125 g of acetylene?
6.25 \(×\) 103 kJ
As reserves of fossil fuels diminish and become more costly to extract, the search is ongoing for replacement fuel sources for the future. Among the most promising biofuels are those derived from algae ((Figure)). The species of algae used are nontoxic, biodegradable, and among the world’s fastest growing organisms. About 50% of algal weight is oil, which can be readily converted into fuel such as biodiesel. Algae can yield 26,000 gallons of biofuel per hectare—much more energy per acre than other crops. Some strains of algae can flourish in brackish water that is not usable for growing other crops. Algae can produce biodiesel, biogasoline, ethanol, butanol, methane, and even jet fuel.

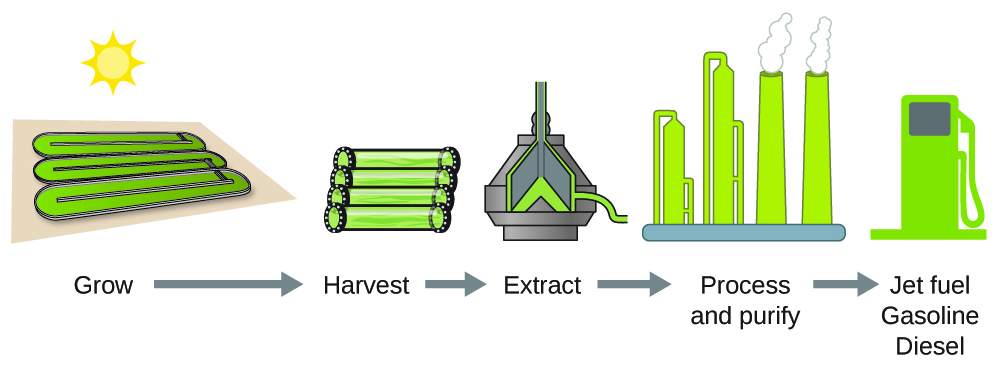
According to the US Department of Energy, only 39,000 square kilometers (about 0.4% of the land mass of the US or less than \(\frac{1}{7}\) of the area used to grow corn) can produce enough algal fuel to replace all the petroleum-based fuel used in the US. The cost of algal fuels is becoming more competitive—for instance, the US Air Force is producing jet fuel from algae at a total cost of under ?5 per gallon.1 The process used to produce algal fuel is as follows: grow the algae (which use sunlight as their energy source and CO2 as a raw material); harvest the algae; extract the fuel compounds (or precursor compounds); process as necessary (e.g., perform a transesterification reaction to make biodiesel); purify; and distribute ((Figure)).
Click here to learn more about the process of creating algae biofuel.
Standard Enthalpy of Formation
A standard enthalpy of formation \(\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°}\) is an enthalpy change for a reaction in which exactly 1 mole of a pure substance is formed from free elements in their most stable states under standard state conditions. These values are especially useful for computing or predicting enthalpy changes for chemical reactions that are impractical or dangerous to carry out, or for processes for which it is difficult to make measurements. If we have values for the appropriate standard enthalpies of formation, we can determine the enthalpy change for any reaction, which we will practice in the next section on Hess’s law.
The standard enthalpy of formation of CO2(g) is −393.5 kJ/mol. This is the enthalpy change for the exothermic reaction:
starting with the reactants at a pressure of 1 atm and 25 °C (with the carbon present as graphite, the most stable form of carbon under these conditions) and ending with one mole of CO2, also at 1 atm and 25 °C. For nitrogen dioxide, NO2(g), \(\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°}\) is 33.2 kJ/mol. This is the enthalpy change for the reaction:
A reaction equation with \(\frac{1}{2}\) mole of N2 and 1 mole of O2 is correct in this case because the standard enthalpy of formation always refers to 1 mole of product, NO2(g).
You will find a table of standard enthalpies of formation of many common substances in Appendix G. These values indicate that formation reactions range from highly exothermic (such as −2984 kJ/mol for the formation of P4O10) to strongly endothermic (such as +226.7 kJ/mol for the formation of acetylene, C2H2). By definition, the standard enthalpy of formation of an element in its most stable form is equal to zero under standard conditions, which is 1 atm for gases and 1 M for solutions.
Evaluating an Enthalpy of Formation Ozone, O3(g), forms from oxygen, O2(g), by an endothermic process. Ultraviolet radiation is the source of the energy that drives this reaction in the upper atmosphere. Assuming that both the reactants and products of the reaction are in their standard states, determine the standard enthalpy of formation, \(\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°}\) of ozone from the following information:
Solution\(\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°}\) is the enthalpy change for the formation of one mole of a substance in its standard state from the elements in their standard states. Thus, \(\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°}\) for O3(g) is the enthalpy change for the reaction:
For the formation of 2 mol of O3(g), \(\text{Δ}H\text{°}=\text{+286 kJ.}\) This ratio, \(\left(\frac{286\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}}{2\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{mol}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{O}}_{3}}\right),\) can be used as a conversion factor to find the heat produced when 1 mole of O3(g) is formed, which is the enthalpy of formation for O3(g):
Therefore, \(\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°}\left[{\text{O}}_{3}\left(g\right)\right]=\text{+143 kJ/mol}.\)
Check Your Learning Hydrogen gas, H2, reacts explosively with gaseous chlorine, Cl2, to form hydrogen chloride, HCl(g). What is the enthalpy change for the reaction of 1 mole of H2(g) with 1 mole of Cl2(g) if both the reactants and products are at standard state conditions? The standard enthalpy of formation of HCl(g) is −92.3 kJ/mol.
