Body Positions
Body position terms are essential to communicate how the patient’s body is placed for any medical examination, surgery, diagnostic procedure, treatment, or recovery. The most common body positions are listed below along with descriptions and accompanying images.
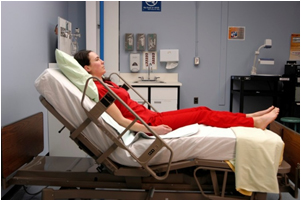
Fowler position: semi-sitting position with slight elevation of the knees
Lateral recumbent position: side lying; right and left precede the term to indicate the patient’s side

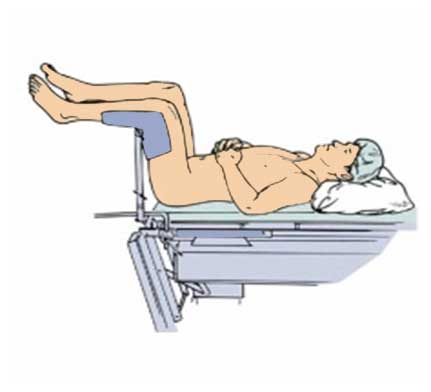
Lithotomy position: lying on back with legs raised and feet in stirrups, both hips and knees flexed, and thighs abducted (away from the body) and externally rotated
Orthopneic position: sitting upright in a chair or in bed supported by pillows behind the back. Sometimes the patient tilts forward, resting on a pillow supported by an overbed table (also called orthopneic position).
Prone position: lying on abdomen, facing downward; head may be turned to one side; a.k.a. ventral recumbent

Recumbent position: lying down in any position; a.k.a. decubitus position
Semi-prone position: lying on side between a lateral and prone position with the upper knee drawn up toward the chest and the lower arm drawn behind parallel to the back. “Right” or “left” precedes the term to indicate the patient’s right or left side.
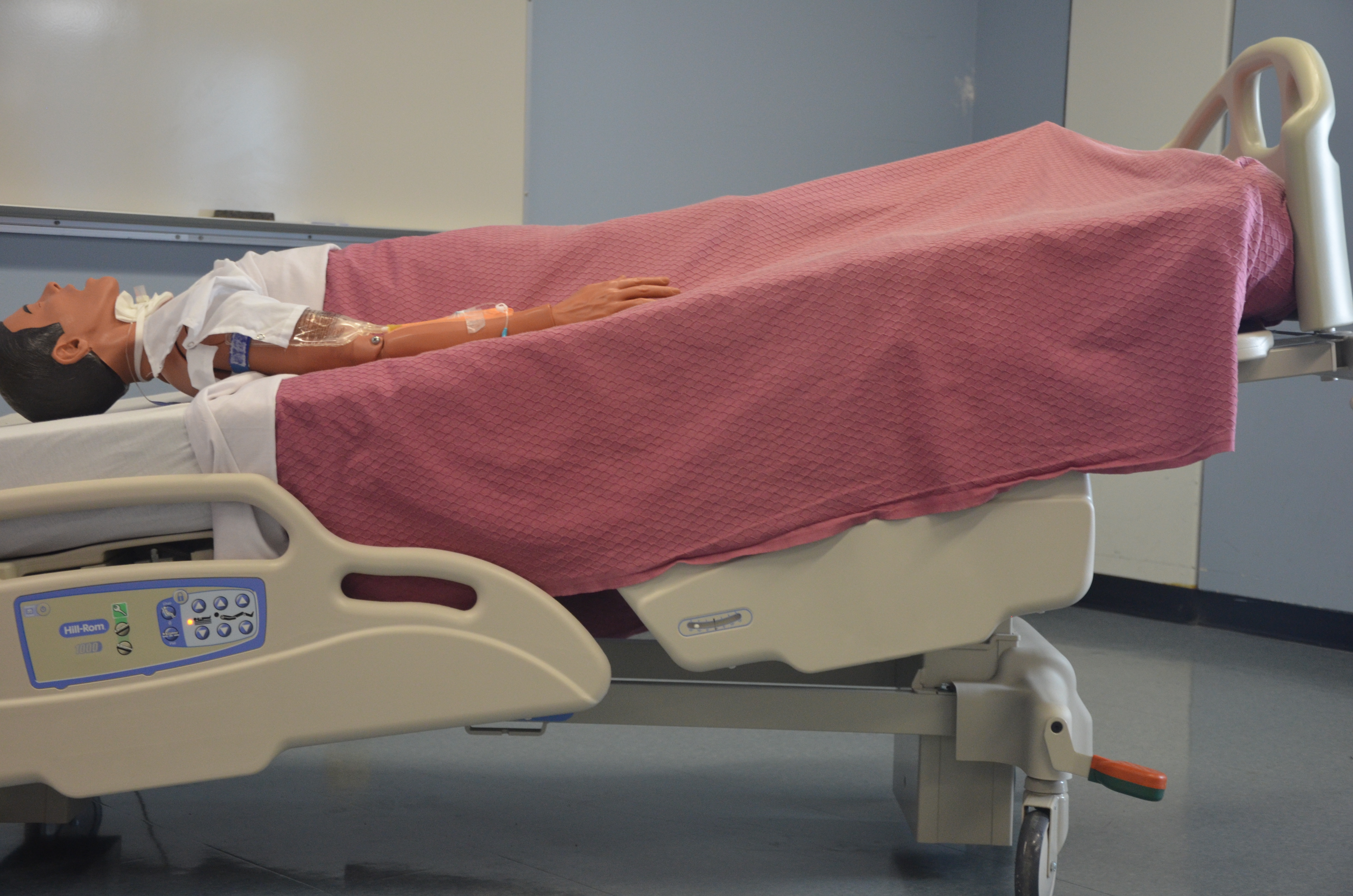
Supine position: lying on back, facing upward; a.k.a. dorsal recumbent position

Trendelenburg position: lying on back with body tilted so that the head is lower than the feet