Medical, Surgical, & Viewing Terms and Abbreviations
Medical Careers & Professional Terminology
doula: a trained non–health care professional who provides physical, emotional, and informational support to parents before, during, and after childbirth
lactation consultant: a health professional who helps new parents and infants with lactation and breastfeeding
midwife: a health professional who cares for mothers and newborns around childbirth
midwifery: the practice of being a midwife
neonatologist: a physician who specializes in newborn infant care
neonatology: the study or medical specialization of newborn care
obstetrician: a physician who specializes in delivering infants
obstetrics: the study or medical specialization of delivering infants
teratologist: a scientist or physician who specializes in abnormal fetal development
teratology: the study or medical specialization of abnormal fetal development
Imaging Techniques/Procedures for the Organ System
amnioscope: the device used to visually examine the amnion
amnioscopy: the process of using an amnioscope to visually examine the amnion
pelvic sonography: visual examination of the pregnancy using ultrasound
Medical, Diagnostic, and Surgical Techniques/Procedures Used for the Organ System
abortion: a miscarriage or elective ending of a pregnancy
alpha-fetoprotein test: a test to measure the amount of alpha-fetoprotein, produced in the liver of the developing fetus, in the gestational parent’s blood
amniocentesis: a procedure that uses a needle to aspirate amniotic fluid for prenatal testing
artificial insemination: introducing semen into the vagina by mechanical/artificial means
cesarean section: delivery of a baby via abdominopelvic surgery
cephalic version: a procedure performed to turn a fetus from a breech or transverse presentation to a cephalic presentation prior to birth
cerclage: stitching the cervix to maintain a pregnancy
chorionic villus sampling: a biopsy taken of a chorionic villus for prenatal testing
dilation & curettage: dilating the cervix and scraping the uterine wall; used after a miscarriage or for obtaining tissue samples for testing purposes
episiotomy: a cut made in the vulva to facilitate a vaginal delivery
gamete intrafallopian transfer: injection of sperm cells and oocytes into a fallopian tube to aid in conception
induction: a medical process that causes labor to begin
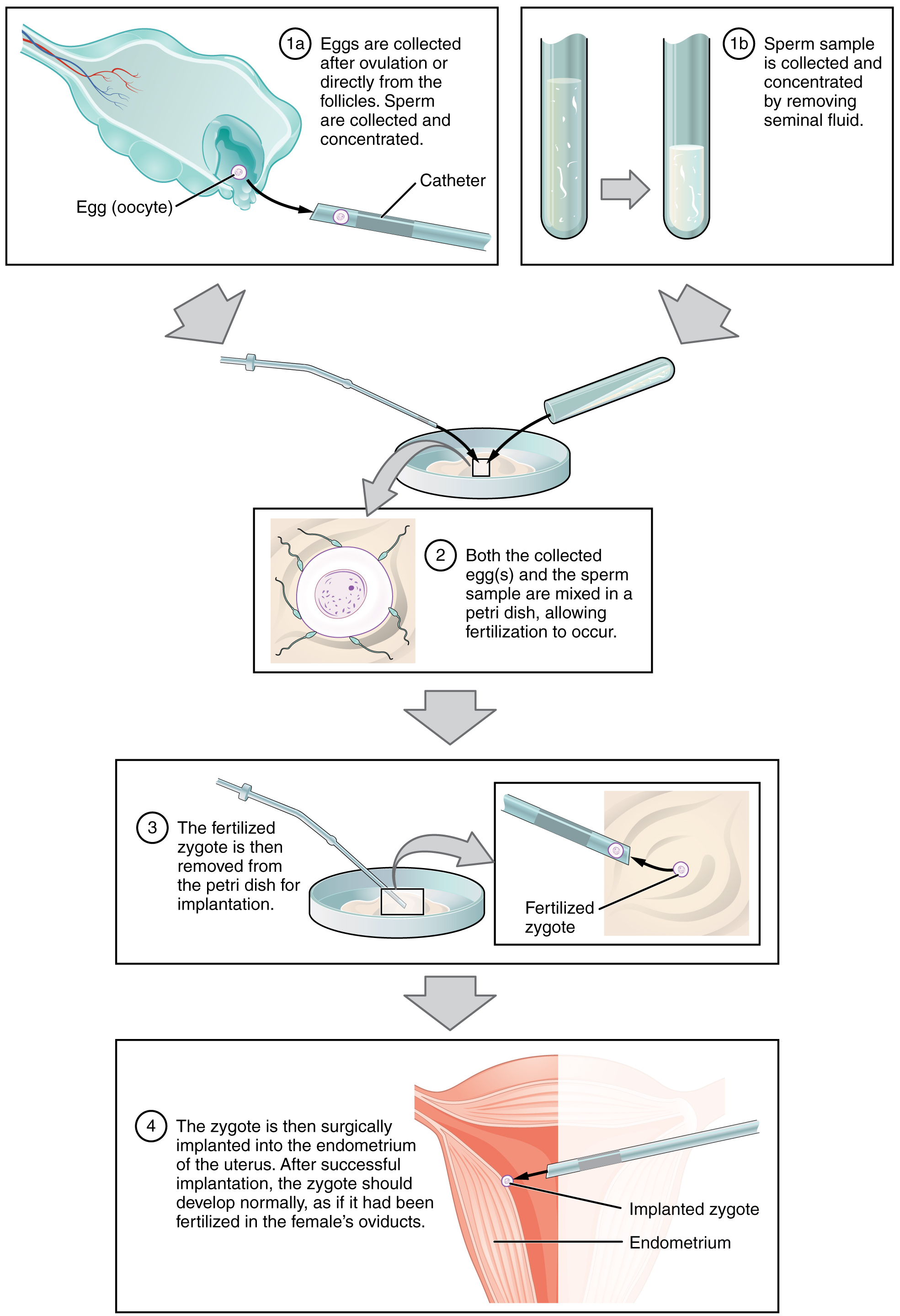
in vitro fertilization: fertilization of oocytes with sperm that takes place in a Petri dish (see Figure 16.3)