For the reaction \({\text{H}}_{2}\left(g\right)+{\text{Cl}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}2\text{HCl}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}H\text{°}=-184.6\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\)
Writing Reaction Equations for \(\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°}\) Write the heat of formation reaction equations for:
(a) C2H5OH(l)
(b) Ca3(PO4)2(s)
Solution Remembering that \(\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°}\) reaction equations are for forming 1 mole of the compound from its constituent elements under standard conditions, we have:
(a) \(2\text{C}\left(s,\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{graphite}\right)+3{\text{H}}_{2}\left(g\right)+\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}\frac{1}{2}{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{C}}_{2}{\text{H}}_{5}\text{OH}\left(l\right)\)
(b) \(3\text{Ca}\left(s\right)+\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}\frac{1}{2}{\text{P}}_{4}\left(s\right)+4{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{Ca}}_{3}\left({\text{PO}}_{4}{\right)}_{2}\left(s\right)\)
Note: The standard state of carbon is graphite, and phosphorus exists as P4.
Check Your Learning Write the heat of formation reaction equations for:
(a) C2H5OC2H5(l)
(b) Na2CO3(s)
(a) \(4\text{C}\left(s,\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{graphite}\right)+5{\text{H}}_{2}\left(g\right)+\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}\frac{1}{2}{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{C}}_{2}{\text{H}}_{5}{\text{OC}}_{2}{\text{H}}_{5}\left(l\right);\) (b) \(2\text{Na}\left(s\right)+\text{C}\left(s,\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{graphite}\right)+\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}\frac{3}{2}{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{Na}}_{2}{\text{CO}}_{3}\left(s\right)\)
Hess’s Law
There are two ways to determine the amount of heat involved in a chemical change: measure it experimentally, or calculate it from other experimentally determined enthalpy changes. Some reactions are difficult, if not impossible, to investigate and make accurate measurements for experimentally. And even when a reaction is not hard to perform or measure, it is convenient to be able to determine the heat involved in a reaction without having to perform an experiment.
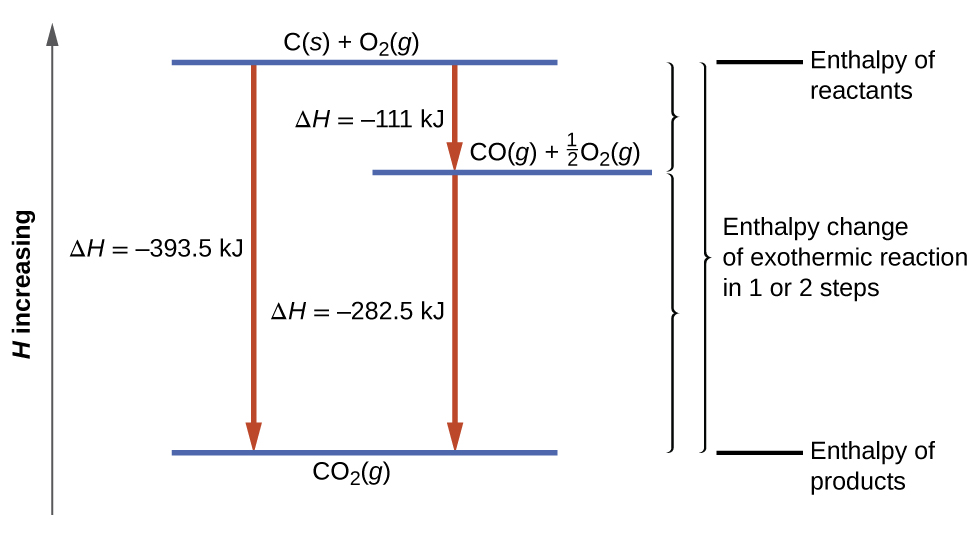
This type of calculation usually involves the use of Hess’s law, which states: If a process can be written as the sum of several stepwise processes, the enthalpy change of the total process equals the sum of the enthalpy changes of the various steps. Hess’s law is valid because enthalpy is a state function: Enthalpy changes depend only on where a chemical process starts and ends, but not on the path it takes from start to finish. For example, we can think of the reaction of carbon with oxygen to form carbon dioxide as occurring either directly or by a two-step process. The direct process is written:
In the two-step process, first carbon monoxide is formed:
Then, carbon monoxide reacts further to form carbon dioxide:
The equation describing the overall reaction is the sum of these two chemical changes:
Because the CO produced in Step 1 is consumed in Step 2, the net change is:
According to Hess’s law, the enthalpy change of the reaction will equal the sum of the enthalpy changes of the steps.
