Chapter 2: Limits and The Derivative
Chapter 2 Review Exercises: The Derivative
From Calculus, Volume 1, by Strang and Herman, OpenStax (Web), licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 License.
True or false?
1. Every function has a derivative.
Solution
False. Counterexample: [latex]f(x) = |x|[/latex]
2. A continuous function has a continuous derivative.
3. A continuous function has a derivative.
Solution
False. Counterexample: [latex]f(x) = |x|[/latex]
4. If a function is differentiable, it is continuous.
Use the limit definition of the derivative to exactly evaluate the derivative.
5. [latex]f(x)=\sqrt{x+4}[/latex]
Solution
[latex]f'(x) =\frac{1}{2\sqrt{x+4}}[/latex]
6. [latex]f(x)=\frac{3}{x}[/latex]
7. [latex]f(x)=\frac{9}{x^2}[/latex]
Solution
[latex]f'(x) = -\frac{18}{x^3}[/latex]
8. [latex]f(x)=\sqrt{3x+1}[/latex]
Find the first derivative of the following functions.
9. [latex]f(x)=3x^3-\frac{4}{x^2} + \pi^6[/latex]
Solution
[latex]f'(x) = 9x^2+\frac{8}{x^3}[/latex]
10. [latex]f(x)=(4-x^2)^3[/latex]
11. [latex]f(x)=\ln(3x^8+2)[/latex]
12. [latex]f(x)=(\sqrt{3x^2+2})(e^{3x} - \ln |x|)[/latex]
13. [latex]v(t)= t^2 - \frac{1}{\sqrt[5]{t}^6}[/latex]
Solution
[latex]v'(t) = 2t + \frac{6}{5} t^{-\frac{11}{5}}[/latex]
14. [latex]f(x) = \sqrt{2x + \sqrt{3x}}[/latex]
15. [latex]f(x)= \log_7 (2x +e^{-x})[/latex]
16. [latex]f(x)= \ln |9x^3 - e^{2x} + 5^{x}|[/latex]
Solution
[latex]f'(x) = \frac{27x^2 -2e^{2x} + 5^x \ln 5}{9x^3 - e^{2x} + 5^{x}}[/latex]
17. [latex]g(x)= \log_2 [\ln (4x^6 -3x + 1][/latex]
18. [latex]2xy = y^2 + 6[/latex]
Solution
[latex]y' = \frac{y}{y-x}[/latex]
19. [latex]f(x) = x^{2x}[/latex]
Solution
[latex]f'(x) = 2x^{2x}(\ln x +1)[/latex]
Find the following derivatives of various orders.
20. Third derivative of [latex]y=(3x+2)^2[/latex]
Find the equation of the tangent line to the following equations at the specified point.
21. [latex]y=x+e^x-\frac{1}{x}[/latex] at [latex]x=1[/latex]
Solution
[latex]y=(2+e)x-2[/latex]
22. [latex]x^2y^3 - x^3 = 3y^2-7[/latex] at the point [latex](2,1)[/latex]
23. [latex]f(x) = (x+2)^{x^2}[/latex] at [latex]x=-1[/latex]
Solution
[latex]y = x+ 2[/latex]
Draw the derivative for the following graphs.
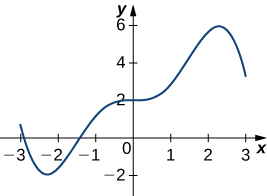
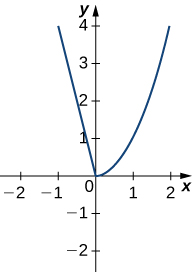
Solution
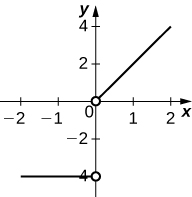
Answer the following questions.
26. A particle moves on a vertical line so that its coordinate at time [latex]t[/latex] is [latex]y= t^3 -18t+7, t \ge 0[/latex].
a) Find the velocity function, [latex]v(t)[/latex].
b) Find the acceleration function, [latex]a(t)[/latex].
c) When is the particle moving upward? When is the particle moving downward?
27. A ball is thrown vertically in the air with an upward velocity of 80 ft per second. Its height after [latex]t[/latex] seconds is [latex]h = 80t - 10t^2[/latex].
a) What is the maximum height reached by the ball? How many seconds does it take for the ball to reach its maximum height?
b) Find the velocity function, [latex]v(t)[/latex].
c) What is the velocity of the ball at [latex]t = 3[/latex]?
d) What is the velocity of the ball [latex]t = 5[/latex]?
e) How long does it take for the ball to reach the ground?
Solution
a) 160 ft; 4 seconds
b) [latex]v(t) = 80 - 20t[/latex]
c) [latex]v(3) = 80 - 20 (3) = 20[/latex] ft/s (upward)
d) [latex]v(5) = 80 - 20 (5) = -20[/latex] ft/s (downward)
e) [latex]0 = 80t - 10t^2[/latex] so [latex]t=8[/latex] seconds
The following questions consider the wind speeds of Hurricane Katrina, which affected New Orleans, Louisiana, in August 2005. The data are displayed in a table.
| Hours after Midnight, August 26 | Wind Speed (mph) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 45 |
| 5 | 75 |
| 11 | 100 |
| 29 | 115 |
| 49 | 145 |
| 58 | 175 |
| 73 | 155 |
| 81 | 125 |
| 85 | 95 |
| 107 | 35 |
28. Using the table, estimate the derivative of the wind speed at hour 39. What is the physical meaning?
29. Estimate the derivative of the wind speed at hour 83. What is the physical meaning?
Solution
-7.5. The wind speed is decreasing at a rate of 7.5 mph/hr
Media Attributions
- CNX_Calc_Figure_03_09_204
- CNX_Calc_Figure_03_09_206
- CNX_Calc_Figure_03_09_207