intrauterine insemination: injecting washed semen directly into the uterus to aid in conception
non-stress test: test to measure fetal heart rate and movement in the latter stages of pregnancy
vaginal birth after cesarean section: delivering a baby vaginally after having a previous cesarean section
zygote intrafallopian transfer: injection of a zygote into a fallopian tube, after which implantation in the uterus may occur (see Figure 16.3)
Abbreviations Commonly Used with the Organ System
AB: abortion
AFP: alpha-fetoprotein test
AI: artificial insemination
CS, C-section: cesarean section
CVS: chorionic villus sampling
D&C: dilation and curettage
DOB: date of birth
EDD: expected or estimated date of delivery
FAS: fetal alcohol syndrome
GIFT: gamete intrafallopian transfer
HDN: hemolytic disease of the newborn
HG: hyperemesis gravidarum
IUI: intrauterine insemination
IVF: in vitro fertilization
LMP: last menstrual period
multip: multipara
NB: newborn
OB: obstetrics
primip: primipara
RDS: respiratory distress syndrome
VBAC: vaginal birth after cesarean section
ZIFT: zygote intrafallopian transfer
Medical Terms Practice
For each card, click the speaker icon to hear the correct pronunciation of the listed term. Practice saying the term to yourself, then attempt to define the term from memory. Click “Turn” to flip the card and see the definition. Use the right and left arrows to toggle through the cards in each set.
Image Descriptions
Figure 16.3 image description: This multi-part figure shows the different steps in in vitro fertilization. The top panel shows how the oocytes and the sperm are collected and prepared. (text label reads: 1a) Eggs are collected after ovulation or directly from the follicles. Sperm are collected and concentrated. (text label reads: 1b) Sperm sample is collected and concentrated by removing seminal fluid. The next panel shows the sperm and oocytes being mixed in a petri dish. (text label reads: 2) Both the collected eggs and the sperm sample are mixed in a petri dish, allowing fertilization to occur. The panel below that shows the fertilized zygote being prepared for implantation. (text label reads: 3a) The fertilized zygote is then removed from the petri dish for implantation. (text label reads: 3b) Fertilized zygote. The last panel shows the fertilized zygote being implanted into the uterus. (text label reads: 4) The zygote is then surgically implanted into the endometrium of the uterus. After successful implantation, the zygote should develop normally, as if it had been fertilized in the female’s oviducts. [Return to Figure 16.3]