The result is shown in (Figure). We see that ΔH of the overall reaction is the same whether it occurs in one step or two. This finding (overall ΔH for the reaction = sum of ΔH values for reaction “steps” in the overall reaction) is true in general for chemical and physical processes.
Before we further practice using Hess’s law, let us recall two important features of ΔH.
-
ΔH is directly proportional to the quantities of reactants or products. For example, the enthalpy change for the reaction forming 1 mole of NO2(g) is +33.2 kJ:
\(\frac{1}{2}{\text{N}}_{2}\left(g\right)+{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{NO}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}\text{H}=\text{+33.2 kJ}\)When 2 moles of NO2 (twice as much) are formed, the ΔH will be twice as large:
\({\text{N}}_{2}\left(g\right)+2{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}2{\text{NO}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}\text{H}=\text{+66.4 kJ}\)In general, if we multiply or divide an equation by a number, then the enthalpy change should also be multiplied or divided by the same number.
-
ΔH for a reaction in one direction is equal in magnitude and opposite in sign to ΔH for the reaction in the reverse direction. For example, given that:
\({\text{H}}_{2}\left(g\right)+{\text{Cl}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}2\text{HCl}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}\text{H}=-184.6\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\)Then, for the “reverse” reaction, the enthalpy change is also “reversed”:
\(2\text{HCl}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{H}}_{2}\left(g\right)+{\text{Cl}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}\text{H}=\text{+184.6 kJ}\)
Stepwise Calculation of \(\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°}\) Using Hess’s Law Determine the enthalpy of formation, \(\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°},\) of FeCl3(s) from the enthalpy changes of the following two-step process that occurs under standard state conditions:
Solution We are trying to find the standard enthalpy of formation of FeCl3(s), which is equal to ΔH° for the reaction:
Looking at the reactions, we see that the reaction for which we want to find ΔH° is the sum of the two reactions with known ΔH values, so we must sum their ΔHs:
The enthalpy of formation, \(\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°},\) of FeCl3(s) is −399.5 kJ/mol.
Check Your Learning Calculate ΔH for the process:
from the following information:
66.4 kJ
Here is a less straightforward example that illustrates the thought process involved in solving many Hess’s law problems. It shows how we can find many standard enthalpies of formation (and other values of ΔH) if they are difficult to determine experimentally.
A More Challenging Problem Using Hess’s Law Chlorine monofluoride can react with fluorine to form chlorine trifluoride:
(i)\(\text{ClF}\left(g\right)+{\text{F}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{ClF}}_{3}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}\text{H}\text{°}=?\)
Use the reactions here to determine the ΔH° for reaction (i):
(ii)\(2{\text{OF}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)+2{\text{F}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}{H}_{\left(ii\right)}^{°}=-49.4\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\)
(iii)\(2\text{ClF}\left(g\right)+{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{Cl}}_{2}\text{O}\left(g\right)+{\text{OF}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}{H}_{\left(iii\right)}^{°}=\text{+205.6 kJ}\)
(iv)\({\text{ClF}}_{3}\left(g\right)+{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\frac{1}{2}{\text{Cl}}_{2}\text{O}\left(g\right)+\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}\frac{3}{2}{\text{OF}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}{H}_{\left(iv\right)}^{°}=\text{+266.7 kJ}\)
Solution Our goal is to manipulate and combine reactions (ii), (iii), and (iv) such that they add up to reaction (i). Going from left to right in (i), we first see that ClF(g) is needed as a reactant. This can be obtained by multiplying reaction (iii) by \(\frac{1}{2},\) which means that the ΔH° change is also multiplied by \(\frac{1}{2}\text{:}\)
Next, we see that F2 is also needed as a reactant. To get this, reverse and halve reaction (ii), which means that the ΔH° changes sign and is halved:
To get ClF3 as a product, reverse (iv), changing the sign of ΔH°:
Now check to make sure that these reactions add up to the reaction we want:
Reactants \(\frac{1}{2}{\text{O}}_{2}\) and \(\frac{1}{2}{\text{O}}_{2}\) cancel out product O2; product \(\frac{1}{2}{\text{Cl}}_{2}\text{O}\) cancels reactant \(\frac{1}{2}{\text{Cl}}_{2}\text{O;}\) and reactant \(\frac{3}{2}{\text{OF}}_{2}\) is cancelled by products \(\frac{1}{2}{\text{OF}}_{2}\) and OF2. This leaves only reactants ClF(g) and F2(g) and product ClF3(g), which are what we want. Since summing these three modified reactions yields the reaction of interest, summing the three modified ΔH° values will give the desired ΔH°:
Check Your Learning Aluminum chloride can be formed from its elements:
(i)\(2\text{Al}\left(s\right)+3{\text{Cl}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}2{\text{AlCl}}_{3}\left(s\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}H\text{°}=?\)
Use the reactions here to determine the ΔH° for reaction (i):
(ii)\(\text{HCl}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{HCl}\left(aq\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}{H}_{\left(ii\right)}^{°}=-74.8\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\)
(iii)\({\text{H}}_{2}\left(g\right)+{\text{Cl}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}2\text{HCl}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}{H}_{\left(iii\right)}^{°}=-185\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\)
(iv)\({\text{AlCl}}_{3}\left(aq\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{AlCl}}_{3}\left(s\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}{H}_{\left(iv\right)}^{°}=+323\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ/mol}\)
(v)\(\text{2Al}\left(s\right)+6\text{HCl}\left(aq\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}2{\text{AlCl}}_{3}\left(aq\right)+3{\text{H}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}{H}_{\left(v\right)}^{°}=-1049\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\)
−1407 kJ
We also can use Hess’s law to determine the enthalpy change of any reaction if the corresponding enthalpies of formation of the reactants and products are available. The stepwise reactions we consider are: (i) decompositions of the reactants into their component elements (for which the enthalpy changes are proportional to the negative of the enthalpies of formation of the reactants), followed by (ii) re-combinations of the elements to give the products (with the enthalpy changes proportional to the enthalpies of formation of the products). The standard enthalpy change of the overall reaction is therefore equal to: (ii) the sum of the standard enthalpies of formation of all the products plus (i) the sum of the negatives of the standard enthalpies of formation of the reactants. This is usually rearranged slightly to be written as follows, with ∑ representing “the sum of” and n standing for the stoichiometric coefficients:
The following example shows in detail why this equation is valid, and how to use it to calculate the enthalpy change for a reaction of interest.
