Substrate Specificity of the Enzyme Lactase
Learning Objectives
After completing the lab, the student will be able to:
- Measure enzymatic activity of the enzyme lactase over time and represent it graphically.
- Determine the specificity of the enzyme lactase.
Activity 3: Pre-Assessment
- How could we determine experimentally the specificity of an enzyme to its substrate?
- Discuss the answer to question 1 with the class.
Activity 3: Substrate Specificity of the Enzyme Lactase
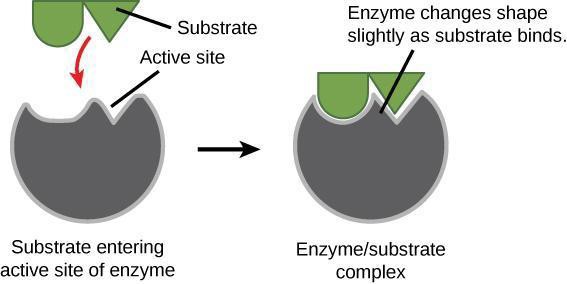
An enzyme’s active site contains side chains of the amino acids that can only bind to certain molecules. For example, if the active site is largely positively charged, then negatively charged substrates will be attracted. Additionally, the three-dimensional shape of the active site within the enzyme is key in determining which substrates will fit into the active site (Figure 7.3). What does this suggest about how specific enzymes are to their substrates?
Safety Precautions
- Goggles should be worn at all times while in laboratory.
- No open-toe shoes worn in laboratory.
- Measure fluids carefully using graduated cylinders to avoid breakage and spillage.
- Inform your teacher immediately of any broken glassware as it could cause injuries.
- Clean up any spilled fluids to prevent other people from slipping.
For this activity, you will need the following:
- Graduated cylinder
- Beaker
- Water
- 20 mg/mL lactose solution
- 20 mg/mL sucrose solution
- Various foods for testing for presence of lactose, including both dairy products and those marketed as lactose-free
- Lactase (obtained from laboratory supply company)
- Test tubes
- Stirring rod
- Timer
- Labeling pencil
- Glucose test strips
- Graph paper
For this activity, you will work in pairs.
Structured Inquiry
Step 1: Prepare two test tubes, one with 2 mL of 20 mg/mL lactose and the other with 2 mL of 20 mg/mL sucrose. Label one tube as lactose-containing and the other as sucrose-containing. Create a data table to enter your results for each of these test tubes over time.
Step 2: Hypothesize/Predict: Based on your knowledge of enzymes and their specificity, predict whether you will observe enzyme activity for each of the two tubes indicated above. Add your predictions to the data table you created in Step 1.
Step 3: Student-led Planning: Discuss with your partner how to calculate a rate of lactase activity for each substrate.
Step 4: Make your lactase enzyme solution per your teacher’s instructions. Add 1 mL of the lactase enzyme solution to each of the two tubes listed above and immediately start timing. Immediately after adding the lactase enzyme solution, determine the glucose concentration in each tube using glucose test strips and the color chart that came with the test strips. Record this in your data table.
Step 5: Every 3 minutes for 15 minutes, record the concentrations of glucose in each tube using the color chart that came with the test strips and record in your data table.
Step 6: Critical Analysis: Calculate the rate of enzymatic activity for lactase in each substrate. Using graph paper, make a bar graph showing the rates of lactase activity in each of the two substrates. Are the predictions you made in step 2 supported by your data? Explain how you know in your notebook.
Guided Inquiry
Step 1: Hypothesize/Predict: Based upon what you have learned, how could we use this assay for lactase activity to determine the relative amounts of lactose in various food products, including typical dairy products as well as those that are advertised as lactose-free? Write your ideas in your notebook.
Step 2: Student-led Planning: With your lab partner, choose two food products to test—one that you suspect contains lactose and one that is supposed to be lactose-free. Determine how you would change the setup of your test tubes above to assay for lactase activity in food products. Once your teacher approves your experimental design, create a table to record your data, prepare your test tubes per your design, and record data on glucose production every 3 minutes for 15 minutes. Determine the rates of lactase enzyme activity for each food product. Make a bar graph showing the lactase activity for each of the two foods chosen.
Step 3: Critical Analysis: Are the predictions you made in Step 1 supported by your data? Is there any way you could improve your experiment? Discuss your answers with your lab partner and write them in your notebook.
Assessments
- How can substrate specificity of an enzyme be used to determine the presence of its substrate in a sample? Explain in terms of the active site.
- What might you conclude if you observed glucose in a lactose-free food at the start of the experiment?
- How could enzyme specificity be used to determine the concentration of a substrate in a food product?