Using Hess’s Law What is the standard enthalpy change for the reaction:
Solution: Using the EquationUse the special form of Hess’s law given previously, and values from Appendix G:
Solution: Supporting Why the General Equation Is Valid Alternatively, we can write this reaction as the sum of the decompositions of 3NO2(g) and 1H2O(l) into their constituent elements, and the formation of 2HNO3(aq) and 1NO(g) from their constituent elements. Writing out these reactions, and noting their relationships to the \(\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°}\) values for these compounds (from Appendix G ), we have:
Summing these reaction equations gives the reaction we are interested in:
Summing their enthalpy changes gives the value we want to determine:
So the standard enthalpy change for this reaction is ΔH° = −138.4 kJ.
Note that this result was obtained by (1) multiplying the \(\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°}\) of each product by its stoichiometric coefficient and summing those values, (2) multiplying the \(\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°}\) of each reactant by its stoichiometric coefficient and summing those values, and then (3) subtracting the result found in (2) from the result found in (1). This is also the procedure in using the general equation, as shown.
Check Your Learning Calculate the heat of combustion of 1 mole of ethanol, C2H5OH(l), when H2O(l) and CO2(g) are formed. Use the following enthalpies of formation: C2H5OH(l), −278 kJ/mol; H2O(l), −286 kJ/mol; and CO2(g), −394 kJ/mol.
−1368 kJ/mol
Key Concepts and Summary
If a chemical change is carried out at constant pressure and the only work done is caused by expansion or contraction, q for the change is called the enthalpy change with the symbol ΔH, or \(\text{Δ}H\text{°}\) for reactions occurring under standard state conditions at 298 K. The value of ΔH for a reaction in one direction is equal in magnitude, but opposite in sign, to ΔH for the reaction in the opposite direction, and ΔH is directly proportional to the quantity of reactants and products. The standard enthalpy of formation, \(\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°},\) is the enthalpy change accompanying the formation of 1 mole of a substance from the elements in their most stable states at 1 bar and 298.15 K. If the enthalpies of formation are available for the reactants and products of a reaction, the enthalpy change can be calculated using Hess’s law: If a process can be written as the sum of several stepwise processes, the enthalpy change of the total process equals the sum of the enthalpy changes of the various steps.
Key Equations
- \(\text{Δ}U=q+w\)
- \(\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{reaction}}^{°}=\sum n\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}×\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°}\text{(products)}-\sum n\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}×\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°}\left(\text{reactants}\right)\)
Chemistry End of Chapter Exercises
Explain how the heat measured in (Figure) differs from the enthalpy change for the exothermic reaction described by the following equation:
\(\text{HCl}\left(aq\right)+\text{NaOH}\left(aq\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{NaCl}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\)
The enthalpy change of the indicated reaction is for exactly 1 mol HCL and 1 mol NaOH; the heat in the example is produced by 0.0500 mol HCl and 0.0500 mol NaOH.
Using the data in the check your learning section of (Figure), calculate ΔH in kJ/mol of AgNO3(aq) for the reaction: \(\text{NaCl}\left(aq\right)+{\text{AgNO}}_{3}\left(aq\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{AgCl}\left(s\right)+{\text{NaNO}}_{3}\left(aq\right)\)
Calculate the enthalpy of solution (ΔH for the dissolution) per mole of NH4NO3 under the conditions described in (Figure).
25 kJ mol−1
Calculate ΔH for the reaction described by the equation. (Hint: Use the value for the approximate amount of heat absorbed by the reaction that you calculated in a previous exercise.)
\(\text{Ba}{\left(\text{OH}\right)}_{2}\text{·}8{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(s\right)+2{\text{NH}}_{4}\text{SCN}\left(aq\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{Ba}{\left(\text{SCN}\right)}_{2}\left(aq\right)+2{\text{NH}}_{3}\left(aq\right)+10{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\)
Calculate the enthalpy of solution (ΔH for the dissolution) per mole of CaCl2 (refer to (Figure)).
81 kJ mol−1
Although the gas used in an oxyacetylene torch ((Figure)) is essentially pure acetylene, the heat produced by combustion of one mole of acetylene in such a torch is likely not equal to the enthalpy of combustion of acetylene listed in (Figure). Considering the conditions for which the tabulated data are reported, suggest an explanation.
How much heat is produced by burning 4.00 moles of acetylene under standard state conditions?
5204.4 kJ
How much heat is produced by combustion of 125 g of methanol under standard state conditions?
How many moles of isooctane must be burned to produce 100 kJ of heat under standard state conditions?
1.83 \(×\) 10−2 mol
What mass of carbon monoxide must be burned to produce 175 kJ of heat under standard state conditions?
When 2.50 g of methane burns in oxygen, 125 kJ of heat is produced. What is the enthalpy of combustion per mole of methane under these conditions?
–802 kJ mol−1
How much heat is produced when 100 mL of 0.250 M HCl (density, 1.00 g/mL) and 200 mL of 0.150 M NaOH (density, 1.00 g/mL) are mixed?
\(\text{HCl}\left(aq\right)+\text{NaOH}\left(aq\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{NaCl}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}H\text{°}=-58\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\)
If both solutions are at the same temperature and the heat capacity of the products is 4.19 J/g °C, how much will the temperature increase? What assumption did you make in your calculation?
A sample of 0.562 g of carbon is burned in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter, producing carbon dioxide. Assume both the reactants and products are under standard state conditions, and that the heat released is directly proportional to the enthalpy of combustion of graphite. The temperature of the calorimeter increases from 26.74 °C to 27.93 °C. What is the heat capacity of the calorimeter and its contents?
15.5 kJ/ºC
Before the introduction of chlorofluorocarbons, sulfur dioxide (enthalpy of vaporization, 6.00 kcal/mol) was used in household refrigerators. What mass of SO2 must be evaporated to remove as much heat as evaporation of 1.00 kg of CCl2F2 (enthalpy of vaporization is 17.4 kJ/mol)?
The vaporization reactions for SO2 and CCl2F2 are \({\text{SO}}_{2}\left(l\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{SO}}_{2}\left(g\right)\) and \({\text{CCl}}_{2}\text{F}\left(l\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{CCl}}_{2}{\text{F}}_{2}\left(g\right),\) respectively.
Homes may be heated by pumping hot water through radiators. What mass of water will provide the same amount of heat when cooled from 95.0 to 35.0 °C, as the heat provided when 100 g of steam is cooled from 110 °C to 100 °C.
7.43 g
Which of the enthalpies of combustion in (Figure) the table are also standard enthalpies of formation?
Does the standard enthalpy of formation of H2O(g) differ from ΔH° for the reaction \({\text{2H}}_{2}\left(g\right)+{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}2{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(g\right)?\)
Yes.
Joseph Priestly prepared oxygen in 1774 by heating red mercury(II) oxide with sunlight focused through a lens. How much heat is required to decompose exactly 1 mole of red HgO(s) to Hg(l) and O2(g) under standard conditions?
How many kilojoules of heat will be released when exactly 1 mole of manganese, Mn, is burned to form Mn3O4(s) at standard state conditions?
459.6 kJ
How many kilojoules of heat will be released when exactly 1 mole of iron, Fe, is burned to form Fe2O3(s) at standard state conditions?
The following sequence of reactions occurs in the commercial production of aqueous nitric acid:
\(4{\text{NH}}_{3}\left(g\right)+5{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}4\text{NO}\left(g\right)+6{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}\text{H}=-907\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\)
\(2\text{NO}\left(g\right)+{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}2{\text{NO}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}\text{H}=-113\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\)
\(3{\text{NO}}_{2}+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}2{\text{HNO}}_{3}\left(aq\right)+\text{NO}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}\text{H}=-139\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\)
Determine the total energy change for the production of one mole of aqueous nitric acid by this process.
−495 kJ/mol
Both graphite and diamond burn.
\(\text{C}\left(s,\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{diamond}\right)+{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{CO}}_{2}\left(g\right)\)
For the conversion of graphite to diamond:
\(\text{C}\left(s,\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{graphite}\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{C}\left(s,\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{diamond}\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}H\text{°}=1.90\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\)
Which produces more heat, the combustion of graphite or the combustion of diamond?
From the molar heats of formation in Appendix G, determine how much heat is required to evaporate one mole of water: \({\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(g\right)\)
44.01 kJ/mol
Which produces more heat?
\(\text{Os}\left(s\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}2{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{OsO}}_{4}\left(s\right)\)
or
\(\text{Os}\left(s\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}2{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{OsO}}_{4}\left(g\right)\)
for the phase change \({\text{OsO}}_{4}\left(s\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{OsO}}_{4}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}\text{H}=56.4\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\)
Calculate \(\text{Δ}H\text{°}\) for the process
\(\text{Sb}\left(s\right)+\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}\frac{5}{2}{\text{Cl}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{SbCl}}_{5}\left(s\right)\)
from the following information:
\(\begin{array}{l}\\ \text{Sb}\left(s\right)+\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}\frac{3}{2}{\text{Cl}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{SbCl}}_{3}\left(s\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}H\text{°}=-314\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\\ {\text{SbCl}}_{3}\left(s\right)+{\text{Cl}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{SbCl}}_{5}\left(s\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}H\text{°}=-80\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\end{array}\)
−394 kJ
Calculate \(\text{Δ}H\text{°}\) for the process \(\text{Zn}\left(s\right)+\text{S}\left(s\right)+2{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{ZnSO}}_{4}\left(s\right)\)
from the following information:
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Zn}\left(s\right)+\text{S}\left(s\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{ZnS}\left(s\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}H\text{°}=-206.0\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\\ \text{ZnS}\left(s\right)+{\text{2O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{ZnSO}}_{4}\left(s\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}H\text{°}=-776.8\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\end{array}\)
Calculate ΔH for the process \({\text{Hg}}_{2}{\text{Cl}}_{2}\left(s\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}2\text{Hg}\left(l\right)+{\text{Cl}}_{2}\left(g\right)\)
from the following information:
\(\begin{array}{l}\text{Hg}\left(l\right)+{\text{Cl}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{HgCl}}_{2}\left(s\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}H=-224\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\\ \text{Hg}\left(l\right)+{\text{HgCl}}_{2}\left(s\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{Hg}}_{2}{\text{Cl}}_{2}\left(s\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}H=-41.2\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\end{array}\)
265 kJ
Calculate \(\text{Δ}H\text{°}\) for the process \({\text{Co}}_{3}{\text{O}}_{4}\left(s\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}3\text{Co}\left(s\right)+2{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\)
from the following information:
\(\begin{array}{}\\ \text{Co}\left(s\right)+\phantom{\rule{0.1em}{0ex}}\frac{1}{2}{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{CoO}\left(s\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}H\text{°}=-237.9\text{kJ}\\ \text{3CoO}\left(s\right)+\frac{1}{2}{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{Co}}_{3}{\text{O}}_{4}\left(s\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}H\text{°}=-177.5\text{kJ}\end{array}\)
Calculate the standard molar enthalpy of formation of NO(g) from the following data:
\(\begin{array}{l}{\text{N}}_{2}\left(g\right)+2{\text{O}}_{2}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}2{\text{NO}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}H\text{°}=66.4\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\\ \text{2NO}\left(g\right)+{\text{O}}_{2}\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}2{\text{NO}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}H\text{°}=-114.1\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\end{array}\)
90.3 kJ/mol
Using the data in Appendix G, calculate the standard enthalpy change for each of the following reactions:
(a) \({\text{N}}_{2}\left(g\right)+{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}2\text{NO}\left(g\right)\)
(b) \(\text{Si}\left(s\right)+2{\text{Cl}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{SiCl}}_{4}\left(g\right)\)
(c) \({\text{Fe}}_{2}{\text{O}}_{3}\left(s\right)+3{\text{H}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}2\text{Fe}\left(s\right)+3{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\)
(d) \(2\text{LiOH}\left(s\right)+{\text{CO}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{Li}}_{2}{\text{CO}}_{3}\left(s\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(g\right)\)
Using the data in Appendix G, calculate the standard enthalpy change for each of the following reactions:
(a) \(\text{Si}\left(s\right)+2{\text{F}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{SiF}}_{4}\left(g\right)\)
(b) \(2\text{C}\left(s\right)+2{\text{H}}_{2}\left(g\right)+{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{CO}}_{2}\text{H}\left(l\right)\)
(c) \({\text{CH}}_{4}\left(g\right)+{\text{N}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{HCN}\left(g\right)+{\text{NH}}_{3}\left(g\right)\text{;}\)
(d) \({\text{CS}}_{2}\left(g\right)+3{\text{Cl}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{CCl}}_{4}\left(g\right)+{\text{S}}_{2}{\text{Cl}}_{2}\left(g\right)\)
(a) −1615.0 kJ mol−1; (b) −484.3 kJ mol−1; (c) 164.2 kJ; (d) −232.1 kJ
The following reactions can be used to prepare samples of metals. Determine the enthalpy change under standard state conditions for each.
(a) \(2{\text{Ag}}_{2}\text{O}\left(s\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}4\text{Ag}\left(s\right)+{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\)
(b) \(\text{SnO}\left(s\right)+\text{CO}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{Sn}\left(s\right)+{\text{CO}}_{2}\left(g\right)\)
(c) \({\text{Cr}}_{2}{\text{O}}_{3}\left(s\right)+3{\text{H}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}2\text{Cr}\left(s\right)+3{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\)
(d) \(2\text{Al}\left(s\right)+{\text{Fe}}_{2}{\text{O}}_{3}\left(s\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{Al}}_{2}{\text{O}}_{3}\left(s\right)+2\text{Fe}\left(s\right)\)
The decomposition of hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, has been used to provide thrust in the control jets of various space vehicles. Using the data in Appendix G, determine how much heat is produced by the decomposition of exactly 1 mole of H2O2 under standard conditions.
\(2{\text{H}}_{2}{\text{O}}_{2}\left(l\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}2{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(g\right)+{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\)
−54.04 kJ mol−1
Calculate the enthalpy of combustion of propane, C3H8(g), for the formation of H2O(g) and CO2(g). The enthalpy of formation of propane is −104 kJ/mol.
Calculate the enthalpy of combustion of butane, C4H10(g) for the formation of H2O(g) and CO2(g). The enthalpy of formation of butane is −126 kJ/mol.
−2660 kJ mol−1
Both propane and butane are used as gaseous fuels. Which compound produces more heat per gram when burned?
The white pigment TiO2 is prepared by the reaction of titanium tetrachloride, TiCl4, with water vapor in the gas phase: \({\text{TiCl}}_{4}\left(g\right)+2{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{TiO}}_{2}\left(s\right)+4\text{HCl}\left(g\right).\)
How much heat is evolved in the production of exactly 1 mole of TiO2(s) under standard state conditions?
67.1 kJ
Water gas, a mixture of H2 and CO, is an important industrial fuel produced by the reaction of steam with red hot coke, essentially pure carbon: \(\text{C}\left(s\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{CO}\left(g\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\left(g\right).\)
(a) Assuming that coke has the same enthalpy of formation as graphite, calculate \(\text{Δ}H\text{°}\) for this reaction.
(b) Methanol, a liquid fuel that could possibly replace gasoline, can be prepared from water gas and additional hydrogen at high temperature and pressure in the presence of a suitable catalyst: \(2{\text{H}}_{2}\left(g\right)+\text{CO}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{CH}}_{3}\text{OH}\left(g\right).\)
Under the conditions of the reaction, methanol forms as a gas. Calculate \(\text{Δ}H\text{°}\) for this reaction and for the condensation of gaseous methanol to liquid methanol.
(c) Calculate the heat of combustion of 1 mole of liquid methanol to H2O(g) and CO2(g).
In the early days of automobiles, illumination at night was provided by burning acetylene, C2H2. Though no longer used as auto headlamps, acetylene is still used as a source of light by some cave explorers. The acetylene is (was) prepared in the lamp by the reaction of water with calcium carbide, CaC2:
\({\text{CaC}}_{2}\left(s\right)+2{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{Ca}{\left(\text{OH}\right)}_{2}\left(s\right)+{\text{C}}_{2}{\text{H}}_{2}\left(g\right).\)
Calculate the standard enthalpy of the reaction. The \(\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°}\) of CaC2 is −15.14 kcal/mol.
−122.8 kJ
From the data in (Figure), determine which of the following fuels produces the greatest amount of heat per gram when burned under standard conditions: CO(g), CH4(g), or C2H2(g).
The enthalpy of combustion of hard coal averages −35 kJ/g, that of gasoline, 1.28 \(×\) 105 kJ/gal. How many kilograms of hard coal provide the same amount of heat as is available from 1.0 gallon of gasoline? Assume that the density of gasoline is 0.692 g/mL (the same as the density of isooctane).
3.7 kg
Ethanol, C2H5OH, is used as a fuel for motor vehicles, particularly in Brazil.
(a) Write the balanced equation for the combustion of ethanol to CO2(g) and H2O(g), and, using the data in Appendix G, calculate the enthalpy of combustion of 1 mole of ethanol.
(b) The density of ethanol is 0.7893 g/mL. Calculate the enthalpy of combustion of exactly 1 L of ethanol.
(c) Assuming that an automobile’s mileage is directly proportional to the heat of combustion of the fuel, calculate how much farther an automobile could be expected to travel on 1 L of gasoline than on 1 L of ethanol. Assume that gasoline has the heat of combustion and the density of n–octane, C8H18 \(\left(\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°}=-208.4\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ/mol;}\) density = 0.7025 g/mL).
Among the substances that react with oxygen and that have been considered as potential rocket fuels are diborane [B2H6, produces B2O3(s) and H2O(g)], methane [CH4, produces CO2(g) and H2O(g)], and hydrazine [N2H4, produces N2(g) and H2O(g)]. On the basis of the heat released by 1.00 g of each substance in its reaction with oxygen, which of these compounds offers the best possibility as a rocket fuel? The \(\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°}\) of B2H6(g), CH4(g), and N2H4(l) may be found in Appendix G.
On the assumption that the best rocket fuel is the one that gives off the most heat, B2H6 is the prime candidate.
How much heat is produced when 1.25 g of chromium metal reacts with oxygen gas under standard conditions?
Ethylene, C2H2, a byproduct from the fractional distillation of petroleum, is fourth among the 50 chemical compounds produced commercially in the largest quantities. About 80% of synthetic ethanol is manufactured from ethylene by its reaction with water in the presence of a suitable catalyst. \({\text{C}}_{2}{\text{H}}_{4}\left(g\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}{\text{C}}_{2}{\text{H}}_{5}\text{OH}\left(l\right)\)
Using the data in the table in Appendix G, calculate ΔH° for the reaction.
−88.2 kJ
The oxidation of the sugar glucose, C6H12O6, is described by the following equation:
\({\text{C}}_{6}{\text{H}}_{12}{\text{O}}_{6}\left(s\right)+6{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}6{\text{CO}}_{2}\left(g\right)+6{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\phantom{\rule{3em}{0ex}}\text{Δ}\text{H}=-2816\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\text{kJ}\)
The metabolism of glucose gives the same products, although the glucose reacts with oxygen in a series of steps in the body.
(a) How much heat in kilojoules can be produced by the metabolism of 1.0 g of glucose?
(b) How many Calories can be produced by the metabolism of 1.0 g of glucose?
Propane, C3H8, is a hydrocarbon that is commonly used as a fuel.
(a) Write a balanced equation for the complete combustion of propane gas.
(b) Calculate the volume of air at 25 °C and 1.00 atmosphere that is needed to completely combust 25.0 grams of propane. Assume that air is 21.0 percent O2 by volume. (Hint: We will see how to do this calculation in a later chapter on gases—for now use the information that 1.00 L of air at 25 °C and 1.00 atm contains 0.275 g of O2 per liter.)
(c) The heat of combustion of propane is −2,219.2 kJ/mol. Calculate the heat of formation, \(\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°}\) of propane given that \(\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°}\) of H2O(l) = −285.8 kJ/mol and \(\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°}\) of CO2(g) = −393.5 kJ/mol.
(d) Assuming that all of the heat released in burning 25.0 grams of propane is transferred to 4.00 kilograms of water, calculate the increase in temperature of the water.
(a) \({\text{C}}_{3}{\text{H}}_{8}\left(g\right)+5{\text{O}}_{2}\left(g\right)\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}⟶\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}3{\text{CO}}_{2}\left(g\right)+4{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right);\) (b) 330 L; (c) −104.5 kJ mol−1; (d) 75.4 °C
During a recent winter month in Sheboygan, Wisconsin, it was necessary to obtain 3500 kWh of heat provided by a natural gas furnace with 89% efficiency to keep a small house warm (the efficiency of a gas furnace is the percent of the heat produced by combustion that is transferred into the house).
(a) Assume that natural gas is pure methane and determine the volume of natural gas in cubic feet that was required to heat the house. The average temperature of the natural gas was 56 °F; at this temperature and a pressure of 1 atm, natural gas has a density of 0.681 g/L.
(b) How many gallons of LPG (liquefied petroleum gas) would be required to replace the natural gas used? Assume the LPG is liquid propane [C3H8: density, 0.5318 g/mL; enthalpy of combustion, 2219 kJ/mol for the formation of CO2(g) and H2O(l)] and the furnace used to burn the LPG has the same efficiency as the gas furnace.
(c) What mass of carbon dioxide is produced by combustion of the methane used to heat the house?
(d) What mass of water is produced by combustion of the methane used to heat the house?
(e) What volume of air is required to provide the oxygen for the combustion of the methane used to heat the house? Air contains 23% oxygen by mass. The average density of air during the month was 1.22 g/L.
(f) How many kilowatt–hours (1 kWh = 3.6 \(×\) 106 J) of electricity would be required to provide the heat necessary to heat the house? Note electricity is 100% efficient in producing heat inside a house.
(g) Although electricity is 100% efficient in producing heat inside a house, production and distribution of electricity is not 100% efficient. The efficiency of production and distribution of electricity produced in a coal-fired power plant is about 40%. A certain type of coal provides 2.26 kWh per pound upon combustion. What mass of this coal in kilograms will be required to produce the electrical energy necessary to heat the house if the efficiency of generation and distribution is 40%?
Footnotes
- 1For more on algal fuel, see http://www.theguardian.com/environment/2010/feb/13/algae-solve-pentagon-fuel-problem.
Glossary
- chemical thermodynamics
- area of science that deals with the relationships between heat, work, and all forms of energy associated with chemical and physical processes
- enthalpy (H)
- sum of a system’s internal energy and the mathematical product of its pressure and volume
- enthalpy change (ΔH)
- heat released or absorbed by a system under constant pressure during a chemical or physical process
- expansion work (pressure-volume work)
- work done as a system expands or contracts against external pressure
- first law of thermodynamics
- internal energy of a system changes due to heat flow in or out of the system or work done on or by the system
- Hess’s law
- if a process can be represented as the sum of several steps, the enthalpy change of the process equals the sum of the enthalpy changes of the steps
- hydrocarbon
- compound composed only of hydrogen and carbon; the major component of fossil fuels
- internal energy (U)
- total of all possible kinds of energy present in a substance or substances
- standard enthalpy of combustion \(\text{(}\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{c}}^{°}\text{)}\)
- heat released when one mole of a compound undergoes complete combustion under standard conditions
- standard enthalpy of formation \(\text{(}\text{Δ}{H}_{\text{f}}^{°}\text{)}\)
- enthalpy change of a chemical reaction in which 1 mole of a pure substance is formed from its elements in their most stable states under standard state conditions
- standard state
- set of physical conditions as accepted as common reference conditions for reporting thermodynamic properties; 1 bar of pressure, and solutions at 1 molar concentrations, usually at a temperature of 298.15 K
- state function
- property depending only on the state of a system, and not the path taken to reach that state

